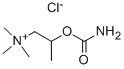
BETHANECHOL
- CAS NO.:674-38-4
- Empirical Formula: C7H17N2O2
- Molecular Weight: 161.22
- MDL number: MFCD01669407
- EINECS: 209-686-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-04-17 18:22:24
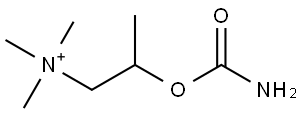
What is BETHANECHOL?
Absorption
After oral administration of bethanechol, maximum effectiveness of the drug on the bladder and GI tract typically occur after 60-90 minutes; however, effects may present as early as 30 minutes after administration. The duration of action of a typical oral dose of bethanechol is around 1 hour while higher doses (300-400 mg) may be effective for up to 6 hours.
Subcutaneously administered bethanechol produces effects more rapidly after 5-15 minutes with maximum effectiveness achieved after 15-30 minutes. The effects of subcutaneous bethanechol subside within 2 hours of administration.
Toxicity
Symptoms of bethanechol overdose include nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, salivation, sweating, and flushing of the skin.
In case of overdose, atropine sulfate is available as an antidote and although subcutaneous administration is preferred, it may be given intravenously in emergencies. In adults, the recommended dose of atropine is 0.6 mg and may be repeated every 2 hours based on the patient’s response. In infants and children up to 12 years of age, the recommended dose of atropine is 0.01 mg/kg (maximum single dose = 0.4 mg) and may be repeated every 2 hours until the desired response is achieved or until adverse effects of atropine limit usage.
In mice, the oral LD50 of bethanechol is 1510 mg/kg.
The Uses of BETHANECHOL
Cholinergic.
Background
Bethanechol is a synthetic ester that was initially synthesized in 1935. As a cholinergic agent, bethanechol is similar in structure and pharmacological function to acetylcholine and is used in specific cases when stimulation of the parasympathetic nervous system is necessary. For example, bethanechol is readily used to treat postoperative or postpartum urinary retention. An advantage of bethanechol is that in contrast to acetylcholine, bethanechol is not degraded by cholinesterase allowing its effects to be longer-lasting.
Indications
Bethanechol is indicated for the treatment of acute, functional postpartum and postoperative urinary retention. It is also indicated for the treatment of neurogenic atony of the bladder with retention.
Definition
ChEBI: The carbamic acid ester of 2-methylcholine. A slowly hydrolysed muscarinic agonist with no nicotinic effects, it is used as its chloride salt to increase smooth muscle tone, as in the gastrointestinal tract following abdominal surgery, treatment of gastro- esophageal reflux disease, and as an alternative to catheterisation in the treatment of non-obstructive urinary retention.
brand name
Duvoid (WellSpring); Myotonachol (Glenwood); Urecholine (Odyssey).
Pharmacokinetics
Bethanechol is selective for muscarinic receptors and has little to no impact on nicotinic receptors. The charged quaternary amine in the structure of bethanechol prevents it from crossing the blood-brain barrier which minimizes central nervous system related adverse effects.
Metabolism
Not Available
Safety information for BETHANECHOL
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
2058-74-4 -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8