BRADYKININ
Synonym(s):Bradykinin - CAS 58-82-2 - Calbiochem;RPPGFSPFR
- CAS NO.:58-82-2
- Empirical Formula: C50H73N15O11
- Molecular Weight: 1060.21
- MDL number: MFCD00076258
- EINECS: 200-398-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 12:07:08
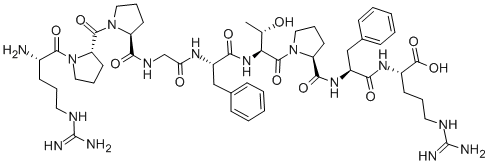
What is BRADYKININ?
Chemical properties
Amorphous solid.
The Uses of BRADYKININ
Bradykinin is used to lower blood pressure, increase bradykinin (by inhibiting its degradation) further lowering blood pressure. Bradykinin dilates blood vessels via the release of prostacyclin, nitric oxide, and endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor.
The Uses of BRADYKININ
Leucine Enkephalin acetate salt hydrate has been used in the calibration of the Q-Tof Micro hybrid, triple quadrupole-orthogonal acceleration time of flight (TOF) instrument in single-stage TOF mode. It has also been used to perform the calibration of mass spectrometry. It has also been used in liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LCMS)/MS for calibration of the system and for relative correction of the spectra.
Definition
ChEBI: A linear nonapeptide messenger belonging to the kinin group of proteins, with amino acid sequence RPPGFSPFR. Enzymatically produced from kallidin in the blood, it is a powerful vasodilator that causes smooth muscle contraction, and may mediate inflammation
Biological Functions
The kallikrein–kinin system is an enzymatic pathway
giving rise to two predominant vasoactive peptides,
kallidin and bradykinin. Kallikrein, the enzyme responsible
for the formation of these peptides, exists in
plasma and tissues. However, circulating levels of the
end products, kallidin and bradykinin, are quite low because
the kallikrein enzymes are present largely in inactive
forms. In addition, the short half-life of these peptides
(15 seconds) also contributes to low plasma levels.
In general, the kinins produce relaxation of vascular
smooth muscle and vasodilation. Bradykinin causes vascular smooth muscle relaxation by stimulating the
endothelium to release prostacyclin and nitric oxide.
Blood flow to the brain, heart, viscera, skeletal muscle,
and glands is increased. In nonvascular smooth muscle,
bradykinin will produce a contractile response.
Other actions of kinins include activation of clotting
factors simultaneously with the production of bradykinin.
In the kidney, bradykinin production results in an
increase in renal papillary blood flow, with a secondary
inhibition of sodium reabsorption in the distal tubule. In
the peripheral nervous system, bradykinin is important
for the initiation of pain signals. It is also associated with
the edema, erythema, and fever of inflammation.
Bradykinin exerts its physiological effects via two
receptors, the B1 and B2 receptors, with most of its
physiological effects being mediated by the B2 receptor.
The precise function of the B1 receptor is unclear;
however, some of the chronic inflammatory responses
to bradykinin may be mediated through actions at this
receptor.
Bradykinin antagonists of the B2 receptor are currently
in development and may find utility in the treatment
of pain associated with burns and such chronic inflammatory
disorders as arthritis, asthma, and chronic
pain.
General Description
Induces the release of nitric oxide. Other physiological functions include stimulation of pain receptors, inhibition of cAMP accumulation, induction of smooth muscle contraction, and vasodilation. Also involved in edema resulting from trauma or injury. Improves post-ischemic recovery of heart via a nitric oxide-dependent mechanism.
Hazard
Powerful vasodilator; increased capillary permeability; stimulates pain receptors; contraction of smooth muscle; teratogen; mutagenic.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Product does not compete with ATP.
Clinical Use
9-peptide, produced in response to tissue damage, inflammation, viral infections, etc. Produces pain, increased vascular permeability, and synthesis of prostaglandins.
Storage
-20°C
Properties of BRADYKININ
| Melting point: | 170°C (rough estimate) |
| Boiling point: | 811.85°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D25 -76.5° (c = 1.37 in 1N acetic acid) |
| Density | 1.1171 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6930 (estimate) |
| RTECS | EE1530000 |
| storage temp. | −20°C |
| solubility | H2O: >40 mg/mL |
| form | White to off-white lyophilized solid |
| pka | 3.34±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | Lyophilized powder |
| Water Solubility | Soluble to 1 mg/ml in water. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 58-82-2 |
Safety information for BRADYKININ
Computed Descriptors for BRADYKININ
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

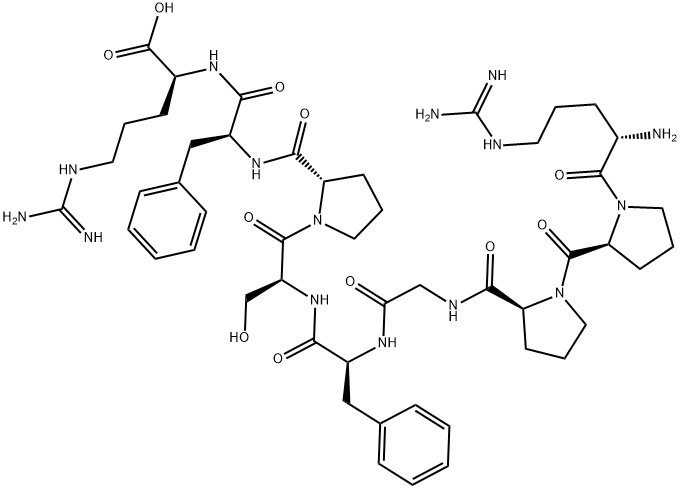
![[PROLYL2,4-3,4-(N)3H]BRADYKININ](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure4/GIF/CB7459836.gif)

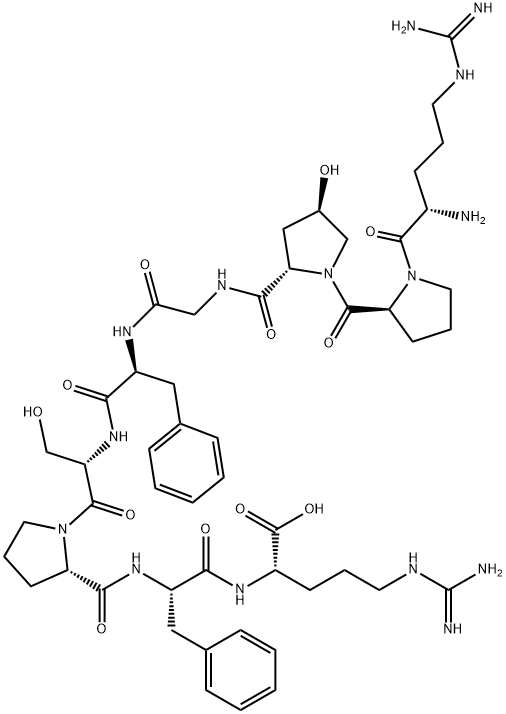
![[(PCL)PHE5,8] BRADYKININ](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/125229-63-2.gif)
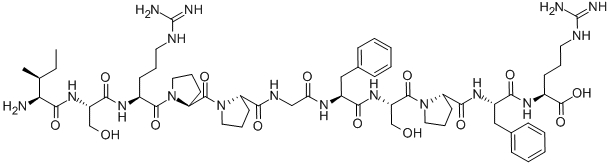
![[TYR5] BRADYKININ](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure1/GIF/CB1319020.gif)
You may like
-
 Bradykinin CAS 58-82-2View Details
Bradykinin CAS 58-82-2View Details
58-82-2 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
