Bulleyaconitine A
- CAS NO.:107668-79-1
- Empirical Formula: C35H49NO9
- Molecular Weight: 627.76
- MDL number: MFCD01714791
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
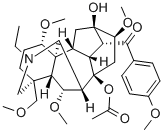
What is Bulleyaconitine A?
Description
Bulleyaconitine A is an aconitine-type two terpene alkaloid, and its molecular formula is C35H49NO10.?As early as 1980, bulleyaconitine was separated and extracted from a traditional analgesic and anti-inflammatory herb in the west of Yunnan called dianxi dula (or dianxi wutou) (Aconitum bulleyanum Diels), by the Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences . At present, bulleyaconitine A can be separated from Aconitum plants, for example, dianxi wutou (Aconitum bulleyanum Diels), cujing wutou (Aconitum crassicaule W.T.?Wang), changhui wutou (Aconitum georgei Comber), and zhiyuan wutou (Aconitum transsectum Diels).
Physical properties
Appearance: white powder. Solubility: soluble in methanol, ethanol, chloroform, and ether; insoluble in water; and easily dissolved in dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sulfuric acid . Melting point: 160–165?°C
History
In 1983, it was confirmed that bulleyaconitine A shows obvious analgesic and antiinflammatory effects by preclinical pharmacological tests . Clinical trials were carried out in 29 hospitals in 9 provinces in 1984. Bulleyaconitine A passed technical appraisals in May 1985 and was first formally put into production by Yunnan Honghe Pingbian pharmaceutical company, where it obtained the trade name “Bulleyaconitine A.” Bulleyaconitine A has been listed into the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (2015). In recent years, bulleyaconitine A has shown a great market growth and competitive power, owing to its exact curative effect and rapid clinical promotion in chronic disease and rheumatic immune disease.
The Uses of Bulleyaconitine A
Bulleyaconitine A is an agent that expresses long-lasting local anaesthetic properties used in the treatment of chronic pain and arthritis. Commonly used in China as a traditional medicine.
Pharmacology
1. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. Bulleyaconitine A plays a significant
anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting the release of prostaglandins. The analgesic effect may be related to the rivalry of 5-HT and the inhibition of inflammatory
chemokines in the brain, because inhibition of PGE2 release may lead to disinhibition of β-endorphin . Further studies showed that bulleyaconitine A achieved
the analgesic effect by effectively reducing sodium ion current, the electrophysiological basis on which pain conduction is dependent . Zhanguo Niu et?al.
found that bulleyaconitine A could be used to treat mild and moderate burn pain,
with less adverse reactions and no addiction . Thus, bulleyaconitine A may be
suitable for long-term use as a choice of analgesic therapy for burn pain. Recently,
through clinical observation on the effect of bulleyaconitine A treatment in acute
gouty arthritis, some scholars discovered that bulleyaconitine A brought about
good effect and could effectively improve the clinical symptoms of patients by
taking 0.4?mg bulleyaconitine A orally three times in daily .
2. Immune regulation. Bulleyaconitine A has obvious inhibitory effects to immune
cells involved in joint inflammation, which may have a close relationship to its
clinical anti-inflammatory effect. Ye Lu et?al. studied the influence of bulleyaconitine A on partial immune functions of BALB/c mice and found that 0.32?mg/kg
bulleyaconitine A inhibits some immune functions of BALB/c mice . Moreover,
it was reported that bulleyaconitine A significantly inhibited the phagocytic function and the ability to secrete nitric oxide (NO) of macrophages .
3. Other pharmacological effects. An injection of 0.1 mg/kg bulleyaconitin A in
fasting rat can inhibit the formation of corneal neovascularization induced by
alkali burn . Bulleyaconitine A also has local anesthesia and antipyretic effect.
Besides, bulleyaconitine A can be used for the treatment of lumbar muscle strain,
scapulohumeral periarthritis, and sprain of limbs.
Clinical Use
1. Rheumatic immune disease. Since listing, bulleyaconitine A has been applied in
clinical treatment for rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, receiving good
curative effects.
2. Chronic pain. Bulleyaconitine A does not belong to NSAID, and it exerts its
effects by regulating the sodium ion channel. So there is little psychological
dependence and organ toxicity, avoiding gastrointestinal/cardiovascular/renal
adverse reactions and drug dependence or other potential dangers caused by
NSAID and opioid analgesics.
Properties of Bulleyaconitine A
| Boiling point: | 690.9±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.28±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Store at 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: 125 mg/mL (199.12 mM) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 13.12±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | White to off-white |
Safety information for Bulleyaconitine A
Computed Descriptors for Bulleyaconitine A
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1