Bronopol
Synonym(s):2-Bromo-2-nitro-1,3-propanediol;BNPD;BNPK;Bronopol
- CAS NO.:52-51-7
- Empirical Formula: C3H6BrNO4
- Molecular Weight: 199.99
- MDL number: MFCD00007390
- EINECS: 200-143-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 11:34:44
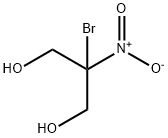
What is Bronopol?
Absorption
Bronopol was rapidly absorbed in animal studies. It may be absorbed via aerosol inhalation, dermal contact, and ingestion . In rats, approximately 40% of the topically applied dose of bronopol was absorbed through the skin within 24 hr . Following oral administration of 1 mg/kg in rats, the peak plasma concentrations of bronopol were reached up to 2 hours post-dosing .
Toxicity
Oral LD50, dermal LD50, and inhalation LD50 in rat are 180 mg/kg , 64-160 mg/kg , and > 5000 mg/m^3 , respectively. In a 90-day dermal toxicity study in rabbits, the NOEL for systemic toxicity was 2 mg/kg/day . In a rat 90-day oral toxicity study, bronopol was associated with a severe gastrointestinal irritation . A chronic feeding or carcinogenicity study with rats resulted in high mortality, stomach lesions, and severe reduction in body weight gain. A reduction in weight gain was also observed in a chronic dermal or carcinogenicity study of mice . Bronopol was not mutagenic in four mutagenicity studies .
History
In 1984, an pesticide product with bronopol as the active ingredient was first registered in the United States for use as an industrial fungicide, slime killer and preservative.
Description
Bronopol, a formaldehyde releaser, was reported as an allergen in dairy workers. In a recent case report, bronopol was contained in a lubricant jelly used for ultrasound examination and caused contact dermatitis in a veterinary surgeon.
Chemical properties
Bronopol is a white or almost white crystalline powder; odorless or with a faint characteristic odor.
Originator
Bronosol,Green Cross,Japan,1977
The Uses of Bronopol
First synthesized in 1897, bronopol was primarily used as an effective preservative agent and possesses a wide spectrum of antibacterial activity and inhibits the growth of fungi and yeasts. It can be used in the formulation of a wide variety of cosmetic and personal care products, especially in leave-on and rinse-off shampoos, creams, lotions, rinses and eye makeup to protect the product integrity by preventing or slowing bacterial growth.
Bronopol is used as a microbiocide/microbiostat in oil field systems, air washer systems, air conditioning/humidifying systems, cooling water systems, papermills, absorbent clays, metal working fluids, printing inks, paints, adhesives and consumer/institutional products. A formulating technical material is also registered.
https://www.ulprospector.com
https://www3.epa.gov
The Uses of Bronopol
Bronopol has been used as reference standard in ultra performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) coupled to inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (UPLC-ICP-MS) method for determination of bromine containing preservatives from cosmetic products.
Background
Bronopol, or 2-Bromo-2-nitro-1,3-propanediol, is an organic compound with wide-spectrum antimicrobial properties. First synthesized in 1897, bronopol was primarily used as a preservative for pharmaceuticals and was registered in the United States in 1984 for use in industrial bactericides, slimicides and preservatives . Bronopol is used as a microbicide or microbiostat in various commercial and industrial applications, including oil field systems, air washer systems, air conditioning or humidifying systems, cooling water systems, papermills, absorbent clays, metal working fluids, printing inks, paints, adhesives and consumer products . Compared to other aliphatic halogen-nitro compounds, bronopol is more stable to hydrolysis in aqueous media under normal conditions . The inhibitory activity against various bacteria, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, was demonstrated in vitro . The agent is largely available commercially as an antibacterial for a variety of industrial purposes while it is predominantly available for purchase as a pet animal litter antibacterial at the domestic consumer level . Nevertheless, ongoing contemporary re-evaluations of bronopol use in large markets such as Canada now place various compositional and product restrictions on the use of the agent in cosmetic products and in other products where it may not primarily be used in the role of a non-medicinal preservative antimicrobial .
Indications
Bronopol as an active ingredient is registered as a commercial biocide and preservative in many industrial processes. Registered biocidal uses include pulp and paper mills, water cooling towers, waste water treatment, evaporative condensers, heat exchangers, food pasteurizing plants, metalworking fluids, and oilfield applications . In addition, preservative uses include household products (e.g., dishwashing liquids, laundry products), latex emulsions, polymer lattices, pigments, leather and milk samples for analysis . Bronopol is also formulated into granular domestic end-use products in the form of cat litter .
Production Methods
Bronopol is synthesized by the reaction of nitromethane with paraformaldehyde in an alkaline environment, followed by bromination. After crystallization, bronopol powder may be milled to produce a powder of the required fineness.
Definition
ChEBI: Bronopol is a nitro compound.
Manufacturing Process
A mixture of 441 g (3 mols) of calcium chloride dihydrate, 61 g (1 mol) of nitromethane, 163 g (2 mols) of formalin (37% formaldehyde solution) and 470 ml of water was cooled to 0°C and mixed with 5 g of calcium hydroxide while stirring. The temperature thereby rose to 30°C. As soon as the temperature had fallen again, a further 32 g of calcium hydroxide (total of 0.5 mol) were added. The mixture was then cooled to 0°C and with intensive cooling and stirring, 159.8 g (1 mol, 51 ml) of bromine were dropped in at a rate so that the temperature remained at around 0°C. After the addition was ended, the mixture was stirred for a further 2 hours, when the reaction product separated in crystalline form. The product was quickly filtered on a suction filter and the crystalline sludge obtained was taken up in 450 ml of ethylene chloride and dissolved at reflux. Then by addition of magnesium sulfate, undissolved inorganic salts were separated and the solution was slowly cooled whereby 140 g (70% yield) of 2-bromo-2-nitropropane-1,3-diol precipitated in colorless crystals melting at 123°-124°C.
Therapeutic Function
Antiseptic
Biological Functions
Bronopol, 2-bromo-2-nitropropan-1,3-diol, is an aliphatic halogenonitro compound with potent antibacterial activity but limited activity against fungi(Guthrie, 1999).Its activity is reduced somewhat by 10% serum and to a greater extent by sulphydryl compounds, but is unaffected by 1% polysorbate or 0.1% lecithin. It has a half-life of about 96 daysat pH 8 and 25oC (Toler, 1985).
Bronopol is most stable under acid conditons;the initial decomposition appears to involve the liberation of formaldehyde and the formulation of bromonitroethanol. A secondorder reaction involving bronopol and formaldehyde occurs simultaneously to produce 2-hydro-xymethyl-2-nitro-1,3-propanediol, which itself decomposes with the loss of formaldehyde. 
Bronopol has been employed extensively as a preservative for pharmaceuticalandcosmetic products.However, its use to preserve products containing secondary amines should be avoided as the by-product of this reaction is nitrosoamine which is carcinogenic. Details of the microbiological activity,chemical stability,toxicology and uses of bronopol are documented by Bryce et al. (1978),Croshaw & Holland (1984),Toler (1985) and Rossmorc and Sondossi (1988). Dcnyer and Wallhausser (1990) have provided useful information about bronopol, the typical in-use concentration of which is 0.01-0.1% w/v. Sulphhydryl compounds act as appropriate neutralizers inpreservative efficacy tests.
General Description
White crystals. Ignite easily and burn readily. May detonate under strong shock. Decomposes when heated, evolving toxic gases. Toxic by skin absorption, inhalation or ingestion.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases, strong reducing agents, acid chlorides and acid anhydrides. 2-Bromo-2-nitro-1,3-propanediol is also incompatible with sulfhydryl compounds or with aluminum or iron containers (it is stable in contact with tin or stainless steel).
Hazard
Toxic by all routes of exposure; skin irritant.
Health Hazard
Fire may produce irritating and/or toxic gases. Contact may cause burns to skin and eyes. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Runoff from fire control may cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Flammable/combustible material. May be ignited by friction, heat, sparks or flames. Some may burn rapidly with flare burning effect. Powders, dusts, shavings, borings, turnings or cuttings may explode or burn with explosive violence. Substance may be transported in a molten form at a temperature that may be above its flash point. May re-ignite after fire is extinguished.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Bronopol 0.01–0.1% w/v is used as an antimicrobial preservative either alone or in combination with other preservatives in topical pharmaceutical formulations, cosmetics, and toiletries; the usual concentration is 0.02% w/v.
Mechanism of action
The mechanism of Bronopol bacterial inhibition is that bronopol catalyses the oxidation of thiol groups, such as cysteine, to disulphides under aerobic conditions. This reaction is accompanied by a rapid consumption of oxygen, which is the final oxidant. During the conversion of cysteine into cystine, free radical anionic intermediates such as superoxides and peroxides are generated by bronopol, thus directly exerting a bactericidal effect. Oxidation of excess thiols alters the redox state, thereby creating hypoxic conditions that lead to a second reaction in which intracellular thiols such as glutathione are oxidised to disulphides. The result is inhibition of enzyme function and a reduction in growth rate after the period of bacterial inhibition1. Under anoxic conditions, the reaction between thiols and Bronopol decelerates without the involvement of oxygen, and consumption of Bronopol dominates. Bronopol is ultimately cleared from the reaction by depletion, and bacterial growth resumes.
Contact allergens
Bronopol is a preservative sometimes considered as a formaldehyde releaser. It was reported to be an allergen in cosmetics, cleaning agents, dairy workers, and a lubricant jelly used for ultrasound examination.
https://www.smartpractice.com
https://www.contactdermatitisinstitute.com
Pharmacokinetics
At concentrations of 12.5 to 50 μg/mL, bronopol mediated an inhibitory activity against various strains of Gram negative and positive bacteria in vitro . The bactericidal activity is reported to be greater against Gram-negative bacteria than against Gram-positive cocci . Bronopol was also demonstrated to be effective against various fungal species, but the inhibitory action is reported to be minimal compared to that of against bacterial species . The inhibitory activity of bronopol decreases with increasing pH of the media . Bronopol also elicits an anti-protozoal activity, as demonstrated with Ichthyophthirius multifiliis in vitro and in vivo . It is proposed that bronopol affects the survival of all free-living stages of I. multifiliis .
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, subcutaneous, intravenous, and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by skin contact. An eye and human skin irritant. An antiseptic. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx, and Br-.
Safety
Bronopol is used widely in topical pharmaceutical formulations and
cosmetics as an antimicrobial preservative.
Although bronopol has been reported to cause both irritant and
hypersensitivity adverse reactions following topical use, it is
generally regarded as a nonirritant and nonsensitizing material at
concentrations up to 0.1% w/v. At a concentration of 0.02% w/v,
bronopol is frequently used as a preservative in ‘hypoallergenic’
formulations.
Animal toxicity studies have shown no evidence of phototoxicity
or tumor occurrence when bronopol is applied to rodents topically
or administered orally; and there is no in vitro or in vivo evidence of
mutagenicity; this is despite the demonstrated potential of
bronopol to liberate nitrite on decomposition, which in the presence
of certain amines may generate nitrosamines. Formation of
nitrosamines in formulations containing amines may be reduced
by limiting the concentration of bronopol to 0.01% w/v and
including an antioxidant such as 0.2% w/v alpha tocopherol or
0.05% w/v butylated hydroxytoluene;(14) other inhibitor systems
may also be appropriate.
LD50 (dog, oral): 250 mg/kg
LD50 (mouse, IP): 15.5 mg/kg
LD50 (mouse, IV): 48 mg/kg
LD50 (mouse, oral): 270 mg/kg
LD50 (mouse, SC): 116 mg/kg
LD50 (mouse, skin): 4.75 g/kg
LD50 (rat, IP): 26 mg/kg
LD50 (rat, IV): 37.4 mg/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 180 mg/kg
LD50 (rat, SC): 170 mg/kg
LD50 (rat, skin): 1.6 g/kg
Hazard
Bronopol is a skin sensitiser with severe acute toxicity and corrosive eye irritation following exposure by the dermal route. Concentrations in cosmetic preparations range from 0.01 to 0.02 per cent. Significant irritation occurs at concentrations of 1 per cent or more. It is flammable and releases irritating or toxic fumes (or gases) in a fire. The finely dispersed particles form explosive mixtures in air.
Metabolism
Bronopol undergoes degradation in aqueous medium to form bromonitroethanol from a retroaldol reaction with the liberation of an equimolar amount of formaldehyde . Formaldehyde is a degradation product of bronopol, which may cause sensitization . Bromonitroethanol further decomposes to formaldehyde and bromonitromethane. Bromonitroethanol may also break down to release a nitrite ion and 2-bromoethanol .
Storage
Bronopol is stable and its antimicrobial activity is practically
unaffected when stored as a solid at room temperature and ambient
relative humidity for up to 2 years.
The pH of a 1.0% w/v aqueous solution is 5.0–6.0 and falls
slowly during storage; solutions are more stable in acid conditions.
Microbiological assay results indicate longer half-lives than
those obtained by HPLC and thus suggest that degradation
products may contribute to antimicrobial activity. Formaldehyde
and nitrites are among the decomposition products, but formaldehyde
arises in such low concentrations that its antimicrobial effect is
not likely to be significant. On exposure to light, especially under
alkaline conditions, solutions become yellow or brown-colored but
the degree of discoloration does not directly correlate with loss of
antimicrobial activity.
The bulk material should be stored in a well-closed, nonaluminum
container protected from light, in a cool, dry place.
Incompatibilities
Sulfhydryl compounds cause significant reductions in the activity of bronopol, and cysteine hydrochloride may be used as the deactivating agent in preservative efficacy tests; lecithin/polysorbate combinations are unsuitable for this purpose. Bronopol is incompatible with sodium thiosulfate, with sodium metabisulfite, and with amine oxide or protein hydrolysate surfactants. Owing to an incompatibility with aluminum, the use of aluminum in the packaging of products that contain bronopol should be avoided.
Regulatory Status
Included in topical pharmaceutical formulations licensed in Europe. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Bronopol
| Melting point: | 130-133 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 358.0±42.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 2.0002 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6200 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 167°C |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature |
| solubility | H2O: soluble100mg/mL, clear, colorless to faintly yellow |
| form | Crystals or Crystalline Powder |
| pka | 12.02±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to yellow |
| Odor | odorless |
| Water Solubility | 25 g/100 mL (22 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,1447 |
| BRN | 1705868 |
| Stability: | Stable. Hygroscopic. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases, strong reducing agents, acid chlorides and anhydrides, moisture. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 52-51-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Bronopol(52-51-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Bronopol (52-51-7) |
Safety information for Bronopol
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Bronopol
Bronopol manufacturer
Surya Fine Chem
Acuro Organics Limited
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Bronopol (2 Bromo 2 Nitro Propane 1 3 Diol 98%View Details
Bronopol (2 Bromo 2 Nitro Propane 1 3 Diol 98%View Details -
 BRONOPOL 99%View Details
BRONOPOL 99%View Details -
 BRONOPOL 99%View Details
BRONOPOL 99%View Details -
 Bronopol 99%View Details
Bronopol 99%View Details -
 2-Bromo-2-Nitro-1,3-Propanediol (Bronopol CAS 52-51-7View Details
2-Bromo-2-Nitro-1,3-Propanediol (Bronopol CAS 52-51-7View Details
52-51-7 -
 Powder 2- Bromo 2- Nitro 1/3- Propanediol (52-51-7), Packaging Type: Bag, Packaging Size: 25 kgView Details
Powder 2- Bromo 2- Nitro 1/3- Propanediol (52-51-7), Packaging Type: Bag, Packaging Size: 25 kgView Details
52-51-7 -
 Powder Bronopol, for CommericalView Details
Powder Bronopol, for CommericalView Details
52-51-7 -
 Bronopol Chemical Powder, Packaging Size: 25 kg, Packaging Type: Fibre DrumView Details
Bronopol Chemical Powder, Packaging Size: 25 kg, Packaging Type: Fibre DrumView Details
52-51-7
