AFLATOXIN B1
Synonym(s):Mycotoxins
- CAS NO.:1162-65-8
- Empirical Formula: C17H12O6
- Molecular Weight: 312.27
- MDL number: MFCD00869647
- EINECS: 214-603-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-04-29 17:45:46
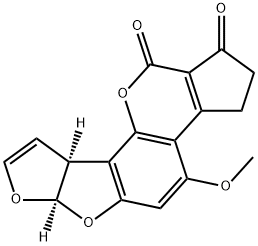
What is AFLATOXIN B1?
Description
Aflatoxins are mycotoxins that are secondary fungal metabolites produced by species such as?Aspergillus flavus?and?A. parasiticus. They were first described by K. Sargeant et al. in 1961. Under certain conditions, notably high humidity, they can contaminate cereal, nut, seed, and spice crops. Aflatoxin B1, a potential carcinogen, accounts for ~60% of all aflatoxins. It was recently found in some samples of commercial Chinese peanut butter and sesame paste.
Chemical properties
The aflatoxins are a group of molds produced by the fungus Aspergillus flavus. They are natural contaminants of fruits, vegetables, and grains. They are also described as a series of condensed ring heterocyclic compounds. They form colorless to pale yellow crystals. Practically insoluble in water.
The Uses of AFLATOXIN B1
Aflatoxin B1 is the major analogue of a family of bisfuranocoumarin mycotoxins produced by Aspergillus flavus and related species. Aflatoxin B1 exhibits a distinctive UV spectrum and blue fluorescence. Aflatoxins are among the most potent mycotoxins known but are in fact "pre-toxins", requiring metabolic activation to the toxic principle. Aflatoxins are found widely in nature in trace amounts, particularly in grains and nuts. The toxicity of these metabolites was first recognised in the 1950s and their structures elucidated in 1963. Aflatoxins have been extensively reviewed.
The Uses of AFLATOXIN B1
Aflatoxin B1 is a carcinogenic compound that induces transversion of G to T at codon 249 of the p53 tumor suppressor gene. Aflatoxin B1 may be used as an internal standard when testing for aflatoxin contamination in food products.
Definition
ChEBI: An aflatoxin having a tetrahydrocyclopenta[c]furo[3',2':4,5]furo[2,3-h]chromene skeleton with oxygen functionality at positions 1, 4 and 11.
General Description
Colorless to pale yellow crystals or white powder. Exhibits blue fluorescence.
Air & Water Reactions
Sensitive to exposure to air and light. Water insoluble.
Reactivity Profile
AFLATOXIN B1 is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids and strong bases.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for AFLATOXIN B1 are not available; however, AFLATOXIN B1 is probably combustible.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Aflatoxin B1 is a carcinogenic compound produced by Aspergillus flavus, a common soil fungus, that induces transversion of G to T at codon 249 of the p53 tumor suppressor gene. Aflatoxin B1 is a food contaminant and a hepatocarcinogen. Aflatoxin is biotransformed to genotoxic intermediates by P450 Phase I enzymes, mainly CYP3A4 via aflatoxin B1 3-hydroxylation. Detoxification depends on Phase II enzymes, such as Glutathione S-Transferase and AFB(1)-aldehyde reductase (AFAR). Aflatoxin B1 is a CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2D6, and CYP3A family substrate.
Safety Profile
Confirmed human carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic, neoplas tigenic, and carcinogenic data. Acute poison by ingestion, intraperitoneal, and possibly other routes. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke. See also various aflatoxins.
Potential Exposure
Aflatoxins are a group of toxic metabolites produced by certain types of fungi. Aflatoxins are not commercially manufactured; they are naturally occurring contaminants that are formed by fungi on food during conditions of high temperatures and high humidity. Most human exposure to aflatoxins occurs through ingestion of contaminated food. The estimated amount of aflatoxins that Americans consume daily is estimated to be 0.15 0.50 μg. Grains, peanuts, tree nuts, and cottonseed meal are among the more common foods on which these fungi grow. Meat, eggs, milk, and other edible products from animals that consume aflatoxincontaminated feed may also contain aflatoxins. Aflatoxins can also be breathed in
Metabolic pathway
Aflatoxin B1 can be activated via the monooxygenase reaction which then reacts with the N7 atom of B-DNA guanine. Conjugation of aflatoxin B1 8,9-epoxide is an important detoxification route. Although aflatoxin B1 8,9-epoxide can be hydrolyzed to the diol by epoxide hydrolase, the diol product is toxic, since it reacts readily with proteins by Schiff base formation or binds to DNA. Glutathione conjugation prevents toxicity of both the epoxide and its hydrolysis product. The aflatoxin glutathione conjugate is subsequently excreted from the hepatocyte into bile as a major biliary metabolite.
Shipping
UN3172 Toxins, extracted from living sources, solid or liquid, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides.
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. Use of oxidizing agents, such as hydrogen peroxide or 5% sodium hypochlorite bleach. Acids and bases may also be used.
Properties of AFLATOXIN B1
| Melting point: | 268-269 °C |
| Boiling point: | 372.21°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D -558° (c = 0.1 in CHCl3); D -480° (c = 0.1 in DMF) |
| Density | 1.2810 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4800 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 2 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMF: 20 mg/ml; DMF:PBS(pH 7.2)(1:1): 0.5 mg/ml; DMSO: 12 mg/ml |
| form | White to yellow powder. |
| color | White to yellow |
| Water Solubility | 15mg/L(temperature not stated) |
| Merck | 13,180 |
| BRN | 1269174 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. May be light or air sensitive. |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Aflatoxin B1 (1162-65-8) |
Safety information for AFLATOXIN B1
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H340:Germ cell mutagenicity H350:Carcinogenicity H361:Reproductive toxicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P262:Do not get in eyes, on skin, or on clothing. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for AFLATOXIN B1
| InChIKey | OQIQSTLJSLGHID-WNWIJWBNSA-N |
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran






You may like
-
 Aflatoxin B1 solution CAS 1162-65-8View Details
Aflatoxin B1 solution CAS 1162-65-8View Details
1162-65-8 -
 Aflatoxin B1 from Aspergillus flavus CAS 1162-65-8View Details
Aflatoxin B1 from Aspergillus flavus CAS 1162-65-8View Details
1162-65-8 -
 Aflatoxin B1 solution CAS 1162-65-8View Details
Aflatoxin B1 solution CAS 1162-65-8View Details
1162-65-8 -
 Aflatoxin B1 solution CAS 1162-65-8View Details
Aflatoxin B1 solution CAS 1162-65-8View Details
1162-65-8 -
 Aflatoxin B1 solution CAS 1162-65-8View Details
Aflatoxin B1 solution CAS 1162-65-8View Details
1162-65-8 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
