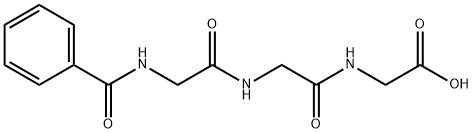
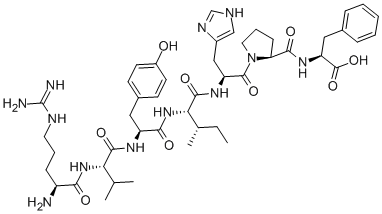
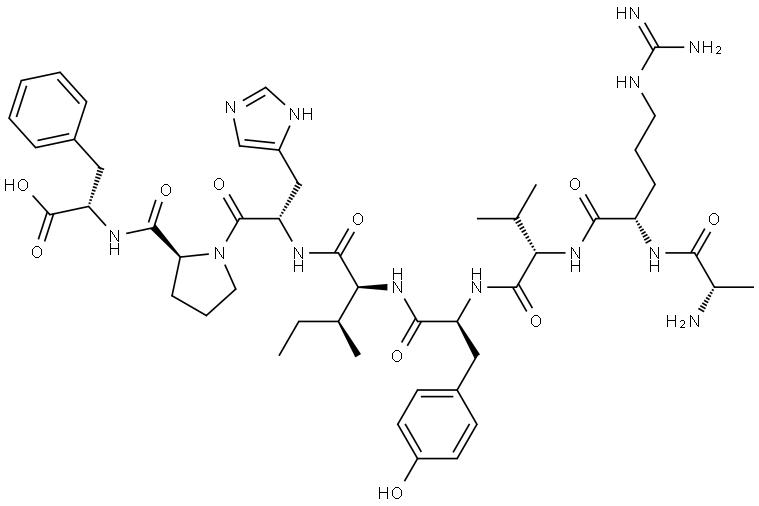
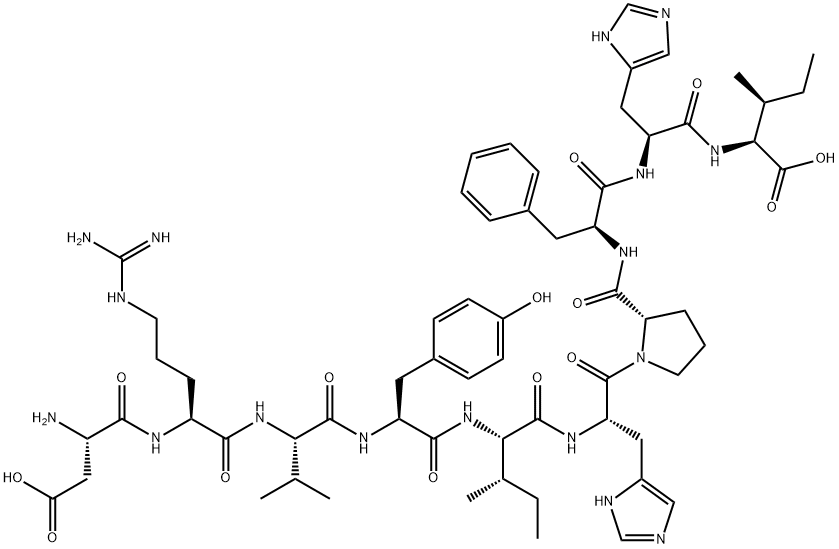
ANGIOTENSIN I HUMAN ACETATE HYDRATE
Synonym(s):Hypertensin I
- CAS NO.:70937-97-2
- Empirical Formula: C62H89N17O14.C2H4O2.H2O
- Molecular Weight: 1374.56
- MDL number: MFCD10567215
- EINECS: 215-804-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-11-16 20:18:48
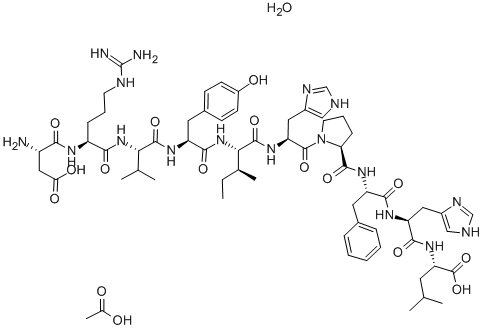
What is ANGIOTENSIN I HUMAN ACETATE HYDRATE?
The Uses of ANGIOTENSIN I HUMAN ACETATE HYDRATE
Angiotensin I human acetate salt hydrate has been used:
- as an external calibration standard, it was applied to α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid (CHCA) and 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid (DHB) matrix,
- to prepare angiotensin I solution gravimetrically for hydrolysis and also used as a model peptide to demonstrate SI (système international) -traceable?amino acid analysis
- as an analyte to deposit on the target in the study of on-line single droplet deposition for matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry
General Description
Angiotensinogen (Angiotensin I) is a renin substrate, which is produced by the liver.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Angiotensin I is a putative neurotransmitter. It is the precursor of angiotensin II and of angiotensin fragment 1-7, which are the hormones involved in regulation of fluid volume and the release of aldosterone.
Purification Methods
Angiotensin is purified using extraction, affinity chromatography and HPLC [Hermann et al. Anal Biochem 159 295 1986].
Properties of ANGIOTENSIN I HUMAN ACETATE HYDRATE
| storage temp. | −20°C |
Safety information for ANGIOTENSIN I HUMAN ACETATE HYDRATE
Computed Descriptors for ANGIOTENSIN I HUMAN ACETATE HYDRATE
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 4-(3-chloropropyl)morpholine phenylhydrazine hydrochloride (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
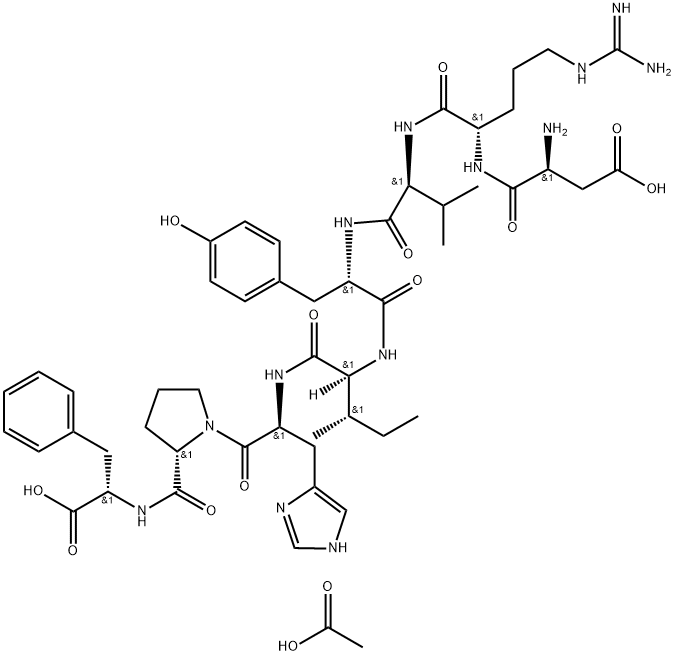

You may like
-
 Angiotensin I human acetate salt hydrate CAS 70937-97-2View Details
Angiotensin I human acetate salt hydrate CAS 70937-97-2View Details
70937-97-2 -
 (9H-fluoren-9-yl)methyl (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) carbonate 82911-69-1 98.0%View Details
(9H-fluoren-9-yl)methyl (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) carbonate 82911-69-1 98.0%View Details
82911-69-1 -
 13057-17-5 95.0%View Details
13057-17-5 95.0%View Details
13057-17-5 -
 4-bromoaniline 106-40-1 99.0%View Details
4-bromoaniline 106-40-1 99.0%View Details
106-40-1 -
 1421517-99-8 99.0%View Details
1421517-99-8 99.0%View Details
1421517-99-8 -
 5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoic acid 99.0%View Details
5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoic acid 99.0%View Details
21739-92-4 -
 2-methyl-5-nitrophenol 98.0%View Details
2-methyl-5-nitrophenol 98.0%View Details
5428-54-6 -
 15761-38-3 97.0%View Details
15761-38-3 97.0%View Details
15761-38-3
Statement: All products displayed on this website are only used for non medical purposes such as industrial applications or scientific research, and cannot be used for clinical diagnosis or treatment of humans or animals. They are not medicinal or edible.