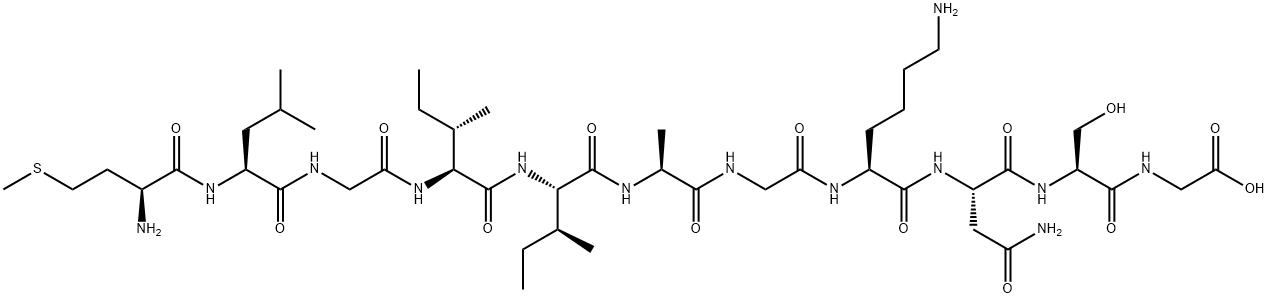
AMYLOID BETA-PROTEIN (HUMAN, 25-35) TRIFLUOROACETATE
- CAS NO.:131602-53-4
- Empirical Formula: C45H81N13O14S
- Molecular Weight: 1060.27
- MDL number: MFCD00133076
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
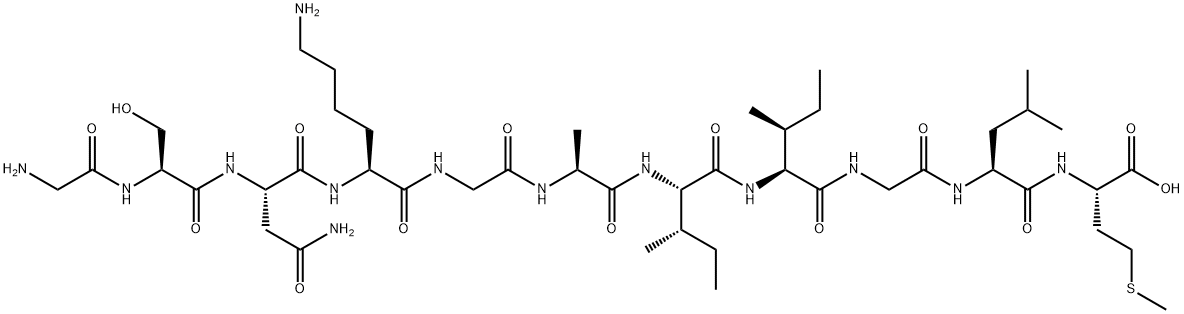
What is AMYLOID BETA-PROTEIN (HUMAN, 25-35) TRIFLUOROACETATE?
Description
Beta-amyloid protein (Abeta), a major component of senile plaques of Alzheimer's disease (AD) in the brain, causes elevation of the intracellular free Ca2+ level and the production of robust free radicals. Beta-amyloid 25-35 induced apoptosis, characterized by decreased cell viability, neuronal DNA condensation, and fragmentation, is associated with an increase in intracellular free Ca2+ level, the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and the activation of caspase-3. All of these effects induced by beta-amyloid 25-35 are reversed by genistein.
The Uses of AMYLOID BETA-PROTEIN (HUMAN, 25-35) TRIFLUOROACETATE
Amyloid β-Protein Fragment 25-35 has been used:
- to induce neurotoxicity in cortical cultures
- to induce Alzheimer′s disease in rat model
- to induce apoptosis in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)
General Description
Amyloid β-Protein Fragment 25-35 (Aβ25-35) is derived from the amyloid-β protein.amyloid-β protein, which is mapped to human chromosome 21q21. Aβ25-35 lacks the N-terminal domain and the metal binding site and is majorly generated by proteolytic cleavage of Aβ(1?40) peptides. It has a β-sheet and β-turn structure.
Biological Activity
Amyloid β-peptide (25-35) (human) is a fragment of human amyloid β-peptide, functionally required for the neurotrophic and neurotoxic effects associated with Alzheimer's disease.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Amyloid β-Protein Fragment 25-35 (Aβ25-35) is involved in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer′s disease. Inhibitors of this transition may serve as a potential agent in managing Alzheimer′s disease. It is present in the subiculum and entorhinal cortex neurons of Alzheimer′s brain samples and inclusion-body myositis (IBM) muscle. It binds to receptors present in microglia and is capable of lipid membrane insertion. The functional domain sequence of Aβ comprising of sequence GSNKGAIIGLM elicits neurotrophic and neurotoxic effects. Aβ25-35 exhibits rapid aggregation and displays age dependant neurotoxicity.
Mechanism of action
Amyloid β (Aβ) peptide is a proven major contributing component of neuritic plaques of Alzheimer's disease (AD) . The formation of fibrillar deposits of Aβ peptide in brain is a key step in the pathogenesis of this disease, since the conversion of Aβ from soluble monomer to insoluble fibril is considered to cause the neuronal degeneration and clinical dementia in AD patients. Recent biophysical studies such as electron microscopy, solid-state NMR, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), and electronic circular dichroism (ECD) spectra indicated that the Aβ fibrils exhibit a high β-sheet content. The conversion of normal Aβ peptides with water-soluble α-helical/random coil structures into the insoluble Aβ aggregates with an extensive β-sheet content is considered to be the predominant event in the onset of AD.
storage
-20°C
Properties of AMYLOID BETA-PROTEIN (HUMAN, 25-35) TRIFLUOROACETATE
| Boiling point: | 1517.3±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.248±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| RTECS | BU7435200 |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | insoluble in EtOH; insoluble in H2O; ≥106 mg/mL in DMSO |
| pka | 3.24±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | Lyophilized. |
| color | Lyophilized White |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water. |
Safety information for AMYLOID BETA-PROTEIN (HUMAN, 25-35) TRIFLUOROACETATE
Computed Descriptors for AMYLOID BETA-PROTEIN (HUMAN, 25-35) TRIFLUOROACETATE
| InChIKey | WIHBNMPFWRHGDF-SLVFWPMISA-N |
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Amyloid β-Protein Fragment 25-35 CAS 131602-53-4View Details
Amyloid β-Protein Fragment 25-35 CAS 131602-53-4View Details
131602-53-4 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1