Disodium stannous citrate
- CAS NO.:25088-96-4
- Empirical Formula: C6H5Na2O7Sn+
- Molecular Weight: 353.78924
- Update Date: 2025-07-04 15:24:24
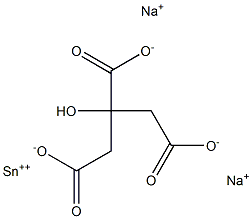
What is Disodium stannous citrate?
Chemical properties
White crystals. Soluble in water, easy to absorb moisture and deliquescence. It is easily oxidized, begins to decompose at 250 ℃, turns yellow at 260 ℃, and turns brown at 283 ℃. Oral LD502.7g/kg for mice, ADI does not require special regulations.
The Uses of Disodium stannous citrate
Disodium stannous citrate is a reducing agent with antioxidant, color protection and antiseptic properties. It can be used in canned fruits and vegetables, mushrooms, and the maximum usage is 0.3g/kg.
The Uses of Disodium stannous citrate
Reducing agent; color-preserving agent; anti-corrosion agent.
Synthesis
The solution of citric acid and stannous chloride was added with sodium hydroxide under stirring, and suction filtration to obtain distannous citrate solution; then add citric acid to give stannous citrate; then add sodium hydroxide to neutralize to obtain the prduct,Disodium stannous citrate.
Physiological effects
Disodium stannous citrate has antioxidant, color-protecting effects, and low toxicity. Its color-protecting effect is better than that of common color-protecting agents such as citric acid, ascorbic acid, and sodium erythorbate, and is comparable to sulfite. At present, the research on the color protection of disodium stannous citrate mainly focuses on canned fruits and vegetables, and there is no research report on the color protection of olive juice.
Safety information for Disodium stannous citrate
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Guanine , 99%View Details
Guanine , 99%View Details
73-40-5 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Potassium Hydroxide 90%View Details
Potassium Hydroxide 90%View Details
1310-58-3 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
2082-79-3 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
