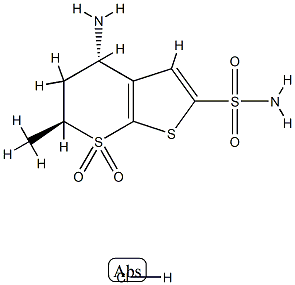
Dorzolamide
Synonym(s):(4S,6S)-4H-Thieno[2,3-b]thiopyran-2-sulfonamide, 4-(ethylamino)-5,6-dihydro-6-methyl-, 7,7-dioxide;4S,6S-Dorzolamide;L-671,152;MK-507
- CAS NO.:120279-96-1
- Empirical Formula: C10H16N2O4S3
- Molecular Weight: 324.44
- MDL number: MFCD00865636
- EINECS: 1533716-785-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-28 23:16:16
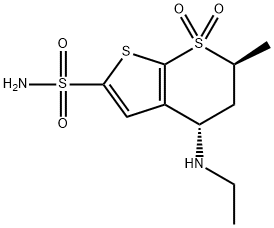
What is Dorzolamide?
Absorption
Dorzolamide readily penetrated into the eye in animal studies. Upon ophthalmic administration, dorzolamide is absorbed via the cornea and stroma. Dorzolamide is reported to be absorbed systematically following topical administration. The systemic exposure of dorzolamide following long-term administration was assessed in healthy subjects receiving an oral dose of 2 mg dorzolamide twice daily, which equates to the ophthalmic dose of 2% dorzolamide three times daily. In these subjects receiving the treatment for 20 weeks, the steady-state was reached within 8 weeks.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 of dorzolamide is 1927 mg/kg in rats and 1320 mg/kg in mice. The subcutaneous LD50 is >2 g/kg in both rats and mice.
Overdose may result in electrolyte imbalance, acidosis, and possibly central nervous system effects; these symptoms should be responded with appropriate supportive treatment. It is advised that the patient's serum electrolyte (particularly potassium) levels and blood pH levels are monitored in the case of a suspected overdose.
The Uses of Dorzolamide
Dorzolamide is an intermediate in synthesizing N-Acetyl Dorzolamide (A173640), a useful synthetic compound.
The Uses of Dorzolamide
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor.
Background
Dorzolamide is a non-bacteriostatic sulfonamide derivative and topical carbonic anhydrase (CA) inhibitor that treats elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) associated with open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. It works by blocking an enzyme in the ciliary process that regulates ion balance and fluid pressure in the eyes. Unlike oral CA inhibitors, dorzolamide has negligible effects of acid-base or electrolyte disturbances and other systemic adverse effects. First marketed in 1995, dorzolamide is available in ophthalmic solutions as monotherapy marketed as Trusopt or in combination with timolol as Cosopt PF.
Indications
Dorzolamide is indicated for the management of elevated intraocular pressure in patients with ocular hypertension or open-angle glaucoma. It can also be used in combination with timolol for the same indication in patients who are insufficiently responsive to ophthalmic beta-blockers.
Its pre-operative use was also investigated to prevent elevated intraocular pressure after neodynium yttrium aluminum garnet laser posterior capsulotomy.
Definition
ChEBI: 5,6-Dihydro-4H-thieno[2,3-b]thiopyran-2-sulfonamide 7,7-dioxide in which hydrogens at the 4 and 6 positions are substituted by ethylamino and methyl groups, respectively (4S, trans-configuration . A carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, it is used as the hydrochloride in ophthalmic solutions to lower increased intraocular pressure in the treatment of open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension.
brand name
Trusopt (Merck).
Pharmacokinetics
Dorzolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor that reduces elevated intraocular pressure in open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. When used in combination with topic beta-adrenergic antagonists, dorzolamide has an additive effect of lowering intraocular pressure. The peak ocular hypotensive effect of dorzolamide is observed at about 2 hours following ophthalmic administration.
Metabolism
Dorzolamide is slowly metabolised to N-desethyldorzolamide, which has a less potent pharmacological activity on CA-II and some inhibitory effect on CA-I. Like the parent drug, N-desethyldorzolamide is also stored in RBCs, where it binds to CA-I. The findings of an in vitro study using liver microsomes from Sprague-Dawley rats suggest the involvement of CYP2B1, CYP2E1, and CYP3A2 in the metabolism of dorzolamide in rat liver.
Properties of Dorzolamide
| Boiling point: | 575.8±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.53±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | DMSO: soluble5mg/mL (clear solution, warmed) |
| pka | pKa 6.35 (Uncertain);8.50 (Uncertain) |
| form | powder |
| color | white to beige |
| optical activity | [α]/D -25 to -35°, c = 1 in methanol |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 120279-96-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Dorzolamide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Dorzolamide
Dorzolamide manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![4H-Thieno[2,3-b]thiopyran-4-amine,N-ethyl-5,6-dihydro-6-methyl-, 7,7-dioxide, (4S,6S)](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/403848-01-1.gif)
![(4S)-4-Acetamide-5,6-Dihydro-6-Methyl-2-Sulfonamide-Thio[2,3-B]Thiopyran7,7Dioxide](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/147200-03-1.gif)
![(4S,6S)-5,6-Dihydro-4-hydroxy-6-Methylthieno[2,3-b]thiopyran-7,7-dioxide](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/147086-81-5.gif)
You may like
-
 120279-96-1 Dorzolamide 98%View Details
120279-96-1 Dorzolamide 98%View Details
120279-96-1 -
 120279-96-1 98%View Details
120279-96-1 98%View Details
120279-96-1 -
 Dorzolamide 98%View Details
Dorzolamide 98%View Details
120279-96-1 -
 120279-96-1 Dorzolamide 99%View Details
120279-96-1 Dorzolamide 99%View Details
120279-96-1 -
 Dorzolamide CAS 120279-96-1View Details
Dorzolamide CAS 120279-96-1View Details
120279-96-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1