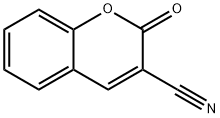
Coumarin
Synonym(s):1,2-Benzopyrone;1-Benzopyran-2-one;2H-Chromen-2-one;5,6-Benzo-2-pyrone;Coumarin
- CAS NO.:91-64-5
- Empirical Formula: C9H6O2
- Molecular Weight: 146.14
- MDL number: MFCD00006850
- EINECS: 202-086-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 13:58:55
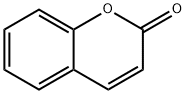
What is Coumarin?
Description
Coumarin is a naturally occurring Benzopyrone compound. It is found in a large number of plants belonging to many different families including tonka beans, woodruff, lavender oil, cassia, melilot (sweet clover), and other plants. It is found in edible plants such as strawberries, cinnamon, peppermint, green tea, carrots, and celery, as well as in partially fermented tea, red wine, beer, and other foodstuffs. Concentrations range from 87 000 ppm in cassia and 40 000 ppm in cinnamon to 20 ppm in peppermint and 5 ppb in tangerines.
Description
Coumarin is a benzopyrone that occurs naturally in plant-derived sources such as tonka beans, lavender oil, woodruff, and sweet clover. Its sweet scent makes it useful in perfume manufacture. It is a potent rodenticide, but it is only moderately toxic to humans. It is used to make warfarin, another rodenticide that is also a widely used anticoagulant drug (trade name Coumadin) for preventing thrombosis and embolism.
Chemical properties
WHITE CRYSTALS OR CRYSTALLINE POWDER
Chemical properties
Coumarin occurs widely in nature and determines, for example, the odor of woodruff. It forms white crystals (mp 70.6°C) with a hay-like, spicy odor. When treated with dilute alkali, coumarin is hydrolyzed to the corresponding coumarinic acid salt [(Z)-2-hydroxycinnamic acid]. Heating with concentrated alkali or with sodium ethanolate in ethanol results in the formation of o-coumaric acid salts [(E)-2-hydroxycinnamic acid]. 3,4-Dihydrocoumarin is obtained by catalytic hydrogenation, for example, with Raney nickel as a catalyst; octahydrocoumarin is obtained if hydrogenation is carried out at high temperature (200–250°C).
Chemical properties
Coumarin has a sweet, fresh, hay-like, odor similar to vanilla seeds, and a burning taste with bitter undertone and nutlike flavor on dilution.
Occurrence
Found in many plants and essential oils such as cassia, melilot, orchid, lavender and balsam of Peru (Sp?th, 1937; Gildemeister & Hoffman, 1966).
The Uses of Coumarin
coumarin is considered a blood thinner, it can also increase blood flow. Some sources cite anti-oxidant capacities, as well. It is a specific plant constituent and is what creates the fragrance of freshly mowed hay. Coumarin is found in such plants as cherries, lavender, licorice, and sweet clover.
The Uses of Coumarin
Pharmaceutic aid (flavor). Found in tonka beans, levender oil, woodruff, sweet clover.
The Uses of Coumarin
antineoplastic, antiinflammatory, antihyperglycaemic
What are the applications of Application
Coumarin is an anticoagulant agent found in certain plants
Definition
ChEBI: A chromenone having the keto group located at the 2-position.
Definition
A colorless crystalline compound with a pleasant odor, used in making perfumes. On hydrolysis with sodium hydroxide it forms coumarinic acid.
Preparation
Coumarin is currently produced by Perkin synthesis from salicylaldehyde.
In the presence of sodium acetate, salicylaldehyde reacts with acetic
anhydride to produce coumarin and acetic acid. The reaction is carried out in the
liquid phase at elevated temperature.
A process for the production of coumarin from hexahydrocoumarin by dehydrogenation has also been elaborated.
Since the odor of coumarin is relatively weak, strong-smelling by-products (e.g.,
vinylphenol) must be removed. Many purification methods have been reported
and patented.
Aroma threshold values
Detection at 34 to 50 ppb; recognition, 250 ppb
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 27, p. 4704, 1962 DOI: 10.1021/jo01059a541
Tetrahedron Letters, 27, p. 3911, 1986 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)83914-3
General Description
Colorless crystals, flakes or colorless to white powder with a pleasant fragrant vanilla odor and a bitter aromatic burning taste.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Coumarin is sensitive to exposure to light. Coumarin is also sensitive to heat. Coumarin is incompatible with strong acids, strong bases and oxidizers. Coumarin is hydrolyzed by hot concentrated alkalis. Coumarin can be halogenated, nitrated and hydrogenated (in the presence of catalysts).
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion; carcinogenic. Use in food products prohibited (FDA). Questionable carcinogen.
Health Hazard
SYMPTOMS: Exposure to Coumarin may cause narcosis. It may also cause irritation and liver damage.
Fire Hazard
Coumarin is combustible.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Biological Activity
Oral anticoagulants can be prepared from compounds with coumarin as a base. Coumarin has been known for well over a century and, in addition to its use pharmaceutically, it is also an excellent odor-enhancing agent. However, because of its toxicity, it is not permitted in food products in the United States (Food and Drug Administration). One commercial drug is 3-(alpha-acetonyl-4-nitrobenzyl)- 4-hydroxycoumarin. This drug reduces the concentration of prothrombin in the blood and increases the prothrombin time by inhibiting the formation of prothrombin in the liver. The drug also interferes with the production of factors VII, IX, and X, so that their concentration in the blood is lowered during therapy. The inhibition of prothrombin involves interference with the action of vitamin K, and it has been postulated that the drug competes with vitamin K for an enzyme essential for prothrombin synthesis. Another commercial drug is bis-hydroxy-coumarin, C19H12O6. The actions of this drug are similar to those just described.
Contact allergens
Coumarin is an aromatic lactone naturally occurring in Tonka beans and other plants. As a fragrance allergen, it has to be mentioned by name in cosmetics within the EU
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, intraperitoneal, and subcutaneous routes. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. Experimental teratogenic effects. Mutation data reported. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and fumes. See also KETONES and ANHYDRIDES.
Synthesis
May be extracted from tonka beans; from salicylaldehyde and acetic anhydride in the presence of sodium acetate; also from o-cresol and carbonyl chloride followed by chlorination of the carbonate and fusion with a mixture of alkali acetate, acetic anhydride and a catalyst.
Environmental Fate
Coumarin toxicity is a function of blood and target tissue levels of coumarin relative to the metabolic capacity of the target organ. Cellular toxicity results when the formation of the toxic moieties exceeds the capacity of the cell to detoxify. This can have significant impact when comparing dosing by gavage to dietary exposure.
Purification Methods
Coumarin crystallises from ethanol or water and sublimes in vacuo at 43o [Srinivasan & deLevie J Phys Chem 91 2904 1987]. [Beilstein 17/10 V 143.]
Toxicity evaluation
Coumarin is readily biodegradable. Coumarin is unlikely to bind to soil. Coumarin does not bioaccumulate; the bioconcentration factor has been determined to be <10–40. Various environmental fate studies have shown that coumarin in the environment would biodegrade and be lost to volatilization. Losses resulting from photolysis may also occur.
Properties of Coumarin
| Melting point: | 68-73 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 298 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 0.935 |
| vapor pressure | 0.01 mm Hg ( 47 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.5100 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 162 °C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 1.7g/l |
| form | Crystals or Crystalline Powder |
| color | White |
| PH Range | Non' uorescence (9.5) to light green ' uorescence (10.5) |
| Odor | at 10.00 % in dipropylene glycol. sweet hay tonka new mown hay |
| Water Solubility | 1.7 g/L (20 ºC) |
| λmax | 275nm |
| Merck | 14,2562 |
| BRN | 383644 |
| Major Application | color filter, organic electroluminescent devices, liquid crystal displays, field emission displays, inks, nickel plating, detergents, deodorant for shoes, petroleum products, cigarettes, personal care products, cosmetics, sunscreen cream, perfumes, nucleic acid sequencing, antiinflammatory agent, treatment of cancer, neurotransmission disorders, bleeding disorders, cerebrovascular disease, thrombosis, hemorrhoids, rheumatic disease, arthritic disease, epilepsy, vaginitis, painkiller, teeth whitening agent, skin whitening agent, wound healing promoter |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 91-64-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Coumarin(91-64-5) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. Sup 7, 77) 2000 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Coumarin (91-64-5) |
Safety information for Coumarin
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for Coumarin
| InChIKey | ZYGHJZDHTFUPRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Coumarin manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Coumarin 98%View Details
Coumarin 98%View Details
91-64-5 -
 Coumarin, 99%+ CAS 91-64-5View Details
Coumarin, 99%+ CAS 91-64-5View Details
91-64-5 -
 Coumarin pure CAS 91-64-5View Details
Coumarin pure CAS 91-64-5View Details
91-64-5 -
 Coumarin 99% (GC) CAS 91-64-5View Details
Coumarin 99% (GC) CAS 91-64-5View Details
91-64-5 -
 Coumarin CAS 91-64-5View Details
Coumarin CAS 91-64-5View Details
91-64-5 -
 Coumarine CAS 91-64-5View Details
Coumarine CAS 91-64-5View Details
91-64-5 -
 COUMARIN For Synthesis CAS 91-64-5View Details
COUMARIN For Synthesis CAS 91-64-5View Details
91-64-5 -
 Thiosemicarbazide CAS 91-64-5View Details
Thiosemicarbazide CAS 91-64-5View Details
91-64-5