Desflurane
- CAS NO.:57041-67-5
- Empirical Formula: C3H2F6O
- Molecular Weight: 168.04
- MDL number: MFCD00236716
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-04 17:34:40
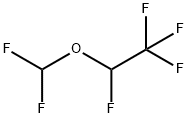
What is Desflurane?
Absorption
Data regarding the Cmax, Tmax, and AUC of desflurane are not readily available.
Toxicity
Patients experiencing a desflurane overdose may experience deepening anesthesia, cardiac or respiratory depression. In the event of an overdose, patients may require symptomatic and supportive treatment to maintain airway, breathing, and circulation. Discontinue desflurane.
Description
Desflurane is a new inhalation anesthetic introduced for induction and maintenance of general anesthesia in adults. Due to reports of respiratory irritation, desflurane may be used only for maintenance in children. Although almost structurally identical to isoflurane, a halogen replacement gives desflurane an improved pharmacokinetic profile. It is less soluble in blood and tissue and produces a fast onset of action and a more rapid recovery from anesthesia.
Chemical properties
Desflurane is a clear, colourless, mobile, heavy liquid. It is similar to isoflurane (CHF2-O-CHCl-CF3) in that both are halogenated compounds of methyl ethane, except that chlorine is replaced with fluorine in the α-ethyl portion. The halogenation of fluorine reduces the solubility of blood and tissues and alters the boiling point, vapor pressure and stability of desflurane, enhancing its molecular stability as well as its resistance to biodegradation and alkaline degradation.
Originator
Anaquest (BOC Healthcare) (U.S.A.)
History
Desflurane was first synthesized by Russel et al U.S. at the 29. of July 1975. The synthesis was started by using floural methyl hemiacetal (CF3CH(OH)OCH3) and converting it to 1,2,2,2- tetraflouroethyl methyl ether (CF3CHFOCH3). Next step was chlorinating two hydrogen atoms of the methyl-group to CF3CHFOCHCl2. This next to last molecule was charged with HF in the presence of antimony pentachloride (SBCL5) to Desflurane. But this way of synthesizing Desfluran was not usable for industrial synthesis, because of the less yield of Desflurane and the expensive educts.
The Uses of Desflurane
Anesthetic.
Indications
Desflurane is indicated for the induction and maintenance of anesthesia in adults, as well as the maintenance of anesthesia in pediatric patients.
Background
Desflurane, or I-653, a a volatile anesthetic that is more rapidly cleared and less metabolized than previous inhaled anesthetics such as methoxyflurane, sevoflurane, enflurane, or isoflurane.. It was developed in the late 1980s out of a need for a more rapidly acting and rapidly cleared inhaled anesthetic.
Desflurane was granted FDA approval on 18 September 1992.
Preparation
Isoflurane and bromine trifluoride were reacted overnight at room temperature to synthesize desflurane in 62% yield.
Definition
ChEBI: Desflurane is an organofluorine compound. It has a role as an inhalation anaesthetic. It is functionally related to a methoxyethane.
brand name
Suprane (Baxter Healthcare).
Biological Functions
Desflurane (Suprane) shares most of the pharmacological
properties of isoflurane. Desflurane has low tissue
and blood solubility compared with other halogenated
hydrocarbons, and its anesthetic partial pressure is thus
established more rapidly. Recovery is similarly prompt
when the patient is switched to room air or oxygen.
Desflurane’s popularity for outpatient procedures stems
from its rapid onset and prompt elimination from the
body by exhalation. A disadvantage is that desflurane irritates
the respiratory tract; thus, it is not preferred for
induction of anesthesia using an inhalational technique.
However, desflurane may be used to maintain anesthesia
after induction with an alternative IV or inhalational
agent, preserving the advantage of rapid recovery.
Desflurane, like other halogenated hydrocarbon
anesthetics, causes a decrease in blood pressure.The reduced
pressure occurs primarily as a consequence of
decreased vascular resistance, and since cardiac output
is well maintained, tissue perfusion is preserved.
Desflurane stimulates the sympathetic nervous system
and causes abrupt transient tachycardia during induction
or as the concentration of the agent is raised to
meet the patient’s changing needs.
Desflurane causes an increase in the rate of ventilation,
a decrease in tidal volume, and a decrease in
minute volume as inspired concentrations only slightly
exceed 1 MAC. Thus should anesthesiologists require
desflurane to be administered near or above MAC levels,
patients are likely to have marked reductions in
PCO2.
General Description
Desflurane is a nonflammable, colorless, very volatile liquidpackaged in amber-colored vials. The boiling point is22.8°C, and it requires a vaporizer specifically designed fordesflurane. The manufacturer states that the vials can bestored at room temperature. Desflurane has a blood:gas partitioncoefficient of 0.42, an MAC of 7.3% and an oil:gaspartition coefficient of 18.7. The low blood:gas partition coefficientleads to fast induction times and short recoverytimes. Desflurane is not recommended for induction anesthesiain children because of the high incidence of laryngospasms(50%), coughing (72%), breath holding (68%),and increase in secretions (21%). Desflurane can producea dose-dependent decrease in blood pressure and concentrationsexceeding 1 MAC may cause transient increases inheart rate. Desflurane can react with desiccated carbon dioxideabsorbents to produce carbon monoxide that may resultin elevated levels of carboxyhemoglobin.24.
Pharmacokinetics
Desflurane is a general inhalation anesthetic. It has a short duration of action as it is rapidly cleared. Patients should be counselled regarding the risks of malignant hyperthermia, perioperative hyperkalemia, respiratory adverse reactions in pediatric patients, QTc prolongation, hepatobiliary disorders, pediatric neurotoxicity, and postoperative agitation in children.
Metabolism
Desflurane is minimally defluorinated by CYP2E1, to the extent that serum fluoride levels do not increase above baseline levels.
Metabolism
Desflurane is not metabolized to any great extent and, therefore, has not been associated with hepatotoxicity or nephrotoxicity. Metabolites, mostly trifluoroacetate, account for less than 0.02% of the administered dose. Whereas desflurane can react with soda lime or Baralyme to form carbon monoxide, no reports of adverse outcomes in patients have appeared.
Properties of Desflurane
| Boiling point: | 23-24°C |
| Density | 1,47 g/cm3 |
| refractive index | 1.3577 (estimate) |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, miscible with anhydrous ethanol. |
| color | Clear |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 57041-67-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ethane, 2-(difluoromethoxy)-1,1,1,2-tetrafluoro-, (+-)- (57041-67-5) |
Safety information for Desflurane
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Desflurane
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4