Dexrazoxane
Synonym(s):(+)-(S)-4,4′-Propylenedi-2,6-piperazinedione;(S)-(+)-1,2-Bis(3,5-dioxopiperazin-1-yl)propane;Cardioxane;Zinecard
- CAS NO.:24584-09-6
- Empirical Formula: C11H16N4O4
- Molecular Weight: 268.27
- MDL number: MFCD00866449
- EINECS: 206-169-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-11 08:41:34

What is Dexrazoxane?
Absorption
IV administration results in complete bioavailability.
Toxicity
Intraperitoneal, mouse LD10 = 500 mg/kg. Intravenous, dog LD10 = 2 gm/kg.
Description
Dexrazoxane is the dextro-isomer of razoxane approved as a protectant against the cardiotoxicity of doxorubicin in breast cancer patients. This agent does not alter the anticancer effect of doxorubicin. Its mode of action suggests a chelation of free radicals. In mice, dexrazoxane also offers protection against cardiac side effects of epirubicin, but not mitoxantrone.
Originator
Imperial Cancer Research Fund (United Kingdom)
The Uses of Dexrazoxane
Dexrazoxane has been used in chromatin remodelling experiments.
The Uses of Dexrazoxane
Cardioprotectant.
The Uses of Dexrazoxane
Dexrazoxane is a cardioprotective compound against anthracyclines. It is highly protective in reducing anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity and extravasation injury. It functions by inhibiting topoisomerase II without inducing DNA strand breaks. Dexrazoxane is a + enantiomer of razoxane.
Background
An antimitotic agent with immunosuppressive properties. Dexrazoxane, the (+)-enantiomorph of razoxane, provides cardioprotection against anthracycline toxicity. It appears to inhibit formation of a toxic iron-anthracycline complex. [PubChem] The Food and Drug Administration has designated dexrazoxane as an orphan drug for use in the prevention or reduction in the incidence and severity of anthracycline-induced cardiomyopathy.
Indications
For reducing the incidence and severity of cardiomyopathy associated with doxorubicin administration in women with metastatic breast cancer who have received a cumulative doxorubicin hydrochloride dose of 300 mg/m^2 and would benefit from continued doxorubicin therapy. Also approved for the treatment of extravasation from intravenous anthracyclines.
What are the applications of Application
Dexrazoxane is an inhibitor of Topo II
Definition
ChEBI: (+)-dexrazoxane is a razoxane. It has a role as a chelator, an antineoplastic agent, a cardiovascular drug and an immunosuppressive agent.
brand name
Zinecard (Pharmacia & Upjohn);Cardioxane.
General Description
Dexrazoxane is a member of bis(2,6-dioxopiperazines), that functions as a topoisomerase 2 catalytic inhibitor. Dexrazoxane is a free radical scavenger. It might protect the heart from doxorubicin-associated damage. Dexrazoxane acts as a cardiopulmonary protectant, while treating Hodgkin′s disease (HD). It functions as a chelating agent, which limits the formation of anthracycline-iron complexes. It is used to synthesize antimalarial drugs.
Biological Activity
Topoisomerase II inhibitor and intracellular ion chelator. Bridges and stabilizes an interface between two ATPase promoters to inhibit topoisomerase II activity. Cardioprotective when co-administered with doxorubicin; decreases formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and activates the PI3K/Akt survival pathway.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Dexrazoxane is a cardioprotective compound against anthracyclines. It functions by inhibiting topoisomerase II without inducing DNA strand breaks. Dexrazoxane is a + enantiomer of razoxane.
Pharmacokinetics
Dexrazoxane is a cardioprotective agent for use in conjunction with doxorubicin indicated for reducing the incidence and severity of cardiomyopathy associated with doxorubicin administration in women with metastatic breast cancer who have received a cumulative doxorubicin dose. Patients receiving anthracycline-derivative antineoplastic agents may experience three types of cardiotoxicity: acute transient type; chronic, subacute type (related to cumulative dose and has a more indolent onset later on); and a late-onset type that manifests years after therapy, mainly in patients that have been exposed to the drug as a child. Although the exact mechanism of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity is not known, it has shown to exert a variety of actions that may result in the development of cardiotoxicity. In animals, anthracyclines cause a selective inhibition of cardiac muscle gene expression for α-actin, troponin, myosin light-chain 2, and the M isoform of creatine kinase. This may lead to myofibrillar loss associated with anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity. Anthracyclines may also cause myocyte damage via calcium overload, altered myocardial adrenergic function, release of vasoactive amines, and proinflammatory cytokines. Furthermore, it has been suggested that the main cause of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity is associated with free-radical damage to DNA. The drugs intercalate DNA, chelate metal ions to produce drug-metal complexes, and generate superoxide radicals via oxidation-reduction reactions. Anthracyclines also contain a quinone structure that can undergo reduction via NADPH-dependent reactions to produce a semiquinone free radical that initiates a cascade of superoxide and hydroxide radical generation. Chelation of metal ions, particularly iron, by anthracyclines results in an anthracycline-metal complex that catalyzes the generation of reactive oxygen free radicals. This complex is a powerful oxidant that can initiate lipid peroxidation in the absence of oxygen free radicals. The toxicity induced by antrhacyclines may be exacerbated in cardiac cells, as these cells do not possess sufficient amounts of certain enzymes (e.g., superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase) involved in detoxifying free radicals and protecting the cells from subsequent damage.
Clinical Use
Cardioxane? Prevention of cardiotoxicity in patients receiving doxorubicin or epirubicin for breast cancer Savene? : Treatment of extravasation caused by anthracyclines
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Dexrazoxane may be useful to attenuate the cardiotoxic effects of
doxorubicin in patients who are showing signs of anthracycline
cardiotoxicity, have cardiac disease, or are at maximum cumulative
dosages of doxorubicin. It is also used to treat extravasation injuries
associated with doxorubicin.
While dexrazoxane has been shown to be cardioprotective when
given at dosages of 10 times the doxorubicin dose, there is evidence
that it may also partially protect the cancer cells being treated.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antiepileptics: may reduce absorption of
fosphenytoin and phenytoin.
Ciclosporin: increased risk of immunosuppression
with risk of lymphoproliferative disease.
Tacrolimus: increased risk of immunosuppression
with risk of lymphoproliferative disease.
Vaccines: risk of generalised infections with live
vaccines - avoid.
Metabolism
Dexrazoxane is hydrolysed by the enzyme dihydropyrimidine amidohydrolase in the liver and kidney to active metabolites that are capable of binding to metal ions.
Metabolism
Dexrazoxane is hydrolysed by the enzyme
dihydropyrimidine amidohydrolase in the liver and
kidney to active metabolites that are capable of binding to
metal ions.
It is excreted unchanged via the kidney
Properties of Dexrazoxane
| Melting point: | 194-196°C |
| Boiling point: | 531.5±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D +11.35° (c = 5 in DMF) |
| Density | 1.333±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: >20mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 2.1(at 25℃) |
| color | white to off-white |
| Merck | 14,8123 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 24584-09-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Dexrazoxane
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Dexrazoxane
| InChIKey | BMKDZUISNHGIBY-ZETCQYMHSA-N |
Dexrazoxane manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![N-(2-Amino-2-oxoethyl)-N-[(1S)-2-(3,5-dioxo-1-piperazinyl)-1-methylethyl]-glycine](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20180703/GIF/120418-77-1.gif)
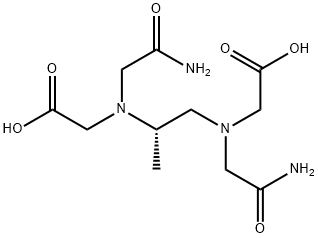
![N-(2-Amino-2-oxoethyl)-N-[(2S)-2-(3,5-dioxo-1-piperazinyl)propyl]-glycine](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20180703/GIF/120418-76-0.gif)
![2,2',2'',2'''-[[(1S)-1-Methyl-1,2-ethanediyl]dinitrilo]tetrakisacetamide](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20150408/GIF/61037-92-1.gif)
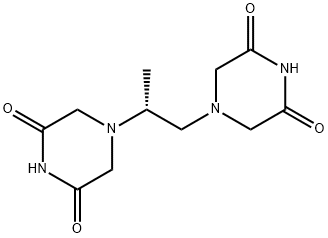
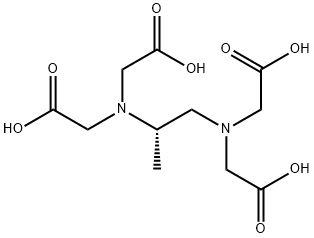
![Glycine, N-(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)-N-[(2R)-2-(3,5-dioxo-1-piperazinyl)propyl]-](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20210305/GIF/151852-25-4.gif)
![Glycine, N-(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)-N-[2-(3,5-dioxo-1-piperazinyl)propyl]-](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20210305/GIF/153042-70-7.gif)
You may like
-
 24584-09-6 Dexrazoxane 98%View Details
24584-09-6 Dexrazoxane 98%View Details
24584-09-6 -
 24584-09-6 98%View Details
24584-09-6 98%View Details
24584-09-6 -
 Dexrazoxane 99%View Details
Dexrazoxane 99%View Details -
 Dexrazoxane 98% CAS 24584-09-6View Details
Dexrazoxane 98% CAS 24584-09-6View Details
24584-09-6 -
 Dexrazoxane CAS 24584-09-6View Details
Dexrazoxane CAS 24584-09-6View Details
24584-09-6 -
 Dexrazoxane CAS 24584-09-6View Details
Dexrazoxane CAS 24584-09-6View Details
24584-09-6 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
