Dibutyltin dilaurate
Synonym(s):DBTDL;Dibutylbis(lauroyloxy)stannane, Dibutyl bis(lauroyloxy)tin;Dibutyltin dilaurate
- CAS NO.:77-58-7
- Empirical Formula: C32H64O4Sn
- Molecular Weight: 631.56
- MDL number: MFCD00008963
- EINECS: 201-039-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
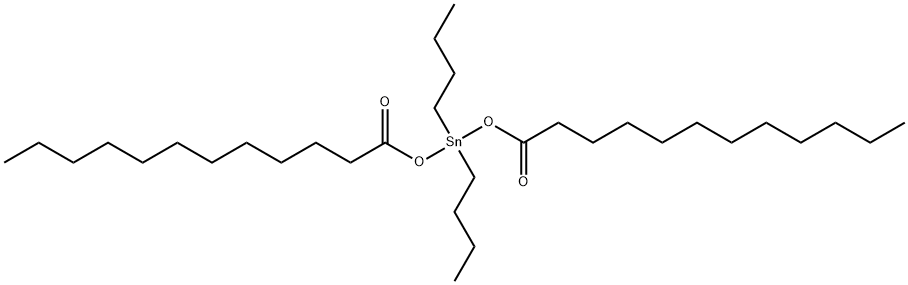
What is Dibutyltin dilaurate?
Chemical properties
yellow liquid
The Uses of Dibutyltin dilaurate
Dibutyltin dilaurate has been used as a catalyst in a protocol for the covalent attachment of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) to silicon oxide to form a hydrophilic non-fouling surface. It can also be used as a catalyst in the preparation of polymers by reacting hydroxyl-terminated macromonomers and aliphatic diisocyanates.
The Uses of Dibutyltin dilaurate
PU catalyst, RTV silicone rubber
The Uses of Dibutyltin dilaurate
Stabilizer for polyvinyl chloride resins. Catalyst for curing certain silicones.
The Uses of Dibutyltin dilaurate
Di-n-butyltin dilaurate is used as a catalyst for the production of polyurethanes as well as for the transesterification reactions. It is involved in the vulcanization of silicones and a stabilizer in polyvinyl chloride (PVC). It acts as a rust inhibitor for polyurethanes, polyols, silicones and as a fuel additive.
General Description
Clear yellow viscous liquid.
Air & Water Reactions
Dibutyltin dilaurate may be sensitive to air or heat. . Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Dibutyltin dilaurate is strongly reactive with many other groups. Incompatible with acids and bases. Organometallics are good reducing agents and therefore incompatible with oxidizing agents.
Fire Hazard
Dibutyltin dilaurate is combustible.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. A skin and eye irritant. Avoid the vapor produced by heating. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame; reacts with oxidizers. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and fumes. See also TIN COMPOUNDS
Properties of Dibutyltin dilaurate
| Melting point: | 22-24°C |
| Boiling point: | >204°C/12mm |
| Density | 1.066 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 0.2 mm Hg ( 160 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | <1.43mg/l |
| form | Oily Liquid |
| color | Clear pale yellow |
| Specific Gravity | 1.066 |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 20 ºC |
| FreezingPoint | 8℃ |
| Merck | 14,3038 |
| BRN | 4156980 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.1 mg/m3; STEL 0.2 mg/m3 (Skin) NIOSH: IDLH 25 mg/m3; TWA 0.1 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stability Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. May be air sensitive. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 77-58-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Dibutyltin dilaurate (77-58-7) |
Safety information for Dibutyltin dilaurate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H341:Germ cell mutagenicity H370:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Dibutyltin dilaurate
| InChIKey | UKLDJPRMSDWDSL-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
Dibutyltin dilaurate manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 77-58-7 Dibutyl tin dilaurate 99%View Details
77-58-7 Dibutyl tin dilaurate 99%View Details
77-58-7 -
 Di-n-butyltin dilaurate CAS 77-58-7View Details
Di-n-butyltin dilaurate CAS 77-58-7View Details
77-58-7 -
 Dibutyltin Dilaurate CAS 77-58-7View Details
Dibutyltin Dilaurate CAS 77-58-7View Details
77-58-7 -
 Dibutyltin dilaurate, 95% CAS 77-58-7View Details
Dibutyltin dilaurate, 95% CAS 77-58-7View Details
77-58-7 -
 Dibutyltin dilaurate CAS 77-58-7View Details
Dibutyltin dilaurate CAS 77-58-7View Details
77-58-7 -
 Dibutyltin dilaurate CAS 77-58-7View Details
Dibutyltin dilaurate CAS 77-58-7View Details
77-58-7 -
 Dibutyltin DilaurateView Details
Dibutyltin DilaurateView Details
77-58-7 -
 Dibutyltin Dilaurate (DBTDL)View Details
Dibutyltin Dilaurate (DBTDL)View Details
77-58-7
