Deferiprone
Synonym(s):3-Hydroxy-1,2-dimethyl-4(1H)-pyridone;Deferiprone
- CAS NO.:30652-11-0
- Empirical Formula: C7H9NO2
- Molecular Weight: 139.15
- MDL number: MFCD00134497
- EINECS: 212-783-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-25 11:31:46
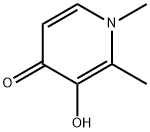
What is Deferiprone?
Absorption
Deferiprone is absorbed in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Absorption is rapid with maximum plasma concentrations occurring after 1 hour in the fasted state and after 2 hours in the fed state.
Toxicity
Agranulocytosis and neutropenia may occur, which can lead to fatal infections. Hepatoxicity is also possible. Most common side effects that lead to discontinuation of therapy were the gastrointestinal adverse effects (diarrhea, ulcer, nausea, gastrointestinal disturbances)
Description
Deferiprone, the first oral iron chelator, was marketed in India for the management of thalassaemia. Patients with thalassaemia, a blood related genetic disorder, require life time transfusion which causes excessive deposition of iron in liver and spleen, subsequent damage to organs and eventually death unless iron is removed by a chelator. Deferiprone is a potent iron chelator that mobilizes excessive iron from iron storage proteins ferritin and hemosiderin, from iron saturated transferrin and lactoferrin, but not from hemoglobin. The deferiprone-iron complex is excreted in urine and bile. Deferiprone was reportedly well accepted by patients and no hematological toxicity was observed. Deferiprone has also been demonstrated as an effective and safe chelator in the mobilization of aluminum.
Chemical properties
White Needles
Originator
Cipla (India)
The Uses of Deferiprone
A chelator that could replace disferrioxamine. It is orally and parenterally effective in the removal of iron in vivo from rabbits and mice and also from transferrin and ferritin in vitro
The Uses of Deferiprone
3-Hydroxy-1,2-dimethyl-4(1H)-pyridone (OH-pyridone) may be used in the bacterial killing assays. It has been employed as hydroxyketone chelating agent and its cytotoxic action against oral human normal and tumor cell lines has been evaluated.
What are the applications of Application
Deferiprone is a chelator that removes transferrin and ferritin in vitro
Background
Deferiprone is an oral iron chelator used as a second line agent in thalassemia syndromes when iron overload from blood transfusions occurs. Thalassemias are a type of hereditary anaemia due a defect in the production of hemoglobin. As a result, erythropoiesis, the production of new red blood cells, is impaired. FDA approved on October 14, 2011.
Indications
Deferiprone is indicated in thalassemia syndromes when first line chelation agents are not adequate to treat transfusional iron overload.
Definition
ChEBI: Deferiprone is a member of the class of 4-pyridones that is pyridin-4(1H)-one substituted at positions 1 and 2 by methyl groups and at position 3 by a hydroxy group. A lipid-soluble iron-chelator used for treatment of thalassaemia. It has a role as an iron chelator and a protective agent.
brand name
Kelfer
General Description
3-Hydroxy-1,2-dimethyl-4(1H)-pyridone (Hdpp, Deferiprone) is a hydroxy ketone derivative. It reacts with uranyl salts [UO2(NO3)2] in aqueous acidic solution to afford mono nuclear complexes ([UO2(dpp)(Hdpp)2(H2O)]ClO4). X-ray studies have been conducted to examine the structure and geometry of these complexes.
Clinical Use
Orally administered chelator:
Treatment of transfusional iron overload
Metabolism
Deferiprone is mainly metabolized by UGT1A6 to the 3-O-glucuronide metabolite. This metabolite cannot chelate iron.
Metabolism
Deferiprone is hepatically metabolised to an inactive glucuronide metabolite and is excreted mainly in the urine as the metabolite and the iron-deferiprone complex, with a small amount of unchanged drug.
References
1) Hider and Hoffbrand (2018),?The Role of Deferiprone in Iron Chelation; N. Engl. J. Med.,?379?2140 2) Sripetchwandee?et al.?(2016),?A combination of an iron chelator with an antioxidant effectively diminishes the dendritic loss, tau-hyperphosphorylation, amyloid-β accumulation and brain mitochondrial dynamic disruption in rats with chronic iron-overload., Neuroscience?332?191 3) Liu?et al.?(2018),?Iron and Alzheimer’s Disease: From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Implications;?Front. Neurosci,?12?632
Properties of Deferiprone
| Melting point: | 272-275 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 255.1°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1997 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4800 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in Water (up to 5 mg/ml with warming). |
| pka | pKa1 3.3, pKa2 9.7(at 25℃) |
| form | Crystalline Powder or Needles |
| color | White to off-white |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in hot water |
| Merck | 14,2859 |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions are not stable and must be prepared fresh daily. |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C7H9NO2/c1-5-7(10)6(9)3-4-8(5)2/h3-4,10H,1-2H3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 30652-11-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Deferiprone
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for Deferiprone
| InChIKey | TZXKOCQBRNJULO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C1(C)N(C)C=CC(=O)C=1O |
Deferiprone manufacturer
SRINI PHARMACEUTICALS PVT LTD
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![3-[(2-CHLORO-6-FLUOROBENZYL)OXY]-1-(2,4-DICHLOROBENZYL)-2-METHYL-4(1H)-PYRIDINONE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB1162073.gif)
![3-[(2-CHLORO-6-FLUOROBENZYL)OXY]-1-[3-CHLORO-5-(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)-2-PYRIDINYL]-2-METHYL-4(1H)-PYRIDINONE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB7771565.gif)
![1-[3-CHLORO-5-(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)-2-PYRIDINYL]-3-[(2,6-DICHLOROBENZYL)OXY]-2-METHYL-4(1H)-PYRIDINONE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB9170270.gif)
![3-[(2-CHLORO-6-FLUOROBENZYL)OXY]-2-METHYL-1-(3-NITRO-2-PYRIDINYL)-4(1H)-PYRIDINONE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB8192475.gif)
![3-[(2,6-DICHLOROBENZYL)OXY]-1-(4-FLUOROBENZYL)-2-METHYL-4(1H)-PYRIDINONE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB9459719.gif)
![1-(4-CHLOROBENZYL)-3-[(2-CHLORO-6-FLUOROBENZYL)OXY]-2-METHYL-4(1H)-PYRIDINONE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB9732751.gif)
![1-BENZYL-3-[(2-CHLORO-6-FLUOROBENZYL)OXY]-2-METHYL-4(1H)-PYRIDINONE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB0444228.gif)
![3-[(4-CHLOROBENZYL)OXY]-1-[3-CHLORO-5-(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)-2-PYRIDINYL]-2-METHYL-4(1H)-PYRIDINONE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB6761297.gif)
You may like
-
 Deferiprone 99%View Details
Deferiprone 99%View Details -
 Deferiprone 98%View Details
Deferiprone 98%View Details
30652-11-0 -
 Deferiprone 99%View Details
Deferiprone 99%View Details -
 Deferiprone 98%View Details
Deferiprone 98%View Details -
 Deferiprone 98%View Details
Deferiprone 98%View Details -
 3-Hydroxy-1,2-dimethyl-4(1H)-pyridone CAS 30652-11-0View Details
3-Hydroxy-1,2-dimethyl-4(1H)-pyridone CAS 30652-11-0View Details
30652-11-0 -
 Deferiprone 99% (HPLC) CAS 30652-11-0View Details
Deferiprone 99% (HPLC) CAS 30652-11-0View Details
30652-11-0 -
 3-Hydroxy-1,2-dimethyl-4(1H)-pyridone CAS 30652-11-0View Details
3-Hydroxy-1,2-dimethyl-4(1H)-pyridone CAS 30652-11-0View Details
30652-11-0
