Belzutifan
- CAS NO.:1672668-24-4
- Empirical Formula: C17H12F3NO4S
- Molecular Weight: 383.34
- MDL number: MFCD32197212
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 15:53:33
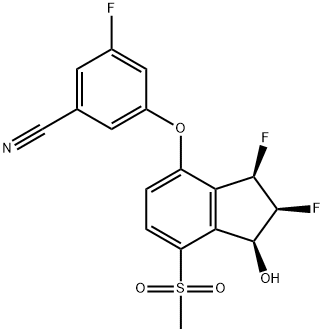
What is Belzutifan?
Absorption
In patients with VHL disease-associated renal cell carcinoma, the mean Cmax and AUC0-24h at steady-state - which was achieved after approximately three days of therapy - were 1.3 μg/mL and 16.7 μg?hr/mL, respectively. The median Tmax is one to two hours following oral administration.
The administration of belzutifan with food has a negligible effect on drug disposition - when given alongside a high-calorie, high-fat meal, the Tmax was delayed by approximately 2 hours with no other clinically meaningful effects observed.
Toxicity
Data regarding overdosage with belzutifan is lacking. There is no specific treatment available for belzutifan overdose - if a patient is suspected to have overdosed, immediately withhold belzutifan and institute standard supportive care. Grade 3 hypoxia has been observed at doses of 120mg twice daily and Grade 4 thrombocytopenia has been observed at doses of 240mg once daily (twice the recommended dose).
Description
Belzutifan is an orally active, small molecule inhibitor of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-2alpha (HIF-2a), with potential antineoplastic activity. The HIF-2α protein was a key player in the growth of certain cancers. Initially considered to be undruggable, a binding pocket was eventually discovered in the HIF-2α molecule which allowed for compounds to bind and inhibit these proteins.
The Uses of Belzutifan
Belzutifan is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease who need treatment for a type of kidney cancer called renal cell carcinoma (RCC), tumors in the brain and spinal cord called central nervous system hemangioblastomas, or a type of pancreatic cancer called pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, that do not need surgery right away.
Background
Belzutifan is an inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor 2α (HIF-2α) used in the treatment of von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease-associated cancers. The HIF-2α protein was first identified in the 1990s by researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center as a key player in the growth of certain cancers. Initially considered to be undruggable, a binding pocket was eventually discovered in the HIF-2α molecule which allowed for compounds to bind and inhibit these proteins. This discovery led to the initial development of belzutifan (at the time called PT2977), which was further developed by a spin-off company named Peloton Pharmaceuticals (which itself was eventually acquired by Merck in 2019).
Belzutifan inhibits the complexation of HIF-2α with another transcription factor, HIF-1β, a necessary step in its activation - by preventing the formation of this complex, belzutifan can slow or stop the growth of VHL-associated tumors. Belzutifan received FDA approval for the treatment of select VHL-associated cancers on August 13, 2021.
Indications
Belzutifan is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease who require therapy for associated renal cell carcinoma (RCC), central nervous system (CNS) hemangioblastomas, or pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNET), who do not require immediate surgery.
Indications
Belzutifan is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease who require therapy for associated renal cell carcinoma (RCC), central nervous system (CNS) hemangioblastomas, or pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNET), who do not require immediate surgery.
Mechanism of action
Belzutifan inhibits the complexation of HIF-2α with another transcription factor, HIF-1β, a necessary step in its activation - by preventing the formation of this complex, belzutifan can slow or stop the growth of VHL-associated tumors. Belzutifan received FDA approval for the treatment of select VHL-associated cancers on August 13, 2021.
Pharmacokinetics
Belzutifan exerts its therapeutic effects by inhibiting a transcription factor necessary for the growth of solid tumors associated with VHL disease. It is taken once daily at approximately the same time each day, with or without food. Both severe anemia and hypoxia have been observed following therapy with belzutifan, and patients should be monitored closely before and during therapy to ensure patients can be managed as clinically indicated. There are no data regarding the use of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents for the treatment of belzutifan-induced anemia, and as such these therapies should be avoided.
Belzutifan may cause embryo-fetal toxicity when administered to pregnant women. Female patients and male patients with female partners of reproductive potential should ensure that an effective form of contraception is used throughout therapy and for one week after the last dose - as belzutifan appears to decrease the efficacy of systemic hormonal contraceptives, patients should be advised to use an additional method of contraception (e.g. condoms) to eliminate the possibility of pregnancy during therapy.
Pharmacokinetics
Upon oral administration, belzutifan binds to and blocks the function of HIF-2alpha, thereby preventing HIF-2alpha heterodimerization and its subsequent binding to DNA. This results in decreased transcription and expression of HIF-2alpha downstream target genes, many of which regulate hypoxic signaling. This inhibits cell growth and survival of HIF-2alpha-expressing tumor cells. HIF-2alpha, the alpha subunit for the heterodimeric transcription factor HIF-2, is overexpressed in many cancers and promotes tumorigenesis.
Side Effects
Side effects ofBelzutifan that was reported:
allergic reactions(skin rash,itchingorhives; swelling of the face, lips, or tongue)
blurred vision OR changes in vision
high blood sugar (increased hunger, thirst or urination; unusually weak or tired, blurry vision)
infection (fever, chills,cough,sore throat,pain;or trouble passing urine)
low calcium levels(fast heartbeat; muscle cramps or;pain;;pain, tingling, or numbness in the hands or feet; seizures)
low red blood cell counts (feeling faint; lightheaded, falls; unusually weak or tired)
trouble breathing
trouble passing urine or change in the amount of urine
Metabolism
Belzutifan is primarily metabolized by UGT2B17 and CYP2C19, and to a lesser extent by CYP3A4.
Properties of Belzutifan
| Boiling point: | 505.8±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.56±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C, stored under nitrogen |
| solubility | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (130.43 mM) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 11.66±0.60(Predicted) |
| color | White to light yellow |
Safety information for Belzutifan
Computed Descriptors for Belzutifan
Belzutifan manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateYou may like
-
 1672668-24-4 Belzutifan 98%View Details
1672668-24-4 Belzutifan 98%View Details
1672668-24-4 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1