Difenacoum
Synonym(s):3-(3-Biphenyl-4-yl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-naphthyl)-4-hydroxycoumarin;3-(3-Biphenyl-4-yl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-naphthalen-1-yl)-4-hydroxychromen-2-one
- CAS NO.:56073-07-5
- Empirical Formula: C31H24O3
- Molecular Weight: 444.52
- MDL number: MFCD01632770
- EINECS: 259-978-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
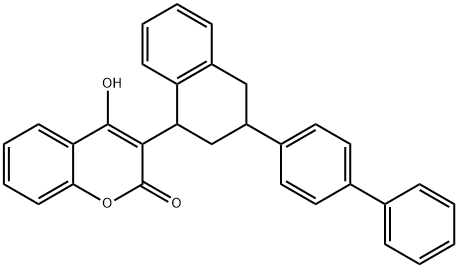
What is Difenacoum?
Description
Difenacoum, is also called 3-(3-biphenyl-4-yl-1,2,3,4- tetrahydro-1-naphthyl)-4-hydroxycoumarin, consists of colorless crystals which are insoluble in water, moderately to readily soluble in acetone, chloroform, ethyl acetate, benzene.Difenacoum is synthesized by the condensation of 4-hydroxycoumarin and 3-biphenyl-4-yl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-naphthol (49).
The Uses of Difenacoum
Difenacoum is a 4-hydroxycouramin derivative. Difenacoum is a second generation anticoagulant rodenticide used against rodent pests such as rats and mice.
The Uses of Difenacoum
Pesticide.
Definition
ChEBI: Difenacoum is a ring assembly, a member of benzenes and a member of naphthalenes.
Agricultural Uses
Rodenticide: Difenacoum is an anticoagulant that is effective against rats and mice, including warfarin-resistant strains. It is used in agriculture and urban rodent control as ready-to-use baits.
Trade name
COMPO®; MATRAK®; NEOSOREXA® PELLETS; NEOSOREXA PP580®; RASTOP®; RATAK®; RATRICK®; SILO; SOREXA GEL; STORM
Safety Profile
A poison by ingestion and skincontact. When heated to decomposition it emits acridsmoke and irritating vapors.
Toxicity evaluation
Appearing in 1974, difenacoum was the first of the new generation of anticoagulants to be commercialized for the control of rodents resistant to warfarin and related compounds (42). LD50 values (acute oral) for warfarinsusceptible rodent strains are about a factor of 2 lower than for warfarin-resistant strains. There is also a degree of specificity. The compound is generally less toxic to nontarget animals than to targets. A wide range of bait types containing 0.005% difenacoum is available, including meals, broken and whole grains, pellets, and wax blocks. A 0.1% contact dust is no longer widely used. Resistance to difenacoum was detected among a population of Norway rats in the United Kingdom in 1978 (50). This remains a problem of local importance but relatively low resistance factors indicate that other behavioral factors also play a significant role (51). Difenacoum resistance has also been recorded in other European countries (39).
Properties of Difenacoum
| Melting point: | 215-217° |
| Boiling point: | 514.5°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.0800 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5500 (estimate) |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| pka | 4.50±1.00(Predicted) |
| form | neat |
| BRN | 8360065 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 56073-07-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Difenacoum (56073-07-5) |
Safety information for Difenacoum
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Difenacoum
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8