DL-Sulforaphane
Synonym(s):1-Isothiocyanato-4-(methylsulfinyl)-butane;1-Isothiocyanato-4-(methylsulfinyl)butane, R,S-Sulforaphane;D,L-Sulforaphane - CAS 4478-93-7 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:4478-93-7
- Empirical Formula: C6H11NOS2
- Molecular Weight: 177.29
- MDL number: MFCD00198068
- EINECS: 200-001-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-18 17:43:10
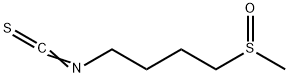
What is DL-Sulforaphane?
Description
Sulforaphane is a compound within the isothiocyanate group of organosulfur compounds and mainly found in cruciferous vegetables. It is produced when the enzyme myrosinase transforms glucoraphanin,a prodrug or storage form of SFN, into SFN upon damage to the plant (such as from chewing),which allows the two compounds to mix and react. Glucoraphanin is one of a few molecules known as isothiocyanates, existing alongside Sinigrin (metabolized into allylisothiocyanate).
Description
Sulforaphane is produced by the enzymatic breakdown of glucosinolates in many plants, especially the cruciferous vegetables broccoli, cabbage, and Brussels sprouts. It combines isothiocyanate and sulfinyl groups to provide bioactivity; and it has been evaluated for its anticancer, antidiabetic, and antimicrobial properties. Recently, it was shown that the release of sulforaphane helps noncruciferous plants fight invasions by pathogenic bacteria. Sulforaphane should not be confused with sulforaphen, its 3:4 unsaturated cousin.
Chemical properties
DL-Sulforaphane (SFN) is a slightly yellow liquid. soluble in DMSO, methanol, or water-like solvents. SFN exists in food in its food-bound form known as Glucoraphanin. It is present in a wide range of vegetables such as cabbage, cauliflower, bok choy, kale, chinese broccoli, mustard, turnip, radish, and watercress.
The Uses of DL-Sulforaphane
Potent, selective inducer of phase II detoxification enzymes with anticarcinogenic properties. Occurs naturally in broccoli. It was found to inhibit chemically induced mammary tumor formation in rats. Antitumor agent
LNCaP prostate cancer cells were treated with DL-Sulforaphane to study the effect on androgen receptor. Effects on malathion toxicity was studied in rats by treating them with DL-Sulforaphane.
Nrf2 activation of the antioxidant response element (ARE) is central to cytoprotective gene expression against oxidative and/or electrophilic stress.
Unless activated by inflammatory, environmental, or oxidative stressors, Nrf2 is sequestered in the cytoplasm by its repressor, Keap1.
Because of its protective capabilities, small molecules that activate Nrf2 signaling are being examined as potential anti-cancer or anti-inflammatory agents.
Sulforaphane is an isothiocyanate derived from cruciferous vegetables, including broccoli, that potently induces chemopreventative enzymes via Keap1-Nrf2 signaling and ARE-driven gene expression.
At 15 μM, sulforaphane inhibits class I and II HDAC activity and suppresses tumor growth by inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis selectively in various cancerous prostate epithelial cells without affecting normal cells.
Differential effects of sulforaphane on histone deacetylases, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in normal prostate cells versus hyperplastic and cancerous prostate cells
What are the applications of Application
D,L-Sulforaphane is a selective inducer of phase II detoxification enzymes used for breast cancer research
Definition
ChEBI: Sulforaphane is an isothiocyanate having a 4-(methylsulfinyl)butyl group attached to the nitrogen. It has a role as an antineoplastic agent, a plant metabolite, an antioxidant and an EC 3.5.1.98 (histone deacetylase) inhibitor. It is a sulfoxide and an isothiocyanate.
Benefits
Sulforaphane(SFN) promotes detoxification,prevents and combats cancer,lowers cholesterol,improves diabetes, can boost the immune system, is antiviral, antibacterial, and antifungal, combats inflammation,protect skin,eyes,kidneys, and brain, and restores its cognitive function. Deep insight in several studies has reported that dietary intake of cruciferous vegetables has a direct association in the decline in the incidence of various tumors such as prostate, cervical, ovarian, and lung cancer. It improves the liver function, attenuates pain, improves hair growth,promotes bone formation, and prevents muscle damage.SFN treatment reducesDNA damage and mutation rate when cancer-causing chemicals bind DNA.Although an ideal dosage is not known, the dietary addition of 0.1-0.5mg/kg SFN to rats has been noted to be bioactive. This is an estimated human dose of 7-34mg for a 1501b person; 9-45mg for a 2001b person; 11-57mg for a 250lb person.
General Description
An isothiocyanate isolated from broccoli that acts as a potent inducer of phase II detoxifying enzymes in mouse tissues and murine hepatoma cells in culture. It has been shown to be an effective agent in prevention of chemically-induced mammary tumors in rats. It also inhibits the phase I cytochrome P450 isoenzymes 2E1 and IA2 which have been associated with the activation of carcinogens. The induction of phase II enzymes is mediated by mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway.
Biological Activity
Selective inducer of phase II detoxification enzymes with anticarcinogenic properties. Organosulfur compound found in cruciferous vegetables, including broccoli.
Sulforaphane is an anti-cancer, anti-microbial and anti-diabetic compound found in cruciferous vegetables. It induces the production of detoxifying enzymes such as quinone reductase and glutathione S-transferase that cause xenobiotic transformation. Sulforaphane also increases the transcription of tumor suppressor proteins and inhibits histone deacetylases. It modulates inflammatory responses by suppressing the LPS-mediated expression of iNOS, COX-2, IL-1β and TNF-α.
Anticancer Research
Sulforaphane is an isothiocyanate compound found in cruciferous vegetables like broccoli,Brussels sprouts, and cabbages. It induces phase II drug metabolism enzymes ofxenobiotic transformation and enhances the transcription of tumor suppressionproteins. It promotes cytotoxicity in p53-deleted colon cancer cells by mitochondriaandlysosome-dependent cell death. Due to the effect of sulforaphane, Bax is alsobeing increased in the presence of inhibition of JNK-induced Bcl-2 followed bymitochondrial cytochrome-C release and activation of apoptosis. Self-renewal Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is downregulated by sulforaphane in breast cancer stemcells. It has been reported to inhibit the activity of histone deacetylase (HDAC) andto reduce the number of polyps in Apcmin/+ mouse by inhibiting AKT and ERKsignaling and protein expression of COX-2 and cyclin-D1. Sulforaphane alsoinhibits the growth of SW620 cells by inducing apoptosis (Clarke et al. 2008). Inhuman colon cancer cells (HT-29), sulforaphane showed increased dose-dependentluciferase activity of AP-1, induced JAK activity, and inhibited NF-κB luciferaseactivation induced by LPS. It is also reported to inhibit cellular proliferation and toinduce apoptosis. In HepG2 human hepatoma cells, sulforaphane significantlyinduces the expression of the Nrf-2 protein and activation of ARE-mediatedtranscription, delays Nrf-2 degradation by inhibition of Keap1, and activates theexpression of transcription of the antioxidant HO-1 enzyme. This activation of thetranscription is partially modulated by the signaling pathway of p38 MAPK, whilep38 MAPK phosphorylates Nrf-2 and improves the binding between the proteinsNrf-2 and Keap1. In the PC-3 cells of human prostate cancer, sulforaphanesuppresses the expression regulated by NF-κB and NF-κB signaling pathway by theIκBα and IKK pathways (Wang et al. 2012).
References
[1] gamet-payrastre l, li p, lumeau s, et al. sulforaphane, a naturally occurring isothiocyanate, induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in ht29 human colon cancer cells[j]. cancer research, 2000, 60(5): 1426-1433.
[2] kansanen e, kuosmanen s m, leinonen h, et al. the keap1-nrf2 pathway: mechanisms of activation and dysregulation in cancer[j]. redox biology, 2013, 1(1): 45-49.
Properties of DL-Sulforaphane
| Boiling point: | 125-135°C |
| Density | 1.17±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO: 40 mg/mL, soluble |
| form | liquid |
| color | slightly yellow |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 4478-93-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for DL-Sulforaphane
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for DL-Sulforaphane
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran








You may like
-
 DL-Sulforaphane, 95% CAS 4478-93-7View Details
DL-Sulforaphane, 95% CAS 4478-93-7View Details
4478-93-7 -
 D,L-Sulforaphane CAS 4478-93-7View Details
D,L-Sulforaphane CAS 4478-93-7View Details
4478-93-7 -
 DL-Sulforaphane CAS 4478-93-7View Details
DL-Sulforaphane CAS 4478-93-7View Details
4478-93-7 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8