Bezafibrate
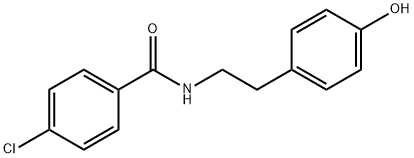
Synonym(s):2-[4-[2-(4-Chlorobenzamido)ethyl]phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoic acid
- CAS NO.:41859-67-0
- Empirical Formula: C19H20ClNO4
- Molecular Weight: 361.82
- MDL number: MFCD00078970
- EINECS: 255-567-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-01 18:09:03

What is Bezafibrate?
Absorption
Bezafibrate is almost completely absorbed after oral administration. The relative bioavailability of bezafibrate retard compared to the standard form is about 70%.
Description
Bezafibrate is a non-selective agonist of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs; EC50s = 50, 60, and 20 μM for human PPARα, PPARγ, and PPARδ, respectively). It reduces triglyceride levels and the size of lipid droplets in an oleic acid-induced HepaRG hepatocyte model of steatosis when used at a concentration of 25 μM. Bezafibrate (10 mg/kg per day) reduces plasma VLDL and LDL mass and triglyceride and free fatty acid levels in a high-fructose plus lard diet-induced rat model of insulin resistance.
Chemical properties
Off-White Solid
Originator
Bezafibrate,Eipico Co.
The Uses of Bezafibrate
Bezafibrate has been used:
- a supplement in the standard diet (SD)?for mice to study its effect on diabetes
- to evaluate its effect on hepatitis C virus (HCV) assembly and secretion
- to evaluate its effect on gonadal steroidogenesis and?spermatogenesis?of zebrafish and also used as standard for HPLC
The Uses of Bezafibrate
Antilipemic
The Uses of Bezafibrate
antihyperlipidemic
The Uses of Bezafibrate
anti-hyperlipoproteinemic
Indications
For the treatment of primary hyperlipidaemia types IIa, IIb, III, IV and V (Fredrickson classification) corresponding to groups I, II and III of the European Atherosclerosis Society guidelines - when diet alone or improvements in lifestyle such as increased exercise or weight reduction do not lead to an adequate response. Also for the treatment of secondary hyperlipidaemias, e.g. severe hypertriglyceridemias, when sufficient improvement does not occur after correction of the underlying disorder (e.g. diabetes mellitus).
Background
Antilipemic agent that lowers cholesterol and triglycerides. It decreases low density lipoproteins and increases high density lipoproteins.
What are the applications of Application
Bezafibrate is a peroxisome proliferator and hypolipidaemic agent
Definition
ChEBI: Bezafibrate is a monocarboxylic acid amide obtained by the formal condensation of the carboxy group of 4-chlorobenzoic acid with the amino group of 2-[4-(2-aminoethyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoic acid. Benafibrate is used for the treatment of hyperlipidaemia. It has a role as a xenobiotic, an environmental contaminant, a geroprotector and an antilipemic drug. It is a monocarboxylic acid, an aromatic ether, a member of monochlorobenzenes and a monocarboxylic acid amide. It is functionally related to a propionic acid.
Manufacturing Process
0.292 moles p-chlorobenzoyl chloride and 50 ml dry pyridine were added
dropwise to 0.146 moles tyramine in 60 ml dry pyridine for 10 minutes. Then
the mixture was poured in about 500 g of ice with water. The fallen-out
crystals was filtered off, washed with diluted HCl, water and NaHCO3 solution
and dried. It was recrystallized from acetone to give di(4-chlorobenzoyl)
tyramine; yield 98 %; MP: 203°-205°C.
0.11 moles above product in 400 ml methanol was mixed with 130 ml 2 N
KOH and heated at 40°-45°C for 1 hour. On cooling 130 ml 2 N HCl was
added. The fallen-out precipitate was filtered off, filtrate was distilled off to
dryness. The residue was washed with water, NaHCO3 solution and
recrystallized from ethanol to give N-(4-chlorobenzoyl)tyramine; yield 91%;
MP: 174°-176°C.
2.14 g sodium was dissolved in 50 ml of absolute methanol and mixed with
0.93 mole N-(4-chlorobenzoyl)tyramine. Methanol was removed in vacuum to
dryness. The residue was slurried in 100 ml absolute toluene and 0.137 moles
2-bromo-2-methylpropionic acid ethyl ester was added. The suspension was
heated for 25 hours at 80°C. Then it was distilled in vacuum to dryness and
the residue was dissolved in CH2Cl2, washed with diluted HCl, NaOH and
water, and dried over CaCl2. On removing of the solvent, the crude 2-{4-[2-
(4-chlorobenzoylamino)ethyl]phenoxy}-2-methylpropionic acid ethyl ester was
obtained. After recrystallization from ether/ ligroin and acetone it had MP:
96°-97°C; yield 67 %.
0.1 mole above ester in 1.5 L of dioxane was slowly mixed with 200 ml 1 N
KOH at ambient temperature and stood for 2 hours, then it was heated at
40°C for 1 hour. The substance was dissolved completely. On cooling the
mixture was neutralized with 200 ml 1 N HCl. The solvents were removed in
vacuum. The residue was washed with water and recrystallized from acetone
to give 2-{4-[2-(4-chlorobenzoylamino)ethyl]phenoxy}-2-methylpropionic
acid; yield 84%; MP: 186°C.
Therapeutic Function
Antihyperlipidemic
Biochem/physiol Actions
The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) is a member of the steroid nuclear receptor superfamily. Bezafibrate is a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonist for PPARα, PPARδ, and PPARγ. Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) activator.PPARgamma agonists, including Bezafibrate, have beneficial effects in the suppression of the inflammatory response during RSV infection and therefore might have clinical efficacy in the course of severe RSV-infection.
Pharmacokinetics
Bezafibrate is an antilipemic agent that lowers cholesterol and triglycerides. It decreases low density lipoproteins and increases high density lipoproteins. Bezafibrate lowers elevated blood lipids (triglycerides and cholesterol). Elevated VLDL and LDL are reduced by treatment with bezafibrate, whilst HDL-levels are increased. The activity of triglyceride lipases (lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipoproteinlipase) involved in the catabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins is increased by bezafibrate. In the course of the intensified degradation of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins (chylomicrons, VLDL) precursors for the formation of HDL are formed which explains an increase in HDL. Furthermore, cholesterol biosynthesis is reduced by bezafibrate, which is accompanied by a stimulation of the LDL-receptor-mediated lipoprotein catabolism. Elevated fibrinogen appears to be an important risk-factor, alongside the lipids, smoking and hypertension, in the development of atheroma. Fibrinogen plays an important role in viscosity, and therefore blood flow, and also appears to play an important role in thrombus development and lysability. Bezafibrate exerts an effect on thrombogenic factors. A significant decrease in elevated plasma fibrinogen levels can be achieved. This may lead, amongst other things, to a reduction in both blood and plasma viscosity. Inhibition of platelet aggregation has also been observed. A reduction in blood glucose concentration due to an increase in glucose tolerance has been reported in diabetic patients. In the same patients, the concentration of fasting and postprandial free fatty acids was reduced by bezafibrate.
Clinical Use
Hyperlipidaemia
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antibacterials: increased risk of myopathy with
daptomycin - try to avoid concomitant use.
Anticoagulants: enhances effect of coumarins and
phenindione; dose of anticoagulant should be
reduced by up to 50% and adjusted by monitoring
INR.
Antidiabetics: may improve glucose tolerance
and have an additive effect with insulin or
sulphonylureas.
Ciclosporin: may increase nephrotoxicity and reduce
ciclosporin levels.
Colchicine: possible increased risk of myopathy.
Lipid-regulating drugs: increased risk of myopathy in
combination with statins and ezetimibe - avoid with
ezetimibe; do not exceed 10 mg of simvastatin and
20 mg of rosuvastatin.
Metabolism
Hepatic.
Metabolism
50% of the administered bezafibrate dose is recovered in the urine as unchanged drug and 20% in the form of glucuronides. Elimination is rapid, with excretion almost exclusively renal. 95% of the activity of the [14C]-labelled drug is recovered in the urine and 3% in the faeces within 48 hours.
Properties of Bezafibrate
| Melting point: | 184 °C |
| Boiling point: | 572.1±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.260±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMF: soluble |
| form | solid |
| pka | 3.29±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Merck | 14,1195 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 41859-67-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Propanoic acid, 2-[4-[2-[(4-chlorobenzoyl)amino]ethyl]phenoxy]-2-methyl- (41859-67-0) |
Safety information for Bezafibrate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for Bezafibrate
Abamectin manufacturer
New Products
4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium SODIUM AAS SOLUTION ZINC AAS SOLUTION BUFFER SOLUTION PH 10.0(BORATE) GOOCH CRUCIBLE SINTERED AQUANIL 5 BERYLLIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![Benzamide, 2-chloro-N-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl]-](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/883800-52-0.gif)

![[4-[2-[(4-chlorobenzoyl)amino]ethyl]phenyl] 4-chlorobenzoate](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20180719/GIF/41859-56-7.gif)



![Propanoic acid, 2-[4-(2-aminoethyl)phenoxy]-2-methyl-](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20200515/GIF/55458-78-1.gif)
You may like
-
 Bezafibrate CAS 41859-67-0View Details
Bezafibrate CAS 41859-67-0View Details
41859-67-0 -
 Bezafibrate 99% (HPLC) CAS 41859-67-0View Details
Bezafibrate 99% (HPLC) CAS 41859-67-0View Details
41859-67-0 -
 Bezafibrate CAS 41859-67-0View Details
Bezafibrate CAS 41859-67-0View Details
41859-67-0 -
 Bezafibrate CAS 41859-67-0View Details
Bezafibrate CAS 41859-67-0View Details
41859-67-0 -
 Bezafibrate CAS 41859-67-0View Details
Bezafibrate CAS 41859-67-0View Details
41859-67-0 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4