Cefixime
- CAS NO.:79350-37-1
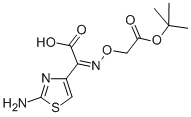
- Empirical Formula: C16H15N5O7S2
- Molecular Weight: 453.45
- MDL number: MFCD03788802
- EINECS: 616-684-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-16 16:15:04
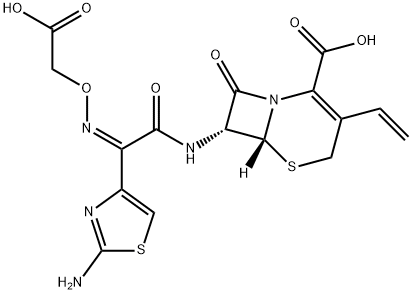
What is Cefixime?
Absorption
About 40%-50% absorbed orally whether administered with or without food, however, time to maximal absorption is increased approximately 0.8 hours when administered with food.
Toxicity
Symptoms of overdose include blood in the urine, diarrhea, nausea, upper abdominal pain, and vomiting.
Description
Cefixime is the first orally active third-generation cephalosponn with a true broad spectrum of activity. It is reportedly more effective against Gram-negative bacteria than conventional oral cephems such as cephalexin and cefaclor.
Chemical properties
Pale Yellow Solid
Chemical properties
Cefixime is an oral third generation cephalosporin antibiotic. It was sold under the trade name Suprax in the United States until 2003. The oral suspension form of “Suprax” was re-launched. Cefixime is prescribed for bacterial infections of the chest, ears, urinary tract, and throat (tonsilitis and pharyngitis), and for uncomplicated gonorrhea, upper and lower respiratory tract infections, acute otitis media, and gonococcal urethritis.
Originator
Fujisawa (Japan)
The Uses of Cefixime
Orally active, third generation cephalosporin antibiotic
The Uses of Cefixime
Cephalosporin antibacterial
The Uses of Cefixime
Orally active, third generation cephalosporin antibiotic.
Indications
For use in the treatment of the following infections when caused by susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms: (1) uncomplicated urinary tract infections caused by Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis, (2) otitis media caused by Haemophilus influenzae (beta-lactamase positive and negative strains), Moraxella catarrhalis (most of which are beta-lactamase positive), and S. pyogenes, (3) pharyngitis and tonsillitis caused by S. pyogenes, (4) acute bronchitis and acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae (beta-lactamase positive and negative strains), and (5) uncomplicated gonorrhea (cervical/urethral) caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae (penicillinase- and non-penicillinase-producing strains).
What are the applications of Application
Cefixime is third generation cephalosporin antibiotic
Background
Cefixime, an antibiotic, is a third-generation cephalosporin like ceftriaxone and cefotaxime. Cefixime is highly stable in the presence of beta-lactamase enzymes. As a result, many organisms resistant to penicillins and some cephalosporins due to the presence of beta-lactamases, may be susceptible to cefixime. The antibacterial effect of cefixime results from inhibition of mucopeptide synthesis in the bacterial cell wall.
Definition
ChEBI: A third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic bearing vinyl and (2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-[(carboxymethoxy)imino]acetamido groups at positions 3 and 7, respectively, of the cephem skeleton. It is used in the treatment of gonorrhoea tonsilitis, pharyngitis, bronchitis, and urinary tract infections.
Manufacturing Process
To a suspension of 7-amino-3-vinyl-3-cephem-4-carboxylic acid (11.25 g), 2- (aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-(tert-butoxycarbonylmethoxyimino)acetic acid S-mercaptobenzothiazole ester (23.88 g) in ethylacetate (266 ml) and water (9 ml) at 2°C is added triethylamine. After completion of the reaction, water is added and pH is adjusted to 2.1 with diluted sulfuric acid. The phases are separated and the aqueous phase is extracted with ethylacetate. The organic extracts are combined and concentrated to a volume of 120 ml, then acetonitrile (100 ml) and formic acid (22 ml) are added. The mixture is stirred at 30-35°C for 1 hour. The mixture is cooled to 2°C, the precipitate is filtered, washed with acetonitrile and dried to obtain 20.86 g of 5-thia-1- azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid, 7-(((2Z)-(2-amino-4- thiazolyl)(carboxymethoxy)imino)acetylamino)-3-ethenyl-8-oxo-, (6R,7R)- (Cefixime).
brand name
Suprax(Lupin);Cefspan.
Therapeutic Function
Antibiotic
Antimicrobial activity
It is active against N. gonorrhoeae, M. catarrhalis, H. influenzae and a wide range of enterobacteria, including most strains of Citrobacter, Enterobacter and Serratia spp. Its antistaphylococcal activity is poor. It is not active against Acinetobacter spp., Ps. aeruginosa or B. fragilis. It is resistant to hydrolysis by common β-lactamases.
Health Hazard
Exposures to cefi xime may cause side effects that include, but are not limited to, stomach and abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, mild skin rash, headache, fever, urticaria, pruritis, eosinophilia, leucopenia, anaphylaxis, superinfection, hemolytic anemia, dyspepsia, and fl atulence. Also, cefi xime may cause transient elevation of SGOT, SGPT, alkaline phosphatase, BUN, and creatinine. Reports have indicated that cefi xime is mainly excreted unchanged in the bile and urine
Pharmacokinetics
Cefixime, an antibiotic, is a third-generation cephalosporin like ceftriaxone and cefotaxime. Cefixime is highly stable in the presence of beta-lactamase enzymes. As a result, many organisms resistant to penicillins and some cephalosporins due to the presence of beta-lactamases, may be susceptible to cefixime. The antibacterial effect of cefixime results from inhibition of mucopeptide synthesis in the bacterial cell wall.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption: c. 50%
Cmax 400 mg oral: 4–5.5 mg/L after 4 h
Plasma half-life: 3-ndash;4 h
Volume of distribution: 0.1 L/kg
Plasma protein binding: 60-ndash;70%
Absorption and distribution
Oral absorption is slow and incomplete, but is unaffected by aluminum magnesium hydroxide. Penetration into cantharides blister fluid was very slow but exceeded the plasma level. CSF concentrations are poor even in the presence of meningeal inflammation, reaching an average of around 0.22 mg/L in children with meningitis.
Metabolism and excretion
It is not metabolized and is excreted unchanged in urine (mainly by glomerular filtration) and in bile, in which concentrations exceeding 100 mg/L have been found. Less than 20% of an oral dose is recovered from the urine over 24 h, falling to less than 5% in patients with severe renal impairment, with a corresponding increase in plasma concentration. It is not removed by peritoneal or hemodialysis.
Clinical Use
Cefixime has been used successfully in uncomplicated cystitis, upper and lower respiratory tract infections and various other infections. Its failure to provide adequate cover for staphylococci should be noted.
Clinical Use
Cefixime (Suprax) is the first orally active, third-generationcephalosporin that is not an ester prodrug to be approved fortherapy in the United States. Oral bioavailability is surprisinglyhigh, ranging from 40% to 50%. Facilitated transportof cefixime across intestinal brush border membranes involvingthe carrier system for dipeptides may explain itssurprisingly good oral absorption. This result was not expectedbecause cefixime lacks the ionizable α-amino grouppresent in dipeptides and β-lactams previously known to betransported by the carrier system.Cefixime is a broad-spectrum cephalosporin that is resistantto many β-lactamases. It is particularly effective againstGram-negative bacilli, including E. coli, Klebsiella spp., P.mirabilis, indole-positive Proteus, Providencia, and someCitrobacter spp. Most Pseudomonas, Enterobacter, andBacteroides spp. are resistant. It also has useful activityagainst streptococci, gonococci, H. influenzae, and M. catarrhalis.It is much less active against S. aureus. Cefixime isused for the treatment of various respiratory tract infections(e.g., acute bronchitis, pharyngitis, and tonsillitis) and otitismedia. It is also used to treat uncomplicated urinary tract infectionsand gonorrhea caused by β-lactamase–producingbacterial strains.
The comparatively long half-life of cefixime (t1/2 is3–4 hours) allows it to be administered on a twice-a-dayschedule. Renal tubular reabsorption and a relatively high fraction of plasma protein binding (~65%) contribute to thelong half-life. It is provided in two-oral dosage forms: 200-or 400-mg tablets and a powder for the preparation of anaqueous suspension.
Side Effects
It is well tolerated, but diarrhea is fairly common and pseudomembranous colitis has been reported. Other side effects common to cephalosporins are occasionally seen.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Uses for cefixime are limited in veterinary medicine. Its use should be reserved for those times when infections (systemic or urinary tract) are caused by susceptible gram-negative organisms where oral treatment is indicated or when approved fluoroquinolones or other 3rd generation cephalosporins (e.g., cefpodoxime) are either contraindicated or ineffective.
in vitro
previous study found that cefixime was more active than cephalexin, cefaclor, and amoxicillin against various gram-negative bacteria. cefixime was also significantly more active than tested reference drugs against clinical isolates of klebsiella pneumoniae, escherichia coli, indole-positive and -negative proteus species, providencia species, and neisseria gonorrhoeae. moreover, cefixime was active against strains of k. pneumoniae, e. coli, as well as proteus mirabilis resistant to the reference agents [1].
in vivo
the therapeutic activities of cefixime in mice infected with gram-negative bacilli were found to be far superior to the activities of cephalexin, cefaclor, and amoxicillin, but they were inferior to the activities against infection with staphylococcus aureus [1].
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anticoagulants: effects of coumarins may be
enhanced.
Metabolism
Hepatic. Approximately 50% of the absorbed dose is excreted unchanged in the urine in 24 hours.
Metabolism
About 20% of an oral dose (or 50% of an absorbed dose) is excreted unchanged in the urine via glomerular filtration within 24 hours. Up to 60% may be eliminated by non-renal mechanisms; there is no evidence of metabolism but some drug is probably excreted into the faeces from bile.
Precautions
Users of cefi xime should be careful in health conditions such as neonates, pregnancy, lactation, and renal failure. Users should follow suitable and appropriate health care measures to control superinfection (if it happens during therapy). It is contraindicated in patients with a known allergy to penicillin or any other ingredients of Taximax. Taxim-O is contraindicated in patients with a known allergy to the cephalosporin group of antibiotics.
References
[1] kamimura, t. ,kojo, h.,matsumoto, y., et al. in vitro and in vivo antibacterial properties of fk 027, a new orally active cephem antibiotic. antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy 25(1), 98-104 (1984).
[2] quintiliani r. cefixime in the treatment of patients with lower respiratory tract infections: results of us
Properties of Cefixime
| Melting point: | 218-225°C |
| Density | 1.85±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,2-8°C |
| solubility | Slightly soluble in water, soluble in methanol, sparingly soluble in anhydrous ethanol, practically insoluble in ethyl acetate. |
| form | Solid |
| pka | pKa 2.10 (Uncertain) |
| color | Off-White to Pale Yellow |
| Water Solubility | 55.11 mg/L |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 79350-37-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Cefixime
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Cefixime
Cefixime manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 Cefixime 98%View Details
Cefixime 98%View Details
79350-37-1 -
 Cefixime 79350-37-1 99%View Details
Cefixime 79350-37-1 99%View Details
79350-37-1 -
 Cefixime 98% (HPLC) CAS 79350-37-1View Details
Cefixime 98% (HPLC) CAS 79350-37-1View Details
79350-37-1 -
 Cefixime CAS 79350-37-1View Details
Cefixime CAS 79350-37-1View Details
79350-37-1 -
 Cefixime Trihydrate API Powder, Greater than 99%View Details
Cefixime Trihydrate API Powder, Greater than 99%View Details
79350-37-1 -
 Cefixime 50 Mg / 5 Ml Dry SyrupView Details
Cefixime 50 Mg / 5 Ml Dry SyrupView Details
79350-37-1 -
 Johncef Dry Syrup Cefixime 50 Mg5MLView Details
Johncef Dry Syrup Cefixime 50 Mg5MLView Details
79350-37-1 -
 Cefixime Trihydrate Powder, 25Kg, >99%View Details
Cefixime Trihydrate Powder, 25Kg, >99%View Details
125110-14-7
