ANTIOXIDANT
- Empirical Formula: C12H16O13
- Molecular Weight: 368.25
- MDL number: MFCD00269795
- Update Date: 2024-11-08 20:21:46

What is ANTIOXIDANT?
Definition
An organic compound added to rubber, natural fats and oils, food products, gasoline, and lubricating oils to retard oxidation, deterioration, rancidity, and gum formation, respectively. Rubber antioxidants are commonly of an aromatic amine type, such as di-β-naphthylp-phenylenediamine and phenyl-β-naphthylamine 1% or less based on the rubber content of a mixture affords adequate protection. Many antioxidants are substituted phenolic compounds (butylated hydroxyanisole, di-tert-butyl-p-cresol, and propyl gallate). Food antioxidants are effective in very low concentration (not more than 0.01% in animal fats) and not only retard rancidity but protect the nutritional value by minimizing the breakdown of vitamins and essential fatty acids. Sequestering agents, such as citric and phosphoric acids, are frequently employed in antioxidant mixtures to ify the harmful effect of traces of metallic impurities.
Definition
A substance that inhibits oxidation. Antioxidants are added to such products as foods, paints, plastics, and rubber to delay their oxidation by atmospheric oxygen. Some work by forming chelates with metal ions, thus neutralizing the catalytic effect of the ions in the oxidation process. Other types remove intermediate oxygen free radicals. Naturally occurring antioxidants can limit tissue or cell damage in the body. These include vitamin E and β-carotene.
Safety information for ANTIOXIDANT
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran
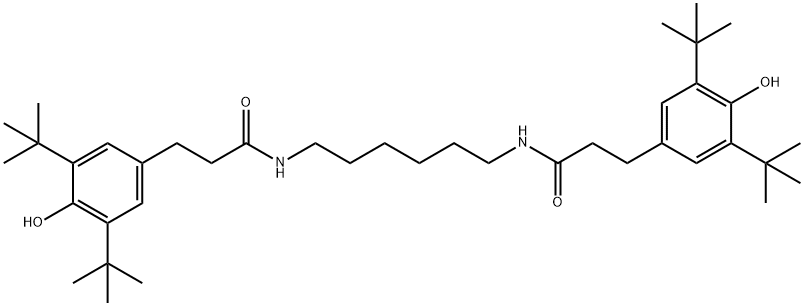



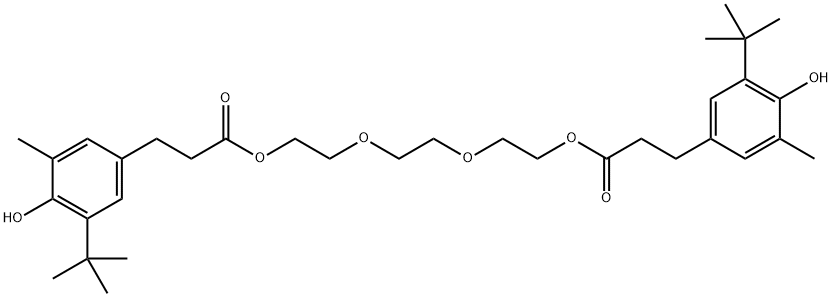

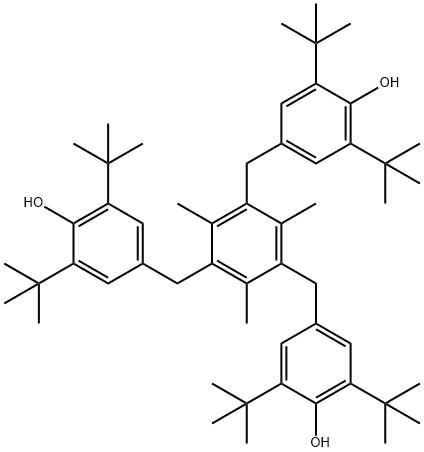

You may like
-
 17604-74-9 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 98+View Details
17604-74-9 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 98+View Details
17604-74-9 -
 131987-69-4 98+View Details
131987-69-4 98+View Details
131987-69-4 -
 2-Hexyn-1-ol 98+View Details
2-Hexyn-1-ol 98+View Details
764-60-3 -
 Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 67967-07-1 98+View Details
Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 67967-07-1 98+View Details
67967-07-1 -
 764-60-3 2-Hexyn-1-ol 98+View Details
764-60-3 2-Hexyn-1-ol 98+View Details
764-60-3 -
 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 98+View Details
2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 98+View Details
5968-21-8 -
 3-Iodophenylacetic acid 1878-69-9 98+View Details
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 1878-69-9 98+View Details
1878-69-9 -
 132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6
