arecoline
- CAS NO.:63-75-2
- Empirical Formula: C8H13NO2
- Molecular Weight: 155.19
- EINECS: 200-565-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
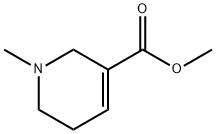
What is arecoline?
Description
Areca catechu L. (Bin Lang), a palm plant native to Malaysia, is mainly distributed in tropical regions of Asia and the Americas. Arecoline is extracted from dry mature seeds of areca. The mature seeds of areca are 3–5 cm in diameter, with fibrous peel and a seed, namely, areca nut. The endosperm of areca nut is hard, with grayish-brown spots. Areca nut is harvested from August to November every year before the fruit is fully mature. The seeds are peeled, boiled, and cut into thin slices. The dried slices are brown or black, and it is an important medicine in traditional Chinese medicine. Areca nut is the raw materials of catechu. Areca nut was used as anthelmintics with arecoline as the main alkaloid in it.
Description
Arecoline is an alkaloid ester found in the seeds of the betel nut palm, which is also called areca palm from its scientific name, Areca catechu. The term “betel nut” is a bit confusing because South and Southeast Asians often chew it along with betel leaf from the vine of the same name (Piper betle). The two plants are not biologically related.
Arecoline has been known since 1891, when German pharmacist E. Jahns isolated it from A. catechu seeds. The first synthesis was reported by Fritz Chemnitius1 at Jena University (Germany) in 1926. It is a moderately strong base, with a pKb value of 6.8. It is miscible with water and most organic solvents. The carboxylic acid corresponding to the arecoline ester is called arecaidine; it also exists in betel nuts.
People consume betel nuts because they provide a “high” similar to that caused by nicotine. Arecoline, however, acts on different receptors than does nicotine: muscarinic (rather than nicotinic) acetylcholine receptors, especially M4, which may be the cause of its effects on the parasympathetic nervous system. Similarly to nicotine, arecoline is addictive. Chewing betel nuts is also dangerous because they contain ingredients that can cause cancers of the mouth and the esophagus.
1. Chemnitius is also known for his 1932 article about chemistry at Jena University from 1629 to 1921.
Chemical properties
Oily Liquid
Physical properties
Appearance: oily liquid. Solubility: mixed with water, ethanol, or ether in any ratio, soluble in chloroform. Density: 1.059?g/cm3 . Boiling point (760?mmHg): 209?°C. Flash point: 81.1?°C. Vapor pressure (25?°C): 0.208?mmHg. Arecoline can be synthesized to salts with organic acids. Arecoline hydrobromide, arecoline acetarsol, and arecoline p-antimony carboxybenzoic acid are commonly used.
History
Arecoline, an alkaloid extracted from Areca catechu L., is first reported by Jahns in
1888. Mujumdar found that there were at least six kinds of alkaloids in areca,
including arecoline, arecaidine, guavacoline, and guavacine. The content of arecoline in the fresh fruit of areca was 0.3–0.63% as determined with HPLC .
It has been found first that arecoline has the effect of antiparasite and is promoting the motility of the gastrointestinal smooth muscle. It activates the M and N
cholinergic receptors, excites the nervous system, promotes the body excitability,
and improves the ability of learning and memory .
The Uses of arecoline
Arecoline has shown regulatory properties of controlling plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression in human buccal mucosa fibroblasts.
The Uses of arecoline
A cholinergic alkaloid from seeds of the betel nut palm Areca catechu. Anthelmintic (Cestodes); cathartic
Definition
ChEBI: A tetrahydropyridine that is 1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine with a methyl group at position 1, and a methoxycarbonyl group at position 3. An alkaloid found in the areca nut, it acts as an agonist of muscarinic acetylcholine.
Indications
This product has no source standard. Tablets: anthelmintics, less used now. Eye drops: cholinergic drugs for glaucoma treatment.
Pharmacology
Paralysis was the main mechanism of the antiparasite effect of arecoline.
The effect of arecoline on cholinergic receptors is similar to that of pilocarpine.
It can agonize M-cholinergic receptors (M1, M2, M3, M4) and increase the
secretion of glands, especially the salivary. It can also agonize N-cholinergic
receptors and activate the muscles of skeletal, ganglia, carotid body, etc. The central
nervous system is also influenced by the cholinergic effect of arecoline. Intravenous
injection of small dosage of arecoline can cause wake-up reaction of the cortex in
cats, which is inhibited or blocked by atropine. Arecoline can cause salivation, vomiting, diuretic, lethargy, and convulsion when overdosed.
In addition, arecoline can enhance intestinal peristalsis, contract bronchus, lower
heart rate, dilate blood vessels, and decrease blood pressure. While in rabbit, it
induces coronary artery contraction.
Eye drops can reduce the pupil.
Pharmacokinetic parameters for arecoline after oral administration of arecoline
(3? mg/kg): Tmax, 120.07? min; Cmax, 60.61? ng/mL; t1/2, 69.32? min; AUC0? – t,
15116.86? min/ng/mL; AUC0-∞, 15771.37? min/ng/mL; plasma clearance, 0.19? L/
min/kg .
Clinical Use
Arecoline is of historical interest, because its structure, like those of many other early medicinal agents, was determined and confirmed by a 19th-century German pharmacist, E. Jahns. Xanomeline may be viewed as a nonclassical bio-isostere of the ester moiety of arecoline. It is a muscarinic M1/M4 agonist that is showing promise in clinical trials for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Although it is not tolerated at orally effective doses, transdermal delivery systems are showing promise.
Safety Profile
Poison by subcutaneous and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion. Questionable carcinogen with experimental neoplastigenic data. It mimics the action of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter, and is a parasympathetic nervous system stimulant. Its action on the central nervous system can cause tremors. Human mutation data reported. It is easily nitrosated to several nitrosamines. See also ESTERS and NITROSAMINES. It is the major alkaloid found in betel quid. Combustible, can react with oxidzing materials. When heated to decomposition it emits hghly toxic fumes of NOx.
Properties of arecoline
| Melting point: | <25℃ |
| Boiling point: | 209℃ |
| Density | 1.0504 g/cm3 (20 ºC) |
| refractive index | 1.4860 (589.3 nm 20℃) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Chloroform (Sparingly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Oil |
| appearance | colorless oily liquid |
| pka | 6.84(at 25℃) |
| color | Oily liquid |
Safety information for arecoline
Computed Descriptors for arecoline
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran





You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1