Chlordiazepoxide
- CAS NO.:58-25-3
- Empirical Formula: C16H14ClN3O
- Molecular Weight: 299.75
- MDL number: MFCD00481188
- EINECS: 200-371-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
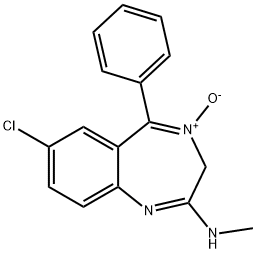
What is Chlordiazepoxide?
Toxicity
LD50=537 mg/kg (Orally in rats). Signs of overdose include respiratory depression, muscle weakness, somnolence (general depressed activity).
Chemical properties
Pale Yellow Solid
Originator
Librium,Roche,W. Germany,1960
The Uses of Chlordiazepoxide
Controlled substance (depressant). Anxiolytic. Prototype of the benzodiazepine anxiolytics
Indications
Chlordiazepoxide is indicated for the management of anxiety disorders or for the short-term relief of symptoms of anxiety, withdrawal symptoms of acute alcoholism, and preoperative apprehension and anxiety.
In combination with amitriptyline, chlordiazepoxide is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe depression. In combination with clidinium, chlordiazepoxide is indicated to control emotional and somatic factors in gastrointestinal disorders, and is used as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of peptic ulcer, irritable bowel syndrome and acute enterocolitis.
Background
An anxiolytic benzodiazepine derivative with anticonvulsant, sedative, and amnesic properties. It has also been used in the symptomatic treatment of alcohol withdrawal.
Definition
ChEBI: A benzodiazepine that is 3H-1,4-benzodiazepine 4-oxide substituted by a chloro group at position 7, a phenyl group at position 5 and a methylamino group at position 2.
Manufacturing Process
A mixture of 202 g 2-amino-5-chlorobenzophenone, 190 g hydroxylamine
hydrochloride, 500 cc pyridine and 1,200 cc alcohol was refluxed for 16 hours,
then concentrated in vacuo to dryness. The residue was treated with a
mixture of ether and water. The water was separated, the ether layer
containing a considerable amount of precipitated reaction product was washed
with some water and diluted with petroleum ether. The crystalline reaction
product, 2-amino-5-chlorobenzophenone-alpha-oxime, was filtered off. The
product was recrystallized from a mixture of ether and petroleum ether
forming colorless prisms, MP 164 to 167°C.
To a warm solution (50°C) of 172.5 g (0.7 mol) of 2-amino-5-
chlorobenzophenone-alpha-oxime in one liter glacial acetic acid were added
110 cc (1.47 mols) chloroacetyl chloride. The mixture was heated for 10
minutes at 50°C and then stirred at room temperature for 15 hours. The
precipitated yellow prisms, 2-chloromethyl-4-phenyl-6-chloroquinazoline 3-
oxide hydrochloride, were filtered off, melting range 128° to 150°C with dec.
The acetic acid mother liquor, containing the rest of the reaction product, was
concentrated in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in methylene chloride and
washed with ice cold sodium carbonate solution. The organic solution was
dried, concentrated in vacuo to a small volume and diluted with ether and
petroleum ether. Fine yellow needles of 2-chloromethyl-4-phenyl-6-
chloroquinazoline 3-oxide precipitated. The pure base was recrystallized from
a mixture of methylene chloride, ether and petroleum ether, MP 133° to
134°C.
Ninety-eight grams of 6-chloro-2-chloromethyl-4-phenylquinazoline 3-oxide
hydrochloride were introduced into 600 cc of ice cold 25% methanolic
methylamine. The mixture was initially cooled to about 30°C and then stirred
at room temperature. After 15 hours the reaction product which precipitated
was filtered off. The mother liquor was concentrated in vacuo to dryness. The
residue was dissolved in methylene chloride, washed with water and dried
with sodium sulfate. The methylene chloride solution was concentrated in
vacuo and the crystalline residue was boiled with a small amount of acetone
to dissolve the more soluble impurities. The mixture was then cooled at 5°C
for 10 hours and filtered. The crystalline product, 7-chloro-2-methylamino-5-
phenyl-3H-1,4-benzodiazepine 4-oxide, was recrystallized from ethanol
forming light yellow plates, MP 236° to 236.5°C.
A solution of 7-chloro-2-methylamino-5-phenyl-3H-1,4-benzodiazepine 4-oxide
in an equivalent amount of methanolic hydrochloric acid was diluted with
ether and petroleum ether.
The precipitated hydrochloride was filtered off and recrystallized from
methanol, MP 213°C.
brand name
Librium (Valeant).
Therapeutic Function
Tranquilizer
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 26, p. 1111, 1961 DOI: 10.1021/jo01063a034
Hazard
Anticonvulsant, sedative, and amnesic properties.
Pharmacokinetics
Chlordiazepoxide has antianxiety, sedative, appetite-stimulating and weak analgesic actions. The drug seems to block EEG arousal from stimulation in the brain stem reticular formation. The drug has been studied extensively in many species of animals and these studies are suggestive of action on the limbic system of the brain, which recent evidence indicates is involved in emotional responses. Hostile monkeys were made tame by oral drug doses which did not cause sedation. Chlordiazepoxide revealed a "taming" action with the elimination of fear and aggression. The taming effect of chlordiazepoxide was further demonstrated in rats made vicious by lesions in the septal area of the brain. The drug dosage which effectively blocked the vicious reaction was well below the dose which caused sedation in these animals.
Metabolism
Hepatic.
Metabolism
Chlordiazepoxide is well absorbed after oral administration, and peak blood concentration usually is reached in approximately 4 hours. Intramuscular absorption of chlordiazepoxide, however, is slower and erratic. The half-life of chlordiazepoxide is variable but usually quite long (6–30 hours). The initial N-demethylation product, N-desmethylchloridiazepoxide, undergoes deamination to form the demoxepam, which is extensively metabolized, and less than 1% of a dose of chlordiazepoxide is excreted as demoxepam. Demoxepam can undergo four different metabolic fates. Removal of the N-oxide moiety yields the active metabolite, N-desmethyldiazepam (desoxydemoxepam). This product is a metabolite of both chlordiazepoxide and diazepam and can be hydroxylated to yield oxazepam, another active metabolite that is rapidly glucuronidated and excreted in the urine. Another possibility for metabolism of demoxepam is hydrolysis to the “opened lactam,” which is inactive. The two other metabolites of demoxepam are the products of ring A hydroxylation (9-hydroxydemoxepam) or ring C hydroxylation (4′-hydroxydemoxepam), both of which are inactive.
Properties of Chlordiazepoxide
| Melting point: | 230-232°C |
| Boiling point: | 549.0±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.2967 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6490 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 9℃ |
| storage temp. | Controlled Substance, -20°C Freezer, Under Inert Atmosphere |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, sparingly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent) |
| form | A crystalline solid |
| pka | 4.8(at 25℃) |
| Water Solubility | 2g/L(room temperature) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 58-25-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzodiazepine-4-oxide, 7-chloro-2-methylamino-5-phenyl-3h-1,4-(58-25-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Chlordiazepoxide (58-25-3) |
Safety information for Chlordiazepoxide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H370:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P311:Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for Chlordiazepoxide
Chlordiazepoxide manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1