Catechol
Synonym(s):Catechol;Pyrocatechol;1,2-Benzenediol;1,2-Dihydroxybenzene;1,2-Dihydroxybenzene, Catechol
- CAS NO.:120-80-9
- Empirical Formula: C6H6O2
- Molecular Weight: 110.11
- MDL number: MFCD00002188
- EINECS: 204-427-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:50:03
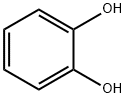
What is Catechol?
Description
Catechol is a white crystalline solid. Turnsbrown on contact with light and air. Molecularweight=110.12; Specific gravity (H2O:1)=1.3; Boilingpoint=245.5℃; Freezing/Melting point=104℃. It sublimes readily; Vapor pressure=10 mmHg at 117℃; Flashpoint=127℃; Autoignition temperature=512℃.Explosive Limits in air: LEL=1.4%; UEL-Unknown.Hazard Identification (based on NFPA 704 M RatingSystem): Health 3, Flammability 1, Reactivity 2. Solubilityin water=44%.
Chemical properties
Catechol also called Pyrocatechol is a white crystalline solid. Turns brown on contact with light and air.
The Uses of Catechol
Catechol is used in photography, in dyeing fur, and as a topical antiseptic.
The Uses of Catechol
In photography; dyeing fur; as reagent.
The Uses of Catechol
In the manufacture of rubber antioxidants and monomer inhibitors to stop radical polymerization; in dyes, as a photographic developer; in formulations for pharmaceuticals, perfumes, inks, and insecticides
Definition
A colourless crystalline PHENOL containing two hydroxyl groups. It is used in photographic developing.
Production Methods
Catechol may be obtained by the fusion of o-phenolsulfonic acid with alkali, by heating chorophenol with a solution of sodium hydroxide at 200°C in an autoclave, or by cleavage of the methyl ether group of guaiacol (obtained from beechwood tar) with hydriodic acid.
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 45, p. 4275, 1980 DOI: 10.1021/jo01310a003
General Description
Solid; white; odorless. Sinks and mixes with water.
Air & Water Reactions
Turns brown on exposure to air and light, especially when moist. Water soluble. Aqueous solutions soon turn brown on exposure to air and light.
Reactivity Profile
POISONOUS GASES MAY BE PRODUCED WHEN HEATED. Pyrocatechol may form toxic fumes at high temperatures. [USCG, 1999]. Pyrocatechol can react with acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, bases and oxidizing agents. Pyrocatechol reacts violently on contact with concentrated nitric acid. Pyrocatechol acts as a reducing agent .
Hazard
Strong irritant. Toxic by skin absorption. Eye and upper respiratory tract irritant, and der- matitis. Possible carcinogen.
Health Hazard
DUST: Irritating to eyes, nose and throat. If inhaled will cause coughing or difficult breathing. SOLID: Will burn skin and eyes. Harmful if swallowed.
Health Hazard
Acute oral and percutaneous toxicity of pyrocatechol is greater than that of phenol; inhalation toxicity is less than that of phenol. The toxic symptoms include weakness, muscular pain, dark urine, tremor, dyspnea, and convulsions. Large amounts can produce degenerative changes in renal tubules. Large doses can cause death due to respiratory failure. Skin contact can cause eczematous dermatitis.
LD50 value, oral (rats): 260 mg/kg
LD50 value, skin (rabbits): 800 mg/kg.
Fire Hazard
Combustible. POISONOUS GASES MAY BE PRODUCED WHEN HEATED. May form toxic fumes at high temperatures.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, subcutaneous, intraperitoneal, intravenous, and parenteral routes. Moderately toxic by skin contact. Experimental reproductive effects. Can cause dermatitis on skin contact. An allergen. Human mutation data reported. Questionable carcinogen. Systemic effects sirmlar to those of phenol. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame; can react vigorously with oxidizing materials. Hypergolic reaction with concentrated nitric acid. To fight fire, use water, CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. See also PHENOL.
Potential Exposure
Used as a chemical intermediate; pharmaceutical and veterinary drug; as an antiseptic; in photography; in dyestuff manufacture and application. It is also used in electroplating, in the formulation of specialty inks; in antioxidants; and light stabilizers.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Note to physician: Treat for methemoglobinemia.Spectrophotometry may be required for precise determination of levels of methemoglobinemia in urine.
Carcinogenicity
Catechol has been extensively studied for its role in carcinogenesis of the rat glandular stomach; it was concluded that pyrocatechol is carcinogenic. When rats and mice were administered 0.8% pyrocatechol in their feed for life, there was an increase in glandular stomach adenocarcinoma in both male and female rats. Pyrocatechol also caused hyperplasia of the glandular stomach in both rats and mice, a mechanism that could cause promotion of carcinogen-initiated cells; no effects on the esophagus or urinary bladder were reported. There were no cutaneous neoplasms when pyrocatechol was applied in dermal studies. Catechol may be classified as a cocarcinogen because it enhanced the number and/or incidence of lesions in the stomach induced by several carcinogenic nitrosamines and cutaneous neoplasms when administered dermally together with several carcinogens.
Storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with catecholyou should be trained on its proper handling and storage.Before entering confined space where this chemical may bepresent, check to make sure that an explosive concentrationdoes not exist. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool,well-ventilated area away from strong oxidizers and acids.Use only nonsparking tools and equipment, especially whenopening and closing containers of this chemical. Sources ofignition, such as smoking and open flames, are prohibitedwhere this chemical is used, handled, or stored in a mannerthat could create a potential fire or explosion hazard.
Shipping
UN 2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
Crystallise catechol from *benzene or toluene and sublime it in vacuo. [Rozo et al. Anal Chem 58 2988 1986, Beilstein 6 IV 5557.]
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides.
Properties of Catechol
| Melting point: | 100-103 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 245 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1,371 g/cm3 |
| vapor density | 3.8 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 75 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.6120 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 279 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 430g/l |
| form | Crystalline Flakes |
| pka | 9.85(at 20℃) |
| color | white to faintly beige |
| PH | 6 (100g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| explosive limit | 1.97%(V) |
| Water Solubility | 430 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Air & Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,7999 |
| BRN | 471401 |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 5 ppm (~22 mg/m3) (ACGIH). . |
| Stability: | Stable. Substances to be avoided include acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, bases, oxidizing agents, nitric acid. Light sensitive; may discolour on exposure to air. Combustible. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 120-80-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 15, Sup 7, 71) 1999 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 1,2-Benzenediol(120-80-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Catechol (120-80-9) |
Safety information for Catechol
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H341:Germ cell mutagenicity H350:Carcinogenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Catechol
Catechol manufacturer
Jaiswal S Cyber Shop
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 Catechol CASView Details
Catechol CASView Details -
 Catechol CAS 120-80-9View Details
Catechol CAS 120-80-9View Details
120-80-9 -
 Pyrocatechol CAS 120-80-9View Details
Pyrocatechol CAS 120-80-9View Details
120-80-9 -
 Pyrocatechol, GR 99%+ CAS 120-80-9View Details
Pyrocatechol, GR 99%+ CAS 120-80-9View Details
120-80-9 -
 Catechol (Pyrocatechol) AR CAS 120-80-9View Details
Catechol (Pyrocatechol) AR CAS 120-80-9View Details
120-80-9 -
 Catechol (Pyrocatechol) CAS 120-80-9View Details
Catechol (Pyrocatechol) CAS 120-80-9View Details
120-80-9 -
 PYROCATECHOL For Synthesis CAS 120-80-9View Details
PYROCATECHOL For Synthesis CAS 120-80-9View Details
120-80-9 -
 JCSSUPER 120-80-9 Catechol for synthesis (Pyrocatechol) 500 gm., Grade Standard: Chemical GradeView Details
JCSSUPER 120-80-9 Catechol for synthesis (Pyrocatechol) 500 gm., Grade Standard: Chemical GradeView Details
120-80-9
