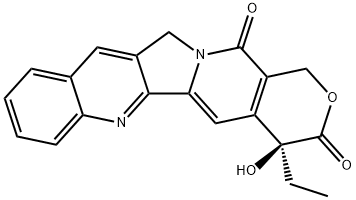
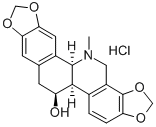
CHELIDONINE
Synonym(s):Stylophorin
- CAS NO.:476-32-4
- Empirical Formula: C20H19NO5
- Molecular Weight: 353.37
- MDL number: MFCD00069660
- EINECS: 207-504-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-19 17:28:17

What is CHELIDONINE?
Description
Chelidonine, also named ranunculine, is a kind of alkaloid isolated from the whole
plant of Chelidonium majus. L . As a kind of traditional Chinese medicine,
Chelidonium majus. L was firstly recorded in Chiu Huang Pen Ts’ao of Ming
dynasty. In the seventeenth century, it has been used for the treatment of jaundice,
biliary colic, and cholelithiasis. In 1941, a researcher from Soviet Union reported
that it showed good effect for the treatment of cutaneous tuberculosis. This plant has
multiple effects on different diseases, including anti-inflammatory, analgesia,
relieving cough, inducing diuresis, anticancer, antifungal, relieving asthma, and
detoxification. It was recorded in the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of
China (1977) .
The material basis for Chelidonium majus. L is alkaloid. Among which, chelidonine,
a benzophenanthridine alkaloid, is the main effective ingredient . Although
great progresses have been made in the chemical synthesis of chelidonine recently,
the biosynthetic pathways of chelidonine remain unclear, which still need in-depth
study and exploration in the future
Description
Chelidonine is a benzophenanthridine alkaloid that has been isolated from C. majus. It induces Bcl-2- and caspase-dependent apoptosis in HepG2 human liver carcinoma cells with an LC50 value of 12 μM and in Jurkat human T cells when used at a concentration of 1 μM. Chelidonine also downregulates hTERT expression in HepG2 cells, reduces telomerase activity, and induces cell senescence.
Chemical properties
White, crystalline powder alkaloid.
Physical properties
Appearance: white crystal or crystalline powder, monoclinic prism crystal. Solubility: insoluble in water; soluble in ethanol, chloroform, and amyl alcohol. Melting point: 135–136 °C. Boiling point: 220 °C. Specific optical rotation: +115°.
History
Chelidonine was isolated from Chelidonium majus. L in 1824 for the first time.
Pharmacological studies found that it exerted antitumor effect via different mechanisms.
However, its poor bioavailability limited its application. Some researchers developed a chelidonine/polylactic acid copolymer nanoparticle using nanotechnology.
The nano-chelidonine showed good tissue distribution without causing any
toxicity in mice and could enter into the brain tissues, showing great application
potential. In addition, nano-chelidonine showed protective effect on liver injury
induced by cadmium in mice .
In 1981, an Austrian researcher isolated a novel compound ukrain (phosphorothioate
derivative of chelidonine) from Chelidonium majus. L. Ukrain could inhibit
tumor cell proliferation through a variety of mechanisms. Currently, ukrain is used
as an antitumor drug for the clinical treatment of lung cancer, breast cancer, prostate
cancer, and pancreatic cancer . In 2004, quarter amine chelidonine phosphorothioate
derivatives have been applied for an invention patent as anticancer drugs in
China.
Chelidonine has morphine-like analgesic effects suggesting that its analgesic
effect is mainly peripheral and cannot be antagonized by the morphine receptor
antagonist naloxone . The 6-alkoxy and 6-acyloxy derivatives of chelidonine can
inhibit the central nervous system, especially for nerve terminal, and show sedative
and hypnotic effects .
The Uses of CHELIDONINE
Poison; central nervous system depres- sant causing sleepiness, depression, slowing of the pulse, coma and circulatory failure.
Definition
ChEBI: Chelidonine is an alkaloid fundamental parent, a benzophenanthridine alkaloid and an alkaloid antibiotic.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Inhibits tubulin polymerisation (IC50=24 μM), thereby disrupting microtubule structure in cells and inducing a G2/M mitotic arrest.
Pharmacology
Chelidonine has a variety of pharmacological effects, mainly manifested in the following
aspects:
1. The effect on nervous system (analgesia, sedation)
Chelidonine, as a protopine, has analgesia effect similar to that of morphine.
After intragastric administration (5–20 mg/kg) to mice, it showed a dose-dependent
analgesic effect, which could sustain 4–48 h . Chelidonine derivatives also have
sedative and hypnotic effects .
2. The effect on cardiovascular systemChelidonine has many effects on cardiovascular system, including exciting heart,
expanding coronary blood vessels, and increasing blood pressure. Chelidonine
(0.01–0.02 mg) leads to the excitement of frog heart in vitro, as well as slowdown
of heart beat. Higher dosage (0.05 mg) of chelidonine could cause arrhythmia and
diastolic cardiac arrest .
3. The antitumor effect
Chelidonine is a toxic substance that can influence mitosis. In vitro studies have
shown that chelidonine had significant inhibitory effects for gastric cancer, leukemia,
nasopharyngeal carcinoma, and hepatoma carcinoma cells. It also could delay
the growth of malignant tumors. Its antitumor effects were mediated by different
mechanisms, which still need further studies .
4. The effect on smooth muscle
Chelidonine has spasmolytic and diastolic effects and can inhibit a variety of
smooth muscle spasm. Obvious spasmolytic effects for gastrointestinal tract and
bronchial and urinary system have been reported .
5. The antibacterial effect
Chelidonine has antibacterial effect. It inhibits Mycobacterium tuberculosis
in vivo and inhibits alpha Streptococcus, Diplococcus pneumoniae, and other gram-positive
bacteria in vitro. In addition, chelidonine also shows inhibitory effect on
Kauffman-Wolf Trichophyta and Epidermophyton floccosum .
6. Other pharmacological effects
Chelidonine showed protective effects on cadmium chloride-induced liver and
kidney toxicity in rats. Chelidonine can inhibit the growth of human keratinocytes.
Guinea pig test confirmed that chelidonine (4–10 mg/kg) could prevent or delay the
anaphylactic shock. In addition, chelidonine has anti-mite effect and good synergistic
effect with trichlorfon or omethoate to prevent cotton bollworm.
Clinical Use
Chelidonine has been used as a painkiller in clinical application due to its significant analgesic effect. Chelidonine phosphate can be used for treatment of gastrointestinal and ulcer pain, as a substitute of morphine preparations. Wei Tong Shu capsule is used to treat pain caused by gastric convulsion, chronic gastritis, gastric ulcer, and duodenal ulcer. Its main effective compositions are chelidonine and protopine. Fu Fang Zhong Yao Tong An injection has collateral dredging and analgesic effects and can be used for the treatment of moderate pain caused by chemoradiotherapy or non-chemoradiotherapy of gastric cancer, lung cancer, and liver cancer. Its two main components are chelidonine and sinomenine. Ukrain (NSC-631570), a phosphorothioate derivative of chelidonine, has been used in clinical treatment as an effective antitumor drug for the treatment of lung cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer, and pancreatic cancer.
Properties of CHELIDONINE
| Melting point: | 135-140°C |
| Boiling point: | bp0.002 220° (air-bath temp) |
| alpha | D22 +115 ±3° (ethanol); D20 +117° (c = 3 in CHCl3) |
| Density | 1.2976 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5800 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in chloroform; slightly soluble in methan |
| form | powder |
| pka | 14.11±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | Colorless |
| Merck | 13,2061 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 476-32-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for CHELIDONINE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
Computed Descriptors for CHELIDONINE
| InChIKey | GHKISGDRQRSCII-ZOCIIQOWSA-N |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Chelidonine CAS 476-32-4View Details
Chelidonine CAS 476-32-4View Details
476-32-4 -
 Chelidonine CAS 476-32-4View Details
Chelidonine CAS 476-32-4View Details
476-32-4 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
