DL-CARNITINE
- CAS NO.:461-06-3
- Empirical Formula: C7H15NO3
- Molecular Weight: 161.2
- MDL number: MFCD00066765
- EINECS: 000-000-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
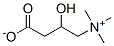
What is DL-CARNITINE?
Originator
Flatistine,Sauba,France,1978
The Uses of DL-CARNITINE
antihyperlipoproteinemic, gastric/ pancreatic secretion stimulant
Definition
ChEBI: Carnitine is an amino-acid betaine that is butanoate substituted with a hydroxy group at position C-3 and a trimethylammonium group at C-4. It has a role as a human metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is functionally related to a butyrate. It is a conjugate base of a carnitinium.
Manufacturing Process
9.3 g of epichlorohydrin was added at a temperature of 40°-50°C under
stirring to 9.6 g of trimethylamine hydrochloride dissolved in 10 cc of water.
Continuing the reaction for an hour at the above temperature, the reaction
product was concentrated under reduced pressure to obtain the crystals of 3-
chloro-2-oxypropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride which were recrystallized
with 25 cc of ethanol. The crystals obtained by concentrating the mother
liquor were also recrystallized. The yield was 17.4 g (MP 190°C, yield 91.5%).
This substance occurs as white, somewhat hygroscopic crystals and is readily
soluble in water or alcohol, but insoluble in benzene, toluene, ether, acetone
or chloroform.
The result of analysis assuming (C6H15C10N)+Cl--calculated value: N, 7.45%;
total Cl, 37.7%; Cl-, 18.88%. Observed value: N, 7.36%; total Cl, 37.54%;
Cl-, 18.98%.
18.8 g of 3-chloro-2-oxypropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride was dissolved in
a mixed solvent composed of 19 cc of methanol and 1 cc of water. 5.1 g of
sodium cyanide dissolved in 8 cc of water was dropped into the solution at
50°C under stirring. After dropping, the mixture was held at this temperature
for 30 minutes under stirring. The reaction product was then neutralized with
6 N hydrochloric acid toward pH 5, and, after cooling, sodium chloride
separated out and was filtered. The filtrate was concentrated to dryness under
reduced pressure, and the residue was washed with small quantity of ethanol.
Drying the residue, dissolving in hot methanol, filtering off insoluble matters,
and cooling mother liquor, the crystals of 3-cyano-2-axypropyl trimethyl
ammonium chloride which deposited out were filtered and dried. Yield 16.7 g
[MP (decomposition) 220°-223°C, yield 93.4%].
12.5 cc of concentrated hydrochloric acid was added to 17.9 g of 3-cyano-2-
oxypropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride. Gradually heating the mixture on a
water bath under stirring, so bringing the temperature up to 98°C at the end
of about 3 hours, 9 cc of water was added. After cooling, free hydrochloric
acid was neutralized with 3 cc of 6 N sodium hydroxide, and then by adding 1
g of active charcoal, the reaction product was decolorized and filtered. The
filtrate was concentrated to almost dryness under reduced pressure. Then,
this concentrate was, after washing with 10 cc of ethanol, dried. Yield 24.7 g.
The dried product was dissolved in 46.5 cc of glacial acetic acid by heating on
a boiling water bath. The insoluble matter is removed by filtering hot, and on
cooling the mother liquor, crystals of carnitine hydrochloride separated out.
The crystals were filtered, washed with 10 cc of ethanol, and dried.
Recrystallizing 19.7 g of the crude carnitine with methanol, 17 g of the refined
carnitine was obtained [MP 195°-198°C (decomposing point), yield 86%], The
overall yield of the refined carnitine through whole steps was about 74%.
Carnitine thus prepared was an odorless, white, crystalline powder, having a
strong acid taste.
Therapeutic Function
Gastric stimulator, Pancreatic stimulator
Purification Methods
The S(L) isomer is levocarnitine, Vitamin B7. The R or S isomers crystallise from EtOH/Me2CO (hygroscopic). The R or S hydrochlorides crystallise from hot EtOH or EtOH/Et2O and have m 142o(dec). The RS-isomer crystallises from hot EtOH (hygroscopic). The RS hydrochloride crystallises in needles from hot EtOH and has m 196o(dec). [(±) Mazzetti & Lemmon J Org Chem 22 228 1957, Beilstein 4 H 513, 4 I 548, 4 II 937-8, 4 III 1632-5, 4 IV 3185.]
Properties of DL-CARNITINE
| CAS DataBase Reference | 461-06-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for DL-CARNITINE
Computed Descriptors for DL-CARNITINE
New Products
Methyl (R)-1-Boc-4,4-difluoropyrrolidine-2-carboxylate 2,2-Difluoropropylamine hydrochloride tert-butyl 3-bromoazetidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Boc-3-hydroxypyrrolidine DIFLUOROACETIC ANHYDRIDE 2,2-Difluoropropionic acid Diallylamine, 99% Calcium hydroxide, 95% Aluminum oxide, basic 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% L-tert-Leucine,97% N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base) 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 5-Cyanophthalide N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide 2-(Methylthio) Benzonitrile Sodium Acetate Anhydrous Allopurinol 1,5-DibromopentaneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
![Cis-2-(Bromomethyl)-2-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-1,3-Dioxolane-4-Ylmethyl Benzoate [CBB] 61397-56-6 99%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) Cis-2-(Bromomethyl)-2-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-1,3-Dioxolane-4-Ylmethyl Benzoate [CBB] 61397-56-6 99%View Details
Cis-2-(Bromomethyl)-2-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-1,3-Dioxolane-4-Ylmethyl Benzoate [CBB] 61397-56-6 99%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 287930-77-2 / 142569-70-8 99%View Details
287930-77-2 / 142569-70-8 99%View Details
287930-77-2 / 142569-70-8 -
![2033-24-1 2,2-Dimethyl-1,3-Dioxane-4,6-Dione [Meldrum Acid] 98%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) 2033-24-1 2,2-Dimethyl-1,3-Dioxane-4,6-Dione [Meldrum Acid] 98%View Details
2033-24-1 2,2-Dimethyl-1,3-Dioxane-4,6-Dione [Meldrum Acid] 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 Ethyl-2-Chloroacetoacetate 609-15-4View Details
Ethyl-2-Chloroacetoacetate 609-15-4View Details
609-15-4 -
 CIS- BROMO BENZOATEView Details
CIS- BROMO BENZOATEView Details
61397-56-6 -
 609-15-4View Details
609-15-4View Details
609-15-4 -
![1-(6-Methylpyridin-3-Yl)-2-[4-(Methylsulfonyl)Phenyl]Ethanone [Ketosulfone] 99%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) 1-(6-Methylpyridin-3-Yl)-2-[4-(Methylsulfonyl)Phenyl]Ethanone [Ketosulfone] 99%View Details
1-(6-Methylpyridin-3-Yl)-2-[4-(Methylsulfonyl)Phenyl]Ethanone [Ketosulfone] 99%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 27143-07-3View Details
27143-07-3View Details
27143-07-3