beta-Hydroxyisovaleric Acid
Synonym(s):3-Hydroxy-3-methylbutyric acid
- CAS NO.:625-08-1
- Empirical Formula: C5H10O3
- Molecular Weight: 118.13
- MDL number: MFCD00059081
- EINECS: 626-699-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
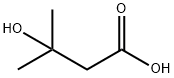
What is beta-Hydroxyisovaleric Acid?
Description
β-Hydroxy β-methylbutyric acid (HMB), or β-hydroxy β- methylbutyrate, is a metabolite of the essential amino acid leucine and is synthesized in the human body. It plays a part in protein synthesis and was discovered by Dr. Steven L. Nissen at Iowa State University. It has been used in scientific studies to purportedly increase muscle mass and decrease muscle breakdown. Nissen held the original patent on the metabolite as a nutritional supplement. It was discovered in pigs, and small quantities can also be found in grapefruit, alfalfa, and catfish. As a supplement it is usually sold as a calcium salt.
Research published in the Journal of Applied Physiology has shown that HMB may have an effect on increasing muscle weight and strength. A review in Nutrition & Metabolism provides an in depth and objective analysis of HMB research. The same study lists as HMB' s proposed mechanisms of action the following:
Increased sarcolemmal integrity via conversion to HMG-CoA
Enhanced protein synthesis via the mTOR pathway
Depression of protein degradation through inhibition of the ubiquitin pathway
Three grams of Calcium beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate per day may help muscles combat protein breakdown, assist in muscle repair and support increased endurance. Studies suggest its benefits may be greater for the untrained. Also, well-controlled scientific studies have found increases in muscle mass and decreases in body fat in 70 year old men. It has helped patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in hospital intensive care units, muscle wasting associated with HIV or AIDS and with cancer, and trauma victims with severe injuries.
The human body produces about 0.2 - 0.4 grams per day. Standard doses in research studies have been 1.5 to 3.0 grams per day, usually divided into two doses.
Chemical properties
colorless to light yellow liquid
The Uses of beta-Hydroxyisovaleric Acid
β-Hydroxyisovaleric Acid is a metabolite of the essential amino acid Leucine and is synthesized in the human body. Studies suggest that β-Hydroxyisovaleric Acid may have an effect on increasing muscle weight and strength. The presence of elevated β-Hydroxyisovaleric Acid is a sensitive marker of biotin deficiency and may indicate the presence of a genetic disorder such as biotinidase deficiency or holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency.
The Uses of beta-Hydroxyisovaleric Acid
3-Hydroxy-3-methylbutyric acid is a useful biochemical for synthesis and proteomics research. It is used as an indicator of biotin deficiency. Further, it is used to increase muscle mass and decrease muscle breakdown. In addition to this, it is involved in the protein synthesis.
Definition
ChEBI: A 3-hydroxy monocarboxylic acid that is isovaleric acid substituted at position 3 by a hydroxy group. Used as indicator of biotin deficiency.
Properties of beta-Hydroxyisovaleric Acid
| Melting point: | -80 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 88 °C/1 mmHg (lit.) |
| Density | 0.938 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 113 °C |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | DMF:10.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);84.65(Max Conc. mM) DMSO:10.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);84.65(Max Conc. mM) Ethanol:10.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);84.65(Max Conc. mM) PBS (pH 7.2):10.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);84.65(Max Conc. mM) |
| pka | 4.38±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Pale yellow |
| Specific Gravity | 1.10 |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water and ethanol. |
| BRN | 1743952 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 625-08-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for beta-Hydroxyisovaleric Acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for beta-Hydroxyisovaleric Acid
| InChIKey | AXFYFNCPONWUHW-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium SODIUM AAS SOLUTION ZINC AAS SOLUTION BUFFER SOLUTION PH 10.0(BORATE) GOOCH CRUCIBLE SINTERED AQUANIL 5 BERYLLIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

![ETHYL 1-OXASPIRO[2.5]OCTANE-2-CARBOXYLATE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/6975-17-3.gif)

You may like
-
 3-Hydroxy-3-methylbutyric acid CAS 625-08-1View Details
3-Hydroxy-3-methylbutyric acid CAS 625-08-1View Details
625-08-1 -
 3-Hydroxy-3-methylbutyric acid CAS 625-08-1View Details
3-Hydroxy-3-methylbutyric acid CAS 625-08-1View Details
625-08-1 -
 3-Hydroxy-3-methylbutyric acid CAS 625-08-1View Details
3-Hydroxy-3-methylbutyric acid CAS 625-08-1View Details
625-08-1 -
 Beta-hydroxyisovaleric acid 95% CAS 625-08-1View Details
Beta-hydroxyisovaleric acid 95% CAS 625-08-1View Details
625-08-1 -
 β-Hydroxyisovaleric Acid CAS 625-08-1View Details
β-Hydroxyisovaleric Acid CAS 625-08-1View Details
625-08-1 -
 Beta-Hydroxyisovaleric Acid CAS 625-08-1View Details
Beta-Hydroxyisovaleric Acid CAS 625-08-1View Details
625-08-1 -
 β-Hydroxyisovaleric acid CAS 625-08-1View Details
β-Hydroxyisovaleric acid CAS 625-08-1View Details
625-08-1 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4