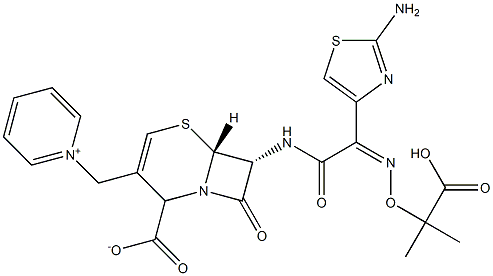
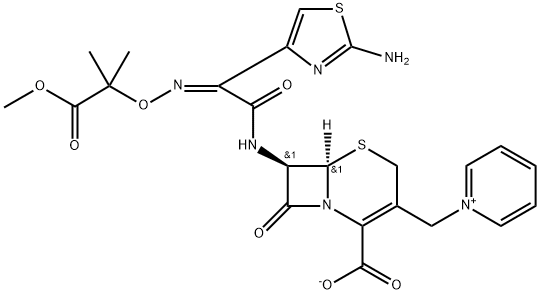
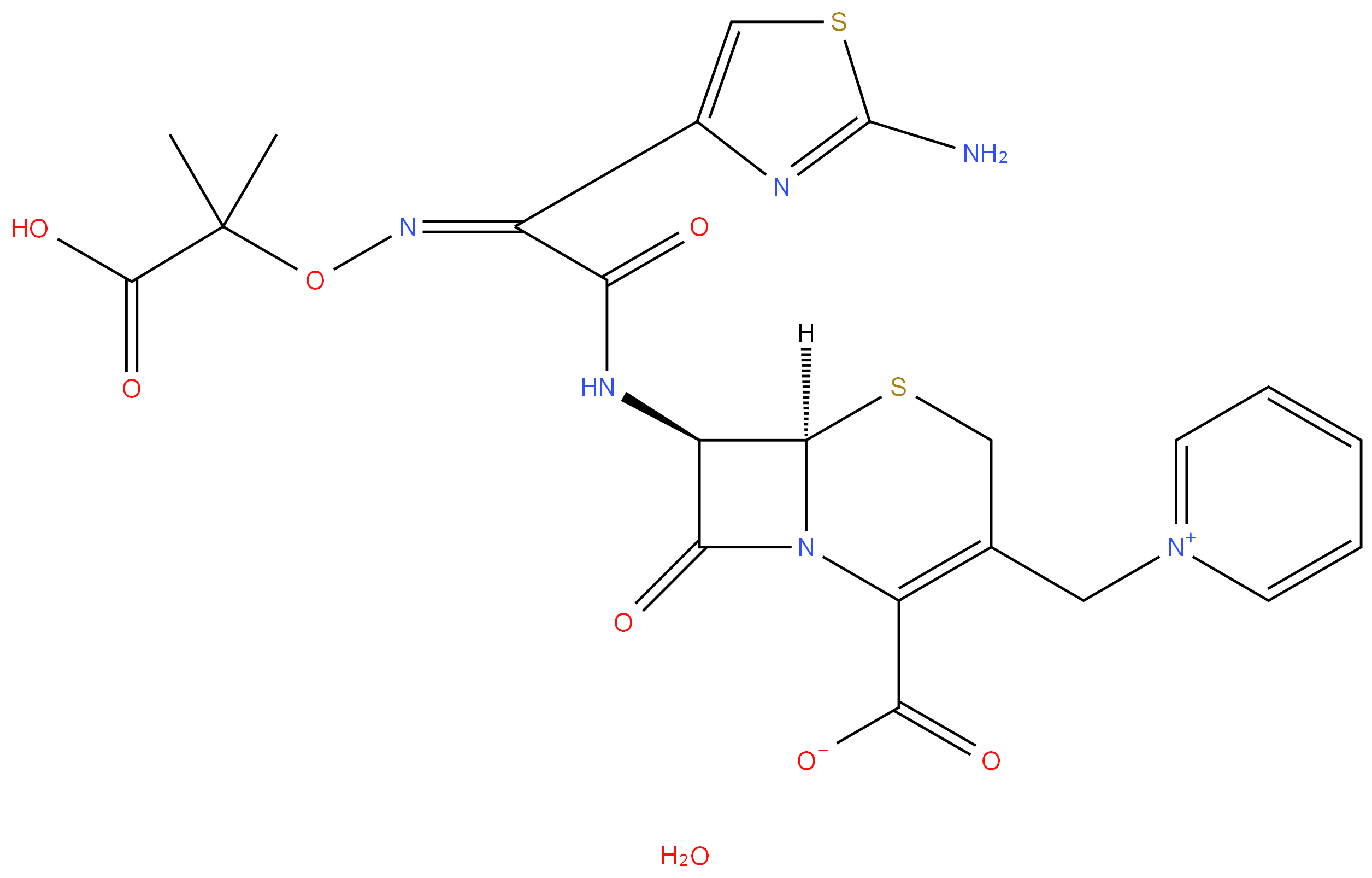
Ceftazidime
- CAS NO.:78439-06-2
- Empirical Formula: C22H24N6O8S2
- Molecular Weight: 564.59
- MDL number: MFCD00153936
- EINECS: 616-626-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-16 21:30:20
What is Ceftazidime?
Description
Ceftazidime is the latest third generation cephalosporin to reach the market. It has one of the broadest spectrums of the cephalosporins, similar in many regards to that of cefotaxime. It is particularly active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, being perhaps 4-5 times more potent in vitro than moxalactam and cefotaxime.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Glaxo (United Kingdom)
The Uses of Ceftazidime
Ceftazidime pentahydrate is an antibacterial agent. It is used especially for Pseudomonas and other gram-negative infections in debilitated patients. It is used in the treatment of patients with infections caused by susceptible strains of organisms in the following diseases: lower respiratory tract infections,skin and skin structure infections, urinary tract infections, bacterial septicemia, bone and joint infections, gynecologic infections, intra abdominal infections (including peritonitis), and central nervous system infections (including meningitis).
The Uses of Ceftazidime
Third generation cephalosporin antibiotic. Antibacterial.
What are the applications of Application
Ceftazidime Pentahydrate is a third generation cephalosporin antibiotic
Definition
ChEBI: A hydrate that is the pentahydrate of ceftazidime, a cephalosporin having 7beta-[(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-{[(2-carboxypropan-2-yl)oxy]imino}acetyl]amino and 3-pyridinium-1-ylmethyl side-groups.
brand name
Fortaz (GlaxoSmithKline); Tazicef (Hospira); Tazidime (Lilly);FORTAM.
Antimicrobial activity
Its activity is comparable to that of cefotaxime and ceftizoxime, but it is more active against Ps. aeruginosa, including almost all gentamicin-resistant strains, and Burk. cepacia. It is, however, less active against Staph. aureus. It is stable to a wide range of β-lactamases, but is hydrolyzed by some TEM variants.
Pharmacokinetics
Cmax 500 mg intramuscular: 18–20 mg/L
2 g intravenous (20-min infusion): 185 mg/L end infusion
Plasma half-life: 1.5–2 h
Volume of distribution: 16 L
Plasma protein binding: c. 10%
No accumulation was seen in subjects receiving 2 g every 12
h over 8 days. In premature infants given 25 mg/kg every 12
h, mean peak plasma concentrations were 77 mg/L after intravenous
and 56 mg/L after intramuscular administration, with
plasma elimination half-lives of 7.3 and 14.2 h, respectively.
Postnatal age was the most important determinant of elimination
rate, which was halved after 5 days. In newborn infants
given 50 mg/kg intravenously over 20 min, mean peak plasma
concentrations varied inversely with gestational age from 102
to 124 mg/L, with half-lives of 2.9–6.7 h.
Distribution
The concentration into serous fluids reaches 50% or more of
the simultaneous serum level. In patients given 1 g intravenously
during abdominal surgery, detectable concentrations
appeared within a few minutes in the peritoneal fluid, reaching
a peak around 67 mg/L with a half-life of 0.9 h. Following
a similar intravenous dose, a mean peak of 9.4 mg/L was
reached at 2 h in ascitic fluid. Concentrations in middle ear
fluid after 1 g intravenously were broadly comparable to those
of the plasma.
In patients with meningitis, CSF concentrations of 2–30
mg/L have been found 2–3 h after doses of 2 g intravenously
over 30 min given every 8 h for four doses. Concentrations are
substantially less in the absence of meningitis. Concentrations
of 3–27 mg/g were found in patients with intracranial abscesses
treated with 0.5–2 g every 8 h. Concentrations around 0.4 mg/g
in skin, 0.6 mg/g in muscle and 0.2 mg/g in fatty tissue have
been found in patients given 2 g intravenously over 5 min
preoperatively. A similar dose has produced mean prostate
tissue:serum ratios of around 0.14. Effective concentrations
are achieved in bone: in patients given 1 g intravenously mean
bone concentrations were 14.4 mg/kg 35–40 min after the
dose. There is secretion in breast milk, peak concentrations
being around 5 mg/L at about 1 h in patients receiving 2 g
intravenously every 8 h.
Metabolism and excretion
No metabolites have been detected. Elimination is almost
exclusively renal, predominantly via the glomerular filtrate,
with 80–90% of the dose appearing in the urine in the first 24 h. Elimination half-life is inversely correlated with creatinine
clearance: as the values fall to 2–12 mL/min, the mean
plasma half-life rises to 16 h. In patients maintained on hemodialysis
the half-life fell to 2.8 h on dialysis. No accumulation
occurred over 10 days in severe renal impairment on a daily
dose of 0.5–1 g.
Concentrations of 6.6–58 mg/L have been found in bile
25–160 min after the dose at times when the mean serum
concentration was 77.4 mg/L. In T-tube bile there was considerable
interpatient variation, with mean concentrations of
34 mg/L at 1–2 h after the dose. No accumulation occurs
in patients with impaired hepatic function, but the presence
of ascites, low plasma albumin and accumulation of proteinbinding
inhibitors may increase the volume of distribution.
Clinical Use
It is used, often combined with an aminoglycoside, to treat a wide range of severe urinary, respiratory and wound infections, mostly due to enterobacteria or Ps. aeruginosa. Reference is made to its use in pneumonia, septicemia, meningitis (especially if caused by Ps. aeruginosa), peritonitis, osteomyelitis, neonatal sepsis, burns and melioidosis. Concern has been expressed at the relative frequency with which failure is associated with superinfection or the emergence of resistance.
Side Effects
It is generally well tolerated. Preparations containing arginine
have replaced those with sodium carbonate, which causes
pain on intramuscular injection. Reactions common to cephalosporins
have been observed in some patients, including positive
antiglobulin tests without hemolysis, raised liver function
test values, eosinophilia, rashes, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia
and diarrhea, occasionally associated with toxigenic
C. difficile.
Failure of therapy has been associated with superinfection
with resistant organisms, including Staph. aureus, enterococci
and Candida. Resistance caused by induction of chromosomal
β-lactamases may emerge in Ps. aeruginosa, Ser. marcescens or
Enterobacter spp.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Ceftazidime is potentially useful in treating serious gramnegative bacterial infections particularly against susceptible Enterobacteriaceae including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, that are not susceptible to other, less-expensive agents, or when aminoglycosides are not indicated (due to their potential toxicity). It is of particular interest for treating gram-negative infections in reptiles due to a very long half-life.
Properties of Ceftazidime
| Melting point: | >1500C (dec.) |
| RTECS | UU2230000 |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Sparingly soluble in aqueous solution |
| form | neat |
| form | Solid |
| pka | pKa 1.8 (Uncertain) |
| color | White |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive, Moisture Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 78439-06-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Ceftazidime
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin H334:Sensitisation, respiratory |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P272:Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P284:Wear respiratory protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P333+P313:IF SKIN irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Ceftazidime
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

![Propanoic acid, 2-[[(Z)-[1-(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)-2-oxo-2-[[(5aR,6R)-1,4,5a,6-tetrahydro-1,7-dioxo-3H,7H-azeto[2,1-b]furo[3,4-d][1,3]thiazin-6-yl]amino]ethylidene]amino]oxy]-2-methyl-](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20200611/GIF/1301254-50-1.gif)

You may like
-
 78439-06-2 Ceftazidime 98%View Details
78439-06-2 Ceftazidime 98%View Details
78439-06-2 -
 Ceftazidime pentahydrate (contains ca. 10% Na2CO3) 95.00% CAS 78439-06-2View Details
Ceftazidime pentahydrate (contains ca. 10% Na2CO3) 95.00% CAS 78439-06-2View Details
78439-06-2 -
 Ceftazidime pentahydrate CAS 78439-06-2View Details
Ceftazidime pentahydrate CAS 78439-06-2View Details
78439-06-2 -
 Ceftazidime pentahydrate >98% CAS 78439-06-2View Details
Ceftazidime pentahydrate >98% CAS 78439-06-2View Details
78439-06-2 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4
