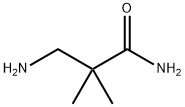
BUTALBITAL
Synonym(s):5-Allyl-5-isobutylbarbituric acid
- CAS NO.:77-26-9
- Empirical Formula: C11H16N2O3
- Molecular Weight: 224.26
- MDL number: MFCD00056089
- EINECS: 201-017-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52
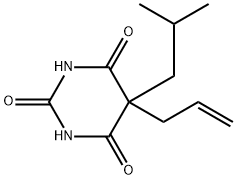
What is BUTALBITAL?
Absorption
Butalbital gets readily and rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The time to reach the peak plasma concentrations is reported to be approximately 2 hours. Typical blood concentrations of butalbital peaked at 2.1 mg/L and declined to 1.5 mg/L at 24 hr. Plasma concentrations of 10 to 20 μg/mL have been associated with toxicity; coma and fatalities have occurred with concentrations of 25 to 30 μg/mL.
Toxicity
Reported oral TDLO (woman) is 400 mg/kg and subcutaneous LD50 in rat is 160 mg/kg. The lowest acute dose of butalbital alone associated with death in adults is 2.0 g. Symptoms of acute barbiturate poisoning include drowsiness, confusion, coma, respiratory depression, hypotension, and shock. Due to the CNS depressant effects, an overdose of barbiturates may lead to death. Barbiturates are also associated with withdrawal reactions, which may lead to death if severe.
Chemical properties
White, crystalline powder; odorless; slightly bitter taste. Soluble in alcohol, ether, and chloroform; almost insoluble in water.
Originator
Axocet,Savage Labs
The Uses of BUTALBITAL
Controlled substance (depressant). Sedative, hypnotic.
Background
Butalbital, or 5-allyl-5-isobutylbarbituric acid, is a derivative of barbituric acid which the hydrogens at position 5 are substituted by an allyl group and an isobutyl group. It is a short-to-intermediate acting member of barbiturates that exhibit muscle-relaxing and anti-anxiety properties that produce central nervous system (CNS) depression that ranges from mild sedation to general anesthesia. Butalbital has a low degree of selectivity and a narrow therapeutic index. Typically indicated to manage tension (or muscle contraction) headaches, butalbital is often combined with one or more therapeutic agents, such as acetylsalicylic acid, acetaminophen, aspirin, and caffeine. There have not been clinical trials that evaluate the clinical efficacy of butalbital in migraines thus it is not indicated for such condition. As with other barbiturates, butalbital carries a risk of abuse or misuse potential, intoxication, hangover, tolerance, dependence, and overdosage possibly leading to death. Butalbital‐containing analgesics can also produce a drug‐induced headache in addition to tolerance and dependence. Due to these risks, the use of butalbital-containing combination products is typically limited for use only in cases where other medications are deemed ineffective and such usage is advised to be carefully monitored.
Indications
Indicated for the management of the symptom complex of tension (or muscle contraction) headache, when other non-opioid analgesics and alternative treatments are inadequate, in various combinations with acetaminophen, aspirin, caffeine, and codeine .
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of barbiturates that is barbituric acid in which the hydrogens at position 5 are substituted by an allyl group and an isobutyl group. Frequently combined with other medicines, such as aspirin, paracetamol and codeine, it is used for reatment of pain and headache.
Manufacturing Process
1 mole of sodium is dissolved in 10 to 12 times its weight of absolute alcohol under a reflux condenser. To this are added 1 mole of ethyl malonic acid ester,
and then gradually about 1.1 moles of 2-isobutyl bromide. The mixture is
gently refluxed for some hours, or until it no longer shows alkaline reaction to
moist litmus paper. Most of the alcohol is removed by vacuum distillation,
leaving an oily residue. Water is added to this residue to dissolve the sodium
bromide; and the oily layer, which is ethyl isopropyl-carbinyl malonic acid
ester, is separated and dried. It is purified by fractional distillation in vacuum.
When thus purified, ethyl isopropyl-carbinyl malonic acid ester is a colorless or
pale yellow liquid, having a boiling point of 103°-105°C at about 4 mm
pressure, and a refractive index at 25°C.
3 moles of sodium are dissolved in 10 to 12 times its weight of absolute
alcohol under a reflux condenser. To this are added 1.6 moles of urea and 1
mole of ethyl isopropyl-carbinyl malonic acid ester. The mixture is gently
refluxed for 2-4 h, after which most of the alcohol is removed by vacuum
distillation. The residue is dissolved in water, and a sufficient amount of dilute
acid is added to completely precipitate the isopropyl-carbinyl barbituric acid.
The precipitate is filtered off, dried, and recrystallized from dilute alcohol.
1 mole of isopropyl-carbinyl barbituric acid is dissolved in a suitable vessel in
a 10%-35% aqueous solution of 1 mole of potassium hydroxide. To this are
added somewhat in excess of 1 mole of allyl bromide, and alcohol equal to
about 10% of the total volume of the solution. The vessel is agitated for 50-
75 h. At the end of this time, the solution, which may still exhibit two layers,
is concentrated to about one-half its volume, to remove the excess allyl
bromide and the alcohol. On cooling, an oily layer, which is isopropyl-carbinyl
allyl barbituric acid, separates out as a sticky viscous mass. It is dried,
washed with petroleum ether, and dissolved in the minimum amount of
benzene. Any unreacted isopropyl-carbinyl barbituric acid, which does not
dissolve, is filtered off. The addition of petroleum ether to the clear filtrate
causes the isopropyl-carbinyl allyl barbituric acid to precipitate as an oily
mass. This is separated, washed with petroleum ether, and dried in vacuum.
brand name
Sandoptal (Novartis).
Therapeutic Function
Hypnotic, Sedative
Pharmacokinetics
Butalbital is a short to intermediate-acting barbiturate that reversibly depresses the activity of excitable tissues, including the central nervous system in a nonselective manner. Barbiturates exhibit muscle-relaxing and anti-anxiety properties and they are capable of producing all levels of CNS mood alteration from excitation to mild sedation, hypnosis, and deep coma. The sedative dose of butalbital in nontolerant individuals is 5-100 mg and the hypnotic dose is 100-200 mg. Pain perception and reaction are relatively unimpaired until the moment of unconsciousness. In some cases, an unwanted paradoxical response of excitement may be observed instead of sedation with barbiturate treatment, which may be due to their depressant effects on inhibitory centers of the CNS. At sufficiently high therapeutic doses, barbiturates induce anesthesia; however, barbiturates are reported to lose their effectiveness for sleep induction and sleep maintenance after 2 weeks. Barbiturates are habit-forming; they can produce tolerance and both dependence and addiction, which is partly explained by decreased drug concentration at the site of action due to enhanced drug metabolism by induced enzymes, or to cellular adaptive changes. In addition, butalbital may lead to analgesic overuse headache.
While butalbital is expected to mediate similar actions as other members of the barbiturate drug class, the effects of butalbital in isolation are not well understood. It is suggested that butalbital is added in combination products to antagonize the unwanted central stimulating effect of stimulatory ingredients such as caffeine. Butalbital may decrease blood pressure and heart rate when administered at sedative and hypnotic doses.
Metabolism
Butalbital is expected to undergo nearly complete hepatic metabolism. It primarily undergoes C5 oxidation to form 5-isobutyl-5-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl) barbituric acid, which is the major metabolite. Butalbital may also undergo omega-hydroxylation to form 5-allyl-5(3-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-propyl) barbituric acid.
Purification Methods
It can be recrystallised from H2O or dilute EtOH, and sublimes at 100-120o/8-12mm. It is soluble in *C6H6, cyclohexane, tetralin and pet ether at 20o. [Butler et al. J Am Chem Soc 77 1486 1955, Beilstein 24 III/IV 2006.]
Properties of BUTALBITAL
| Melting point: | 139-140 °C |
| Boiling point: | 365.66°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1672 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5000 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 11 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | soluble in DMSO, Methanol |
| form | Solid |
| pka | pKa 12.36±0.05(H2O t=38.0 I=0.1) (Uncertain) |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | 1.702g/L(25 ºC) |
| BRN | 202119 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-Pyrimidinetrione, 5-(2-methylpropyl)-5-(2-propen-1-yl)- (77-26-9) |
Safety information for BUTALBITAL
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H317:Sensitisation, Skin |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for BUTALBITAL
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
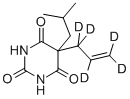
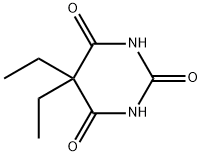
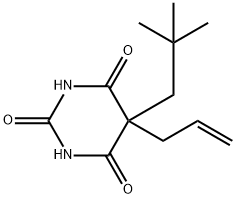
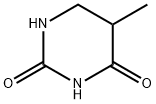
You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1