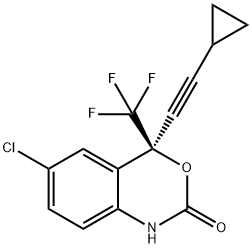
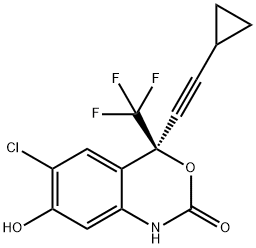
Efavirenz
Synonym(s):(4S)-6-Chloro-4-(2-cyclopropylethynyl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)-2,4-dihydro-1H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one;(4S)-6-Chloro-4-(2-cyclopropylethynyl)-1,4-dihydro-4-(trifluoromethyl)-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one;Aryl halide chemistry informer library compound X17;Efavirenz
- CAS NO.:154598-52-4
- Empirical Formula: C14H9ClF3NO2
- Molecular Weight: 315.67
- MDL number: MFCD05662344
- EINECS: 620-492-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 11:34:44
What is Efavirenz?
Description
Efavirenz D5 was launched as Sustiva in the US for the treatment of infection by HIV, the virus causing AIDS, in combination with other anti-retroviral agents.
Efavirenz D5 is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) belonging to the 3,1-benzoxazin-2-one chemical class. It is the third non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor to have been launched to date, after Nevirapine (1996) and Delavirdine (1997), increasing the arsenal of anti-HIV drugs for treating infected patients in dual or triple combination with nucleoside or other non-nucleoside RTIs, or protease inhibitors.
Efavirenz D5 can be obtained by two related ways of six steps from 4-chloroaniline ; one of them is based on asymmetric synthesis by enantioselective addition of an acetylide to a trifluoroacetophenone. The anti-HIV activity of Efavirenz D5 was demonstrated against most wild-type and clinical strains of HIV-1, including those with the most frequently observed mutations. Efavirenz D5 has a better pharmacokinetic profile when compared with the preceding drugs of this class ; in particular, in a long-term experiment conducted in cynomolgus monkeys, Efavirenz D5 was shown to easily cross the blood brain barrier leading to an increase of the antiviral concentration in cerebrospinal fluid.
Chemical properties
White to Slightly Pink Crystalline Powder
Originator
Merck & Co. (US)
The Uses of Efavirenz
Efavirenz D5 is a nonnucleoside HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitor. Antiviral
The Uses of Efavirenz
antiviral;reverse transcriptase inhibitor
The Uses of Efavirenz
For use in combination treatment of HIV infection (AIDS)
Indications
For use in combination treatment of HIV infection (AIDS)
Background
Efavirenz (brand names Sustiva? and Stocrin?) is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) and is used as part of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) for the treatment of a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1.
For HIV infection that has not previously been treated, efavirenz and lamivudine in combination with zidovudine or tenofovir is the preferred NNRTI-based regimen.
Efavirenz is also used in combination with other antiretroviral agents as part of an expanded postexposure prophylaxis regimen to prevent HIV transmission for those exposed to materials associated with a high risk for HIV transmission.
What are the applications of Application
Efavirenz is a nonnucleoside HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: 1,4-Dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one substituted at the 4 position by cyclopropylethynyl and trifluoromethyl groups (S configuration) and at the 6 position by chlorine. A non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor wit activity against HIV, it is used with other antiretrovirals for combination therapy of HIV infection.
Indications
Efavirenz (Sustiva) is approved for the therapy of HIV infection of adults and children and is also used for postexposure prophylaxis. It is the only NNRTI approved for once-daily dosing. Rash, although rarely severe, is a common adverse effect of efavirenz. Elevated liver enzymes and serum cholesterol also may occur. Central nervous system (CNS) effects in approximately half of patients may include dizziness, headache, insomnia, drowsiness, euphoria, agitation, impaired cognition, nightmares, vivid dreams, and hallucinations. These effects often subside after several weeks to months of therapy.
Manufacturing Process
(-)-6-Chloro-4-cyclopropylethynyl-4-trifluoromethyl-1,4-dihydro-2H-3,1-
benzoxazin-2-one and (+) 6-Chloro-4-cyclopropylethynyl-4-trifluoromethyl-
1,4-dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one
The above products can be produced in the next steps:
Step A: 2-(2-Amino-5-chlorophenyl)-4-cyclopropyl-1,1,1-trifluoro-3-butyn-2-
ol.
A solution, was prepared from 23 g of cyclopropylacetylene (0.348 mol) in
250 mL of THF by dropwise addition of 116 mL of a 3.0 M solution of
ethylmagnesium bromide in ether (0.348 mol) over 1 h. This solution was
maintained at 0°C for 1 h, then at 40°C for 3 h. To this solution, recooled to
0°C, 15.56 g of 1-(2-amino-5-chlorophenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoromethylethanone
(0.0696 mol), was added as a solid, portionwise over 5 min. The reaction
mixture was allowed to stir at 0°C for 1.5 hours. The reaction was quenched
at 0°C by dropwise addition of 700 mL of saturated aqueous ammonium
chloride solution. The mixture was extracted with 2 times 400 mL portions of
ethyl acetate, the combined organic phases were washed with brine and dried
over MgSO4. Removal of the drying agent and solvents left a yellow solid. This
material was recrystallized from boiling hexanes (100 mL final volume) to
afford 14.67 g of 2-(2-amino-5-chlorophenyl)-4-cyclopropyl-1,1,1-trifluoro-3-
butyn-2-ol. A second crop (2.1 g) was obtained from concentrating the
mother liquors. M.p.: 153°-154°C.
Step B: ()-6-Chloro-4-cyclopropylethynyl-4-trifluoromethyl-1,4-dihydro-2H-
3,1-benzoxazin-2-one.
A solution of 2-(2-amino-5-chlorophenyl)-4-cyclopropyl-1,1,1-trifluoro-3-
butyn-2-ol (15.00 g, 0.0518 mol) and 41.98 g (0.259 mol) of 1,1'-
carbonyldiimidazole in 250 mL of dry THF was stirred under argon at 55°C for
24 hours. The solvent was removed on a rotary evaporator and the residue
was partitioned between 500 mL of ethyl acetate and 400 mL of water. The
layers were separated and the aqueous phase was extracted once more with
ethyl acetate. The combined ethyl acetate extracts were washed with 2 times
200 mL of 2% aqueous HCl, saturated aqueous NaHCO3, and brine. Drying
over MgSO4, filtration, and removal of the solvent in vacuo provided 16.42 g
of the title compound as a solid. Recrystallization from ethyl acetate/hexane
afforded 12.97 g of analytically pure ()-6-chloro-4-cyclopropylethynyl-4-
trifluoromethyl-1,4-dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one as a white crystals.
Melting point: 178°-180°C.
Step C: 6-Chloro-1-(1S)-camphanoyl-4-cyclopropylethynyl-4-trifluoromethyl-
1,4-dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one.
To a solution containing (+)-6-chloro-4-cyclopropylethynyl-4-trifluoromethyl-
1,4-dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one (12.97 g, 0.041 mol), 4-
dimethylaminopyridine (1.02 g, 0.0083 mol), and (-)-camphanic acid chloride
(14.22 g, 0.06556 mol) in 350 mL of dry dichloromethane, stirred under
argon in an ice bath, was added triethylamine (22.84 mL, 0.164 mol). The
cooling bath was removed and the reaction was allowed to proceed at room
temperature. After 75 min. the reaction was judged complete by thin layer
chromatography (SiO2, 4% EtOAc in CHCl3), and the solution was diluted with
500 mL of CHCl3 then washed with 10% citric acid (2X), water (1X), and brine
(1X). Drying (MgSO4), filtration, and removal of the solvent in vacuo left a
colorless foam. This material was triturated with 200 mL of boiling hexane. On
cooling to room temperature the desired diastereomeric camphanate imide
precipitated. The solid was collected on a frit, washed with a little cold
hexanes and dried in vacuo to give 7.79 g of 6-chloro-1-(1S)-camphanoyl-4-
cyclopropylethynyl-4-trifluoromethyl-1,4-dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one as
white crystals. Melting point: 164°-165°C. HPLC purity: 99.2% γ 254 nm.
Step D: (-)-6-Chloro-4-cyclopropylethynyl-4-trifluoromethyl-1,4-dihydro-2H-
3,1-benzoxazin-2-one.
6-Chloro-1-(1S)-camphanoyl-4-cyclopropylethynyl-4-trifluoromethyl-1,2-
dihydro-4(H)-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one(7.50 g, 0.01512 mol) was dissolved in
150 mL of n-butanol at 60°C under an atmosphere of argon. To this solution
was added 10 mL of 1 N HCl. This solution was maintained at 60°C for 72 h.
The mixture was neutralized with aqueous NaHCO3 and the n-butanol was
removed in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in 150 mL of THF and treated
with 50 mL of 2 N LiOH for 3 h at room temperature. This mixture was diluted
with ethyl acetate and washed with two portions of water and one of brine.
Drying (MgSO4), filtration and removal of the solvent in vacuo gave a white
solid. This material was recrystallized from hot hexane to give 3.43 g of (-)-6-
chloro-4-cyclopropylethynyl-4-trifluoromethyl-1,4-dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-
2-one as white crystals, melting point 131°-132°C, [α]D20 = - 84.7° (CHCl3,
c=0.005 g /mL).Step E: (+)-6-Chloro-4-cyclopropylethynyl-4-trifluoromethyl-1,4-dihydro-2H-
3,1-benzoxazin-2-one.
The mother liquors from Step C above were purified by column
chromatography on silica gel using 10% ethyl acetate in hexanes as eluant.
The pure, undesired diastereomer (a colorless foam) was hydroylzed according
to Step D. The enantiomeric benzoxazinone, (+)-6-chloro-4-
cyclopropylethynyl-4-trifluoromethyl-1,4-dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one,
was obtained as white crystals. Melting point 131°-132°C; [α]D20 =+84.4°
(CHCl3, c=0.005 g/mL).
brand name
Sustiva (Bristol-Myers Squibb).
Therapeutic Function
Antiviral
Acquired resistance
One or more single-codon substitutions in the HIV reverse transcriptase genome at positions 100, 103, 106, 108, 181, 188, 190 and 225 confer reduced susceptibility. Many, but not all, of these point mutations confer reduced susceptibility to other non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors.
General Description
Efavirenz D5 (Sustiva)84 is also mandated for use with at leasttwo other antiretroviral agents. The compound is morethan 99% protein bound, and CSF concentrations exceedthe free fraction in the serum. Metabolism occurs in theliver. The half-life of a single dose of Efavirenz D5 is 52 to 76hours, and 40 to 55 after multiple doses (the drug inducesits own metabolism). Peak concentration is achieved in 3to 8 hours. Elimination is 14% to 34% in urine (as metabolites)and 16% to 41% in feces (primarily as Efavirenz D5).The oral dosage form is supplied as a capsule.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Efavirenz D5 is a synthetic heterocyclic compound formulated for oral administration.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Efavirenz is a nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI). It is an anti-HIV drug, commonly used in combination therapy for AIDs treatment. It is part of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) for the treatment of a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1.
Pharmacokinetics
Efavirenz (dideoxyinosine, ddI) is an oral non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI). It is a synthetic purine derivative and, similar to zidovudine, zalcitabine, and stavudine. Efavirenz was originally approved specifically for the treatment of HIV infections in patients who failed therapy with zidovudine. Currently, the CDC recommends that Efavirenz be given as part of a three-drug regimen that includes another nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (e.g., lamivudine, stavudine, zidovudine) and a protease inhibitor or efavirenz when treating HIV infection.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption: Not known/available
Cmax 600 mg oral once daily: c. 4.07 mg/L
Cmin 600 mg oral once daily: c. 1.77 mg/L
Plasma half-life: c. 45 h
Volume of distribution: c. 2.4 L/kg
Plasma protein binding: >99%
Absorption and distribution
Bioavailability following a standard high-fat meal was increased by an average of 50%, but was unaffected by a standard meal. Distribution into body tissues and fluids has not been fully characterized. It penetrates moderately well into the CNS. The semen:plasma ratio is 0.09 (0.03–0.43). The mean concentration in breast milk is 3.51 mg/L; significant linear correlations have been found between maternal plasma and breast milk.
Metabolism and excretion
It is metabolized by cytochrome P450 systems to hydroxylated intermediates and excreted after subsequent glucuronidation. Metabolites are not active against HIV.
It is excreted principally in the feces, both as metabolites and unchanged drug. Up to 34% is recovered in the urine, <1% as unchanged drug. Given this, the impact of renal impairment on efavirenz is likely to be minimal. Caution is recommended in patients with mild–moderate liver disease; it is contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
Dose adjustment is unnecessary when it is co-administered with HIV protease inhibitors or rifampicin (rifampin).
Pharmacology
Efavirenz interacts with many drugs via the cytochrome P450 pathways. It induces and is metabolized by CYP3A4 and inhibits CYP2C9 and CYP2C19. It should not be given with cisapride, ergot alkaloids, midazolam, or triazolam because of the potential for lifethreatening reactions. Efavirenz has the potential to decrease blood levels of methadone, rifabutin, ketoconazole, and itraconazole. It may inhibit the metabolism of drugs such as alosetron, diazepam, ethinyl estradiol, imipramine, losartan, omeprazole, warfarin, tolbutamide, and topiramate. Efavirenz interacts with cytochrome P450 inducers and substrates (e.g., phenytoin, phenobarbital) in a complex manner; blood levels and side effects should be closely monitored. Patients taking efavirenz should avoid herbal preparations containing St. John’s wort because the herb induces CYP3A4 and may cause drug failure or viral resistance. Saquinavir should not be used as the sole protease inhibitor in a regimen containing efavirenz.
Clinical Use
Treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults and children (in combination with other antiretroviral drugs)
Side Effects
The most common (>5%, moderate–severe) adverse effects associated with Efavirenz D5 therapy are rash, dizziness, nausea, headache, fatigue, insomnia and vomiting. Rash occurs in up to 26% of patients, mostly in the first 2 weeks of therapy. It usually resolves within 1 month, but is sufficiently severe to limit treatment in a few cases.
Dizziness, insomnia, somnolence, impaired concentration, abnormal dreaming and other CNS disturbances have been reported in around 52% of clinical trial participants, with events of moderate to severe intensity occurring in about 3% of patients. Rare (0.2% of patients) episodes of severe delusional or inappropriate behavior and severe acute depression have also been reported. The symptoms commonly begin in the first 2 weeks of treatment but often resolve or substantially improve within a month.
Elevations in serum hepatic transaminase to levels more than five times the upper limit of normal are observed in about 3% of patients and 8% of those co-infected with viral hepatitis B or C.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antibacterials: concentration of rifabutin reduced.
Anticoagulants: possibly affects concentration of coumarins.
Antidepressants: concentration reduced by St John’s wort - avoid.
Antifungals: itraconazole, posaconazole and
voriconazole concentration reduced; voriconazole
increases efavirenz concentration - reduce dose of
efavirenz by 50% and increase dose of voriconazole
to 400 mg twice daily; possibly reduces caspofungin
concentration - may possibly need to increase caspofungin dose.
Antimalarials: concentration of artemether with
lumefantrine reduced.
Antipsychotics: possibly increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with pimozide - avoid; possibly reduces
aripiprazole concentration - increase aripiprazole dose
Antivirals: concentration of atazanavir and
boceprevir reduced - avoid; saquinavir concentration
significantly reduced; concentration of daclatasvir,
darunavir, dolutegravir, indinavir, lopinavir, telaprevir
and possibly etravirine and maraviroc reduced -
adjust daclatasvir, darunavir, dolutegravir, lopinavir,
maraviroc and telaprevir dose, avoid with etravirine;
concentration reduced by nevirapine; monitor LFTs
when used in combination with ritonavir.
Anxiolytics and hypnotics: risk of prolonged sedation
with midazolam - avoid.
Atovaquone: concentration of atovaquone reduced - avoid.
Ciclosporin: concentration of ciclosporin possibly reduced.
Cytotoxics: concentration of bosutinib possibly reduced - avoid
Ergot alkaloids: risk of ergotism - avoid.
Grapefruit juice: concentration possiblyincreased.
Guanfacine: concentration of guanfacine possibly
reduced, increase dose of guanfacine
Oestrogens and progestogens: possibly reduced
contraceptive effect.
Orlistat: absorption possibly reduced by orlistat.
Tacrolimus: possibly affects tacrolimus
concentration.
Ulipristal: possibly reduced contraceptive effect.
Metabolism
Efavirenz is principally metabolized by the cytochrome P450 system to hydroxylated metabolites with subsequent glucuronidation of these hydroxylated metabolites. These metabolites are essentially inactive against HIV-1.
Metabolism
Studies in humans and in vitro studies using human
liver microsomes have demonstrated that efavirenz
is principally metabolised by the cytochrome P450
system to hydroxylated metabolites with subsequent
glucuronidation of these hydroxylated metabolites. These
metabolites are essentially inactive against HIV-1. The
in vitro studies suggest that CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 are
the major isozymes responsible for efavirenz metabolism
and that it inhibited P450 isozymes 2C9, 2C19, and 3A4.
In in vitro studies efavirenz did not inhibit CYP2E1 and
inhibited CYP2D6 and CYP1A2 only at concentrations
well above those achieved clinically
Approximately 14-34% of a radiolabelled dose of
efavirenz was recovered in the urine.
References
[1] young s d, britcher s f, tran l o, et al. l-743, 726 (dmp-266): a novel, highly potent nonnucleoside inhibitor of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy, 1995, 39(12): 2602-2605.
[2] de béthune m p. non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (nnrtis), their discovery, development, and use in the treatment of hiv-1 infection: a review of the last 20 years (1989–2009). antiviral research, 2010, 85(1): 75-90.
Properties of Efavirenz
| Melting point: | 139-141°C |
| Boiling point: | 340.6±42.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D20 -84.7° (c = 0.005 g/ml in CH3Cl); D25 -94.1° (c = 0.300 in methanol) |
| Density | 1.53±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| Flash point: | 2℃ |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO: soluble15mg/mL, clear |
| form | powder or crystals |
| pka | 10.2(at 25℃) |
| color | white to beige |
| optical activity | [α]/D -90 to -100°, c = 1 in methanol |
| Water Solubility | 8mg/L(temperature not stated) |
| λmax | 247nm(MeOH)(lit.) |
| Merck | 14,3521 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2H-3,1-Benzoxazin-2-one, 6-chloro-4-(2-cyclopropylethynyl)-1,4-dihydro-4-(trifluoromethyl)-, (4S)- (154598-52-4) |
Safety information for Efavirenz
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H360:Reproductive toxicity H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Efavirenz
Efavirenz manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
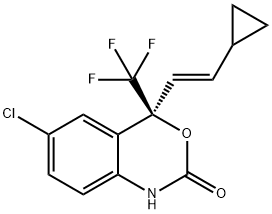
You may like
-
 Efavirenz 98%View Details
Efavirenz 98%View Details
154598-52-4 -
 Efavirenz 154598-52-4 98%View Details
Efavirenz 154598-52-4 98%View Details
154598-52-4 -
 154598-52-4 98%View Details
154598-52-4 98%View Details
154598-52-4 -
 Efavirenz 99%View Details
Efavirenz 99%View Details
154598-52-4 -
 154598-52-4 98%View Details
154598-52-4 98%View Details
154598-52-4 -
 Efavirenz 154598-52-4 99%View Details
Efavirenz 154598-52-4 99%View Details
154598-52-4 -
 Efavirenz 98% CAS 154598-52-4View Details
Efavirenz 98% CAS 154598-52-4View Details
154598-52-4 -
 Efavirenz CAS 154598-52-4View Details
Efavirenz CAS 154598-52-4View Details
154598-52-4
