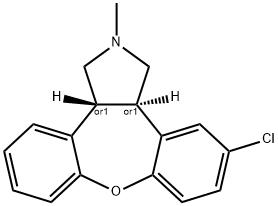
Asenapine
- CAS NO.:65576-45-6
- Empirical Formula: C17H16ClNO
- Molecular Weight: 285.772
- MDL number: MFCD09838016
- EINECS: 2658294
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-07-02 08:55:12
What is Asenapine?
Absorption
Cmax, single 5 mg dose = 4 ng/mL (within 1 hour); Bioavailability, sublingual administration = 35%; Bioavailability, oral administration (swallowed) = <2%; Time to steady state, 5 mg = 3 days; Peak plasma concentration occurs within 0.5 to 1.5 hours. Doubling dose of asenapine results in 1.7-fold increase in maximum concentration and exposure. Drinking water within 2-5 minutes post administration of asenapine results in a decrease in exposure.
Description
(±)-Asenapine is an atypical antipsychotic. It binds to dopamine D1-4, α-adrenergic, and histamine receptors (Kis = 0.42-1.45, 0.32-1.26, and 1-6.17 nM, respectively), as well as the serotonin (5-HT) receptor subtypes 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, 5-HT2C, 5-HT5A, 5-HT6, and 5-HT7 (Kis = 0.03-3.98 nM). (±)-Asenapine inhibits the suppression of neuron firing induced by the 5-HT2A, dopamine D2, and α2-adrenergic receptor agonists 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine (DOI), apomorphine, and clonidine , respectively, in rat brain (ED50s = 75, 40, and 85 μg/kg, respectively). In vivo, (±)-asenapine (0.05-0.2 mg/kg, s.c.) increases extracellular dopamine levels in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), nucleus accumbens (NAc), and lateral striatum and suppresses the conditioned avoidance response in rats. It prevents acute and chronic phencyclidine-induced deficits in cued reversal learning in rats when administered at a dose of 0.075 mg/kg. Formulations containing asenapine have been used in the treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar I disorder.
Chemical properties
Yellow Oil
The Uses of Asenapine
Combined serotonin (5HT2) and dopamine (D2) receptor antagonist; structurally related to Mianserin. Antipsychotic
Background
Developed by Schering-Plough after its merger with Organon International, asenapine is a sublingually administered, atypical antipsychotic for treatment of schizophrenia and acute mania associated with bipolar disorder. Asenapine also belongs to the dibenzo-oxepino pyrrole class. It is also for severe post-traumatic stress disorder nightmares in soldiers as an off-label use. FDA approved on August 13, 2009.
What are the applications of Application
Asenapine maleate is An antagonist of noradrenalin, dopamine, 5-HT and receptors
What are the applications of Application
Asenapine is a combined 5HT2, adrenergic, and D2 receptor antagonist
Indications
Used for treatment in psychosis, schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorders, manic disorders, and bipolar disorders as monotherapy or in combination.
Definition
ChEBI: (R,R)-asenapine is a 5-chloro-2-methyl-2,3,3a,12b-tetrahydrodibenzo[2,3:6,7]oxepino[4,5-c]pyrrole in which both of the stereocentres have R configuration. It is a conjugate base of a (R,R)-asenapine(1+). It is an enantiomer of a (S,S)-asenapine.
Biological Activity
Novel psychopharmacologic agent. Displays antagonist activity at 5-HT, dopamine, noradrenalin and histamine receptor subtypes (pK i values are 8.60, 8.40, 10.15, 9.75, 10.46, 8.84, 9.60, 9.94, 8.85, 8.90, 8.84, 9.38, 8.95, 8.93, 8.9, 9.49, 8.91, 9.00 and 8.21 for 5-HT 1A , 5-HT 1B , 5-HT 2A , 5-HT 2B , 5-HT 2C , 5-HT 5A , 5-HT 6 , 5-HT 7 , D 1 , D 2L , D 2S , D 3 , D 4 , α 1A , α 2A , α 2B , α 2C , H 1 and H 2 receptors respectively). Displays no appreciable affinity for muscarinic receptors. Exhibits potent activity in animal models predictive of antipsychotic efficacy.
Pharmacokinetics
Asenapine is a serotonin, dopamine, noradrenaline, and histamine antagonist in which asenapine possess more potent activity with serotonin receptors than dopamine. Sedation in patients is associated with asenapine's antagonist activity at histamine receptors. Its lower incidence of extrapyramidal effects are associated with the upregulation of D1 receptors. This upregulation occurs due to asenapine's dose-dependent effects on glutamate transmission in the brain. It does not have any significant activity with muscarinic, cholinergic receptors therefore symptoms associated with anticholinergic drug activity like dry mouth or constipation are not expected to be observed. Asenapine has a higher affinity for all aforementioned receptors compared to first-generation and second-generation antipsychotics except for 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptors.
Clinical Use
Atypical antipsychotic
Treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar disease
Enzyme inhibitor
This atypical antipsychotic agent (FW = 285.77 g/mol; CAS 65576-45-6), marketed under the trade names Saphris ?, and also known as Org 5222 and (3aRS,12bRS)-rel-5-chloro-2,3,3a,12b-tetrahydro-2-methyl-1H-dibenz[2,3: 6,7]-oxepino-[4,5-c]pyrrole, is multi-receptor antagonist with the following spectrum of binding interactions: serotonin 5-HT1A receptor, Ki = 2.5 nM; serotonin 5-HT1B receptor, Ki = 4.0 nM; serotonin 5-HT2A receptor, Ki = 0.06 nM; serotonin 5-HT2B receptor, Ki = 0.16 nM; serotonin 5-HT2C receptor, Ki = 0.03 nM; serotonin 5-HT5A receptor, Ki = 1.6 nM; serotonin 5-HT6 receptor, Ki = 1.5 nM; serotonin 5-HT7 receptor, Ki = 0.13 nM; a1- Adrenergic receptor, Ki = 1.2 nM; a2A-Adrenergic receptor, Ki = 1.2 nM; a2B-Adrenergic receptor, Ki = 0.25 nM; a2C-Adrenergic receptor, Ki = 1.2 nM; dopamine D1-receptor, Ki = 1.4 nM; dopamine D2-receptor, Ki = 1.3 nM; dopamine D3-receptor, Ki = 0.4 nM; dopamine D4-receptor, Ki = 1.1 nM; histamine H1-receptor, Ki = 1.0 nM; and histamine H2-receptor, Ki = 6 nM. Like other atypical antipsychotic drugs, asenapine preferentially enhances dopamine and acetylcholine efflux in the rat medial prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. See Reference-x for asenapine’s UV, IR, NMR, and mass spectra as well as X-ray analysis, thermal properties, solubilities and partition coefficient.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anaesthetics: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Analgesics: increased risk of convulsions with
tramadol; enhanced hypotensive and sedative effects
with opioids.
Anti-arrhythmics: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with anti-arrhythmics that prolong the
QT interval; avoid with amiodarone, disopyramide
and procainamide (risk of ventricular arrhythmias).
Antidepressants: concentration possibly increased
by fluvoxamine; possibly increased paroxetine
concentration; concentration of tricyclics possibly
increased.
Antiepileptics: antagonises anticonvulsant effect.
Antimalarials: avoid with artemether/lumefantrine.
Antivirals: concentration possibly increased by
ritonavir.
Anxiolytics and hypnotics: increased sedative effects.
Metabolism
Asenapine is oxidized via CYP1A2 and undergoes direct glucuronidation via UGT1A4. Oxidation via CYP1A2 is asenapine's primary mode of metabolism.
Metabolism
Metabolism is by direct glucuronidation by UGT1A4
and oxidative metabolism by cytochrome P450
isoenzymes (predominantly CYP1A2) are the primary
metabolic pathways for asenapine.
Excretion is 50% renal and 50% via the faeces.
Properties of Asenapine
| Boiling point: | 357.9±42.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.231 |
| storage temp. | Store at +4°C |
| solubility | DMSO:50.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);174.97(Max Conc. mM) |
| form | A solid |
| pka | 9.50±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | White to off-white |
Safety information for Asenapine
Computed Descriptors for Asenapine
Asenapine manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

![1H-Dibenz[2,3:6,7]oxepino[4,5-c]pyrrol-1-one, 11-chloro-2,3,3a,12b-tetrahydro-2-Methyl-, (3aR,12bS)-rel-](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20180808/GIF/165890-26-6.gif)

![(3aS,12bS)-2-Methyl-2,3,3a,12b-tetrahydro-1H-dibenzo[2,3:6,7]oxepino[4,5-c]pyrrole](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20210111/GIF/65576-39-8.gif)
![(3aR,12bR)-rel-5-Chloro-2,3,3a,12b-tetrahydro-2-methyl-1H-dibenz[2,3:6,7]oxepino[4,5-c]pyrrol-1-one](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20180808/GIF/912356-08-2.gif)
You may like
-
 65576-45-6 trans-5-Chloro-2,3,3A,12B-tetrahydro-2-methyl-1H-dibenz(2,3:6,7)oxepino(4,5-C)pyrrole 98%View Details
65576-45-6 trans-5-Chloro-2,3,3A,12B-tetrahydro-2-methyl-1H-dibenz(2,3:6,7)oxepino(4,5-C)pyrrole 98%View Details
65576-45-6 -
 Asenapine 98%View Details
Asenapine 98%View Details
65576-45-6 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1