Caffeic acid
Synonym(s):Caffeic acid;3,4-Dihydroxycinnamic acid;3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-2-propenoic acid;3,4-Dihydroxybenzeneacrylic acid;trans-3,4-Dihydroxycinnamic acid
- CAS NO.:331-39-5
- Empirical Formula: C9H8O4
- Molecular Weight: 180.16
- MDL number: MFCD00004392
- EINECS: 206-361-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 13:58:55
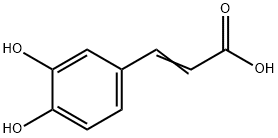
What is Caffeic acid?
Description
Caffeic acid is abundant in the whole plant of Solidago decurrens Lour. (Yi Zhi
Huang Hua), fruit of Crataegus pinnatifida Bge. var. major N.E.Br. (Shan Li
Hong), Salix myrtillacea Anderss. (Po Liu), rhizome of Cimicifuga foetida L., rhizome of Polypodiaceae Polypodium vulgare L. (Ou Ya Shui Long Gu), peel of
Rutaceae Citrus limonum (Ning Meng), the whole plant of Polygonaceae Polygonum
aviculare L. (Pian Xu), root of Valeriana officinalis L. (Xie Cao), the whole plant of
Thymus mongolicus Ronn (She Xiang), leaves of Eucommia ulmoides (Du Zhong),
and other herbal plants. It is a kind of polyhydroxy styrene acid, with the general
chemical properties of phenolic acid. It is easily oxidized for the reason of the unsaturated double bonds, particularly unstable in alkaline solution
Caffeic acid has both cis and trans isomers, and the two isomers of caffeic acid
have a mutual transformation in plants, which may regulate some important physiological process. Caffeic acid exists in plants in the main form of complexes; free
state accounts for a few proportion.
Description
Caffeic acid is an inhibitor of 5-
Chemical properties
Light yellow to greenish-yellow powder
Physical properties
Appearance: yellow crystal. The crystal from the concentrated solution does not
contain crystal water, and the crystal from the dilute solution contains one molecule
crystal water. Melting point: 223?225?°C. Solubility: It is slightly soluble in cold
water but soluble in hot water, cold ethanol, and ethyl acetate. The basic solution is
orange-red. Ferric chloride solution was dark green.
The Uses of Caffeic acid
Caffeic Acid is a constituent of plants, probably occurs in plants only in conjugated forms. Caffeic acid is found in all plants because it is a key intermediate in the biosynthesis of lignin, one of the principal sources of biomass. Caffeic acid is one of the main natural phenols in argan oi.
The Uses of Caffeic acid
antineoplastic, PGE2 synthase inhibitor, PK inhibitor
The Uses of Caffeic acid
Caffeic acid has been used as a standard of phenolic acid in the study to determine the total phenolic acid content in vegetables after subjecting to alkaline and acid hydrolysis. It has also been used to determine its antioxidant activity by various assay methods.
What are the applications of Application
Caffeic Acid is an inhibitor of 5-LO and 12-LO
Indications
It is used for preventing or stopping bleeding during surgery, as well as hemostasis in the department of medicine, obstetrics and gynecology, etc. It is also used for various causes of neutropenia and thrombocytopenia.
Definition
ChEBI: Caffeic acid is a hydroxycinnamic acid that is cinnamic acid in which the phenyl ring is substituted by hydroxy groups at positions 3 and 4. It exists in cis and trans forms; the latter is the more common. It has a role as a plant metabolite, an EC 1.13.11.33 (arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase) inhibitor, an EC 2.5.1.18 (glutathione transferase) inhibitor, an EC 1.13.11.34 (arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase) inhibitor, an antioxidant and an EC 3.5.1.98 (histone deacetylase) inhibitor. It is a hydroxycinnamic acid and a member of catechols.
General Description
Yellow prisms or plates (from chloroform or ligroin) or pale yellow granules. Alkaline solutions turn from yellow to orange.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Caffeic acid is a carboxylic acid. Carboxylic acids donate hydrogen ions if a base is present to accept them. They react in this way with all bases, both organic (for example, the amines) and inorganic. Their reactions with bases, called "neutralizations", are accompanied by the evolution of substantial amounts of heat. Neutralization between an acid and a base produces water plus a salt. Insoluble carboxylic acids react rapidly with aqueous solutions containing a chemical base and dissolve as the neutralization generates a soluble salt. Carboxylic acids in aqueous solution and liquid or molten carboxylic acids can react with active metals to form gaseous hydrogen and a metal salt. Such reactions occur in principle for solid carboxylic acids as well, but are slow if the solid acid remains dry. Even "insoluble" carboxylic acids may absorb enough water from the air and dissolve sufficiently in Caffeic acid to corrode or dissolve iron, steel, and aluminum parts and containers. Carboxylic acids, like other acids, react with cyanide salts to generate gaseous hydrogen cyanide. The reaction is slower for dry, solid carboxylic acids. Insoluble carboxylic acids react with solutions of cyanides to cause the release of gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Flammable and/or toxic gases and heat are generated by the reaction of carboxylic acids with diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides. Carboxylic acids, especially in aqueous solution, also react with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), to generate flammable and/or toxic gases and heat. Their reaction with carbonates and bicarbonates generates a harmless gas (carbon dioxide) but still heat. Like other organic compounds, carboxylic acids can be oxidized by strong oxidizing agents and reduced by strong reducing agents. These reactions generate heat. A wide variety of products is possible. Like other acids, carboxylic acids may initiate polymerization reactions; like other acids, they often catalyze (increase the rate of) chemical reactions.
Health Hazard
ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: When heated to decomposition Caffeic acid emits acrid smoke and fumes.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Caffeic acid are not available; however, Caffeic acid is probably combustible.
Biochem/physiol Actions
A natural dietary phenolic compound found in plants that is an anti-oxidant. Inhibits the synthesis of leukotrienes that are involved in immunoregulation, inflammation and allergy. Inhibits Cu2+-induced LDL oxidation.
Purification Methods
Recrystallise this antioxidant from water. [Beilstein 10 IV 1776.]
Properties of Caffeic acid
| Melting point: | 211-213 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 272.96°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.2933 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4500 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | ethanol: 50 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 4.58±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | yellow to tan |
| Water Solubility | soluble in hot water |
| Merck | 14,1635 |
| BRN | 2210883 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 331-39-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 56) 1993 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Cinnamic acid, 3,4-dihydroxy-(331-39-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2-Propenoic acid, 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)- (331-39-5) |
Safety information for Caffeic acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H351:Carcinogenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Caffeic acid
| InChIKey | QAIPRVGONGVQAS-DUXPYHPUSA-N |
Caffeic acid manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![8-[(E)-2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethenyl]-1,3-diethyl-7-methyl-purine-2,6 -dione](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/155270-99-8.gif)
You may like
-
 331-39-5 3,4-Dihydroxycinnamic acid 99%View Details
331-39-5 3,4-Dihydroxycinnamic acid 99%View Details
331-39-5 -
 Caffeic acid 98%View Details
Caffeic acid 98%View Details -
 Caffeic acid 331-39-5 98%View Details
Caffeic acid 331-39-5 98%View Details
331-39-5 -
 331-39-5 Caffeic acid 98%View Details
331-39-5 Caffeic acid 98%View Details
331-39-5 -
 Caffeic acid CAS 331-39-5View Details
Caffeic acid CAS 331-39-5View Details
331-39-5 -
 Caffeic Acid CAS 331-39-5View Details
Caffeic Acid CAS 331-39-5View Details
331-39-5 -
 Caffeic acid CAS 331-39-5View Details
Caffeic acid CAS 331-39-5View Details
331-39-5 -
 Caffeic Acid CAS No. 331-39-5.View Details
Caffeic Acid CAS No. 331-39-5.View Details
331-39-5
