Benzalkonium chloride
Synonym(s):Alkylbenzyldimethylammonium chloride;Benzalkonium chloride solution
- CAS NO.:8001-54-5
- Empirical Formula: C17H30ClN
- Molecular Weight: 283.88
- MDL number: MFCD00050250
- EINECS: 616-786-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-18 14:26:18
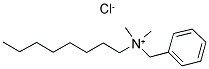
What is Benzalkonium chloride?
Absorption
Percutaneous absorption is considered to be insignificant .
In one study, benzalkonium chloride absorption was evaluated in women using tampons containing the agent. Venous blood samples were drawn 15 minutes before the tampon application and then again at 15 min, 1 h, 3 h, and 24 h after application. Benzalkonium chloride was not detected in any of the blood samples at any time tested.
Similarly, in another study, benzalkonium chloride absorption was tested in women using tampons containing the agent. Venous blood and breast milk samples were taken 15 minutes before application and 3 h and 24 h after tampon administration. Benzalkonium chloride was not found in any of the subjects' samples. .
Moreover, in a study where benzalkonium chloride solution was placed on the corneal surface of rabbit subjects, at various intervals after administration, the rabbits' eyes would be washed with 1 mL saline and the following tissues and fluids were removed: bulbar and palpebral conjunctiva, aqueous humour, corneal epithelium, endothelium and stroma, iris-ciliary body, lens, vitreous, retina, and choroid. Plasma samples were obtained with direct cardiac punctures. After administration of one drop, benzalkonium chloride was found in the corneal epithelium, endothelium, and stroma, and in the bulbar and palpebral conjunctivae. Benzalkonium chloride loss from ocular tissues was such that about one-third to two thirds of its concentration (depending on the tissue) at 30 min remained after 24 hr; measurable values existed for as long as 120 hr. The administration of multiple drops led to continued accumulation of benzalkonium chloride. .
Toxicity
An oral dose of 100-400 mg/kg or a parenteral dose of 5-15 mg/kg is believed to be fatal in humans .
A potential concern for larger concentrations of benzalkonium chloride to possibly cause corneal damage when implemented as an excipient ingredient in aqueous eye products is an issue that should be discussed between potential patents and their health care providers . Since decreased regular blinking and tear generation in patients experiencing dry eyes due to any number of eye conditions can result in reduced dilution of applied eye drops containing the benzalkonium chloride preservative , alternative options including benzalkonium chloride-free products should be considered.
Additionally, benzalkonium chloride has been reported to cause punctate keratopathy and/or toxic ulcerative keratopathy. In addition, benzalkonium chloride may cause eye irritation and is known to discolour soft contact lenses . There may also be the possibility of benzalkonium chloride containing eye drops to cause some stinging and pain .
There is the possibility of ototoxicity occurring when benzalkonium chloride containing ear drops are applied to the ear .
Benzalkonium chloride used as a preservative in nebulised solutions of anti-asthma drugs has been reported to cause dose-related bronchoconstriction especially in asthmatic patients and has been associated with the precipitation of respiratory arrest .
Despite the fairly widespread cutaneous use of benzalkonium chloride, only limited human evidence of sensitization in relatively small populations of individuals have been reported . Nevertheless, the main adverse effect for topical formulations of benzalkonium chloride is usually the warning 'may cause local irritation' .
Chemical properties
Benzalkonium chloride occurs as a white or yellowish-white amorphous powder, a thick gel, or gelatinous flakes. It is hygroscopic, soapy to the touch, and has a mild aromatic odor and very bitter taste.
The Uses of Benzalkonium chloride
Benzalkonium chloride is a preservative with anti-microbial and deodorant properties. It can also be used as a surfactant. It is used prior to surgical procedures or for minor wound care to reduce risks of infection. For most multidose aqueous nasal, ophthalmic and otic products, benzalkonium chloride is the preservative of choice.
Indications
When used as an active ingredient in products like antibacterial, antiseptic, or disinfectant soaps, topical sanitizers, or cleaning agents, benzalkonium is primarily implemented in its salt form, benzalkonium chloride, where it may often be the only active ingredient present and indicated for the primary purpose of topical washing to decrease bacteria on skin .
Conversely, when implemented as an excipient ingredient in a variety of multidose aqueous nose, eye, or ear products, benzalkonium chloride is being used as the antimicrobial preservative of choice to facilitate effective bactericidal and fungicidal actions to help minimize the growth of unwanted organisms in the multidose containers .
Background
Benzalkonium is a quaternary ammonium compound used as a biocide, a cationic surfactant, and as a phase transfer agent . Benzalkonium is more commonly contained in consumer products in its salt form, benzalkonium chloride . This salt is used in a great variety of international pharmaceutical products such as eye, ear, and nasal drops or sprays as an excipient ingredient serving as an antimicrobial preservative . When used as an ingredient in antiseptic and disinfectant products however, it is an active antimicrobial agent .
Production Methods
Benzalkonium chloride is formed by the reaction of a solution of Nalkyl- N-methylbenzamine with methyl chloride in an organic solvent suitable for precipitating the quaternary compound as it is formed.
Definition
ChEBI: A class of quaternary ammonium chloride salts in which the nitrogen is substituted by a benzyl group, two methyl groups and an even-numbered alkyl chain.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Benzalkonium chloride is a quaternary ammonium compound used
in pharmaceutical formulations as an antimicrobial preservative in
applications similar to other cationic surfactants, such as cetrimide.
In ophthalmic preparations, benzalkonium chloride is one of the
most widely used preservatives,at a concentration of
0.01–0.02% w/v. Often it is used in combination with other
preservatives or excipients, particularly 0.1% w/v disodium edetate,
to enhance its antimicrobial activity against strains of Pseudomonas.
In nasal, and otic formulations a concentration of
0.002–0.02% w/v is used, sometimes in combination with
0.002–0.005% w/v thimerosal. Benzalkonium chloride 0.01%
w/v is also employed as a preservative in small-volume parenteral
products. Benzalkonium chloride was also shown to enhance the
topical penetration of lorazepam.
Benzalkonium chloride is additionally used as a preservative in
cosmetics.
Contact allergens
This quaternary ammonium cationic surfactant is a mixture of alkyl, dimethyl, and benzyl ammonium chlorides (-R). It is an irritant rather than a sensitizer, but may cause allergic contact dermatitis from creams, detergents/antiseptics, ophthalmic preparations, and in nursing, veterinary, dental, and medical personnel. Its presence was observed in plaster of Paris.
Pharmacokinetics
Benzalkonium chloride solutions are generally categorized as biocidal agents with relative long durations of action. Their spectrum of activity has been demonstrated against bacteria, to some viruses, fungi, and protozoa , although bacterial spores are treated as being resistant to the agent. Additionally, the agent generally shows more activity against gram-positive than gram-negative bacteria . Finally, solutions of benzalkonium chloride are bacteriostatic or bactericidal based on their concentration. Bacteriostatic agents act to prevent further growth of bacterial organisms that are present while bactericidal agents function to kill bacteria that are present . In general, the activity of the agent is not largely affected by pH, but such activity does increase substantially at higher temperatures and prolonged exposure times.
Side Effects
Clinically, benzalkonium chloride may cause eye irritation and is known to discolour soft contact lenses. Benzalkonium chloride in eye drops has also been reported to cause punctate keratopathy and/or toxic ulcerative keratopathy, especially in frequent or prolonged use or in conditions where the cornea is compromised.
Metabolism
Since benzalkonium chloride is structurally a large, positively charged molecule it is likely poorly absorbed and eliminated largely in faeces, similar to other quaternary ammonium compounds .
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with aluminum, anionic surfactants, citrates, cotton,
fluorescein, hydrogen peroxide, hypromellose,iodides, kaolin,
lanolin, nitrates, nonionic surfactants in high concentration,
permanganates, protein, salicylates, silver salts, soaps, sulfonamides,
tartrates, zinc oxide, zinc sulfate, some rubber mixes, and
some plastic mixes.
Benzalkonium chloride has been shown to be adsorbed to
various filtering membranes, especially those that are hydrophobic
or anionic.
Regulatory Status
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (inhalations, IM injections, nasal, ophthalmic, otic, and topical preparations). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. It is also included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Benzalkonium chloride
| Boiling point: | >100°C/760mmHg |
| Density | 0.98 |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | Very soluble in water and in ethanol (96 per cent). An aqueous solution froths copiously when shaken. |
| form | Viscous Solution |
| color | Clear or white to yellow, may contain yellow-white fragments |
| Specific Gravity | 0.98 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, moisture. Hygroscopic. |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C10H16N.ClH/c1-11(2,3)9-10-7-5-4-6-8-10;/h4-8H,9H2,1-3H3;1H/q+1;/p-1 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 8001-54-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Benzalkonium chloride (8001-54-5) |
Safety information for Benzalkonium chloride
Computed Descriptors for Benzalkonium chloride
| InChIKey | KXHPPCXNWTUNSB-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| SMILES | C1C=C(C[N+](C)(C)C)C=CC=1.[Cl-] |
Benzalkonium chloride manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Chemtech Marketing
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran





You may like
-
 BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE BKC 99%View Details
BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE BKC 99%View Details
8001-54-5 -
 Benzalkonium chloride 80 % 8001-54-5 99%View Details
Benzalkonium chloride 80 % 8001-54-5 99%View Details
8001-54-5 -
 Benzalkonium Chloride CAS 8001-54-5View Details
Benzalkonium Chloride CAS 8001-54-5View Details
8001-54-5 -
 Benzalkonium chloride CAS 8001-54-5View Details
Benzalkonium chloride CAS 8001-54-5View Details
8001-54-5 -
 Liquid Antiozonants Alkyl Dimethyl Benzyl Ammonium Chloride, ADBAC, DrumView Details
Liquid Antiozonants Alkyl Dimethyl Benzyl Ammonium Chloride, ADBAC, DrumView Details
8001-54-5 -
 Alkylbenzyldimethylammonium Chloride Cas no : 63449-41-2, LiquidView Details
Alkylbenzyldimethylammonium Chloride Cas no : 63449-41-2, LiquidView Details
63449-41-2 -
 Liquid Benzalkonium ChlorideView Details
Liquid Benzalkonium ChlorideView Details
8001-54-5 -
 Benzalkonium Chloride 80%View Details
Benzalkonium Chloride 80%View Details
8001-54-5
