ABT-267
- CAS NO.:1258226-87-7
- Empirical Formula: C50H67N7O8
- Molecular Weight: 894.11
- MDL number: MFCD28386270
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-16 17:52:58
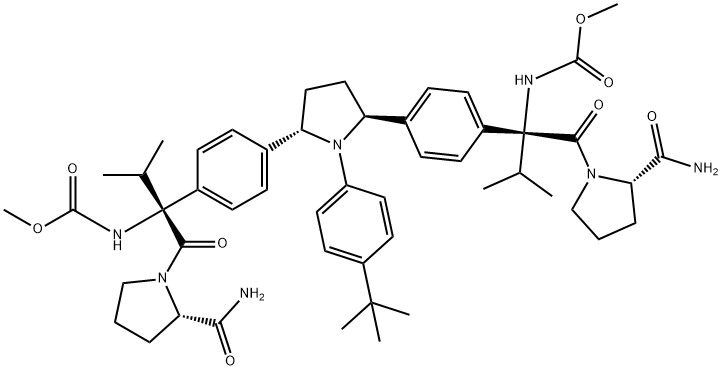
What is ABT-267?
Absorption
Ombitasvir reaches peak plasma concentration 5 hours after administration . It has an absolute bioavailability of 48%. Taking ombitasvir with high or normal fat meals increases exposure by 1.76 or 1.82 fold respectively.
Toxicity
The most common adverse effects of Viekira Pak either in combination with or without Ribavirin were pruritus, nausea, insomnia, and asthenia . The most common adverse effects of Technivie with or without Ribavirin were asthenia, fatigue, nausea, insomnia and pruritus .
Description
Ombitasvir hydrate is a NS5A non-nucleoside polymerase inhibitor which is approved as part of a four drug combination for the treatment of adults with genotype 1 hepatitis C virus infection including those with compensated cirrhosis. The four drug combination treatment consists of ombitasvir, paritaprevir (XXVII), ritonavir, and dasabuvir (X). This combination treatment is marketed as Viekira Pak and was developed by Abbvie as an all oral treatment that eliminates the need for pegylated interferon- a injections.
The Uses of ABT-267
Ombitasvir is a pharmaceutical drug that is used in the treatment of hepatitis C virus in patients with HCV genotype 1 infection. It inhibits an important viral phosphoprotein, NS5A, which is involved in viral replication, assembly, and secretion.
Indications
When used in combination with Paritaprevir and Ritonavir (as the fixed dose product Technivie), Ombitasvir is indicated in combination with Ribavirin for the treatment of patients with genotype 4 chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection without cirrhosis .
When used in combination with Paritaprevir, Ritonavir, and Dasabuvir (as the fixed dose product Viekira Pak), Ombitasvir is indicated for the treatment of HCV genotype 1b and ,when combined with Ribavirin, for the treatment of HCV genotype 1a
Background
Ombitasvir is a direct acting antiviral medication used as part of combination therapy to treat chronic Hepatitis C, an infectious liver disease caused by infection with Hepatitis C Virus (HCV). HCV is a single-stranded RNA virus that is categorized into nine distinct genotypes, with genotype 1 being the most common in the United States, and affecting 72% of all chronic HCV patients . Treatment options for chronic Hepatitis C have advanced significantly since 2011, with the development of Direct Acting Antivirals (DAAs) such as Ombitasvir. Ombitasvir is an inhibitor of NS5A, a protein essential for viral replication and virion assembly . The barrier for develoment of resistance to NS5A inhibitors is lower than that of NS5B inhibitors, another class of DAAs .
In a joint recommendation published in 2016, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) and the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) recommend Ombitasvir as a first line therapy option when used in combination with other antivirals for genotypes 1a, 1b, and 4 . Depending on the genotype, Ombitasvir is often used in combination with other antivirals such as Dasabuvir, Paritaprevir, Ritonavir, and Ribavirin with the intent to cure, or achieve a sustained virologic response (SVR), after 12 weeks of daily therapy. SVR and eradication of HCV infection is associated with significant long-term health benefits including reduced liver-related damage, improved quality of life, reduced incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma, and reduced all-cause mortality . Treatment with direct acting antivirals such as Ombitasvir is associated with very minimal side effects, with the most common being headache and fatigue . Lack of significant side effects and short duration of therapy is a considerable advantage over older interferon-based regimens, which were limited by infusion site reactions, reduced blood count, and neuropsychiatric effects .
Ombutasvir first came on the market as a fixed-dose combination product with Dasabuvir, Paritaprevir, and Ritonavir as the FDA-approved product Viekira Pak. First approved in December 2014, Viekira Pak is indicated for the treatment of HCV genotype 1b without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis, and when combined with Ribavirin for the treatment of HCV genotype 1a without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis.
Ombutasvir is also available as a fixed-dose combination product with Paritaprevir and Ritonavir as the FDA- and Health Canada-approved product Technivie. First approved in July 2015, Technivie is indicated in combination with Ribavirin for the treatment of patients with genotype 4 chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis.
In Canada, Ombutasvir is also available as a fixed-dose combination product with Dasabuvir, Paritaprevir, and Ritonavir as the Health Canada-approved, commercially available product Holkira Pak. First approved in January 2015, Holkira Pak is indicated for the treatment of HCV genotype 1b with or without cirrhosis, and when combined with Ribavirin for the treatment of HCV genotype 1a with or without cirrhosis.
Definition
ChEBI: A dipeptide derivative which is used which is in combination with dasabuvir sodium hydrate, paritaprevir and ritonavir (under the trade name Viekira Pak) for treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection as well as cirrhosis of the liver.
Pharmacokinetics
Ombitasvir is classified as a direct acting antiviral and acts against HCV to inhibit viral replication .
Clinical Use
Treatment of chronic hepatitis C infection
Synthesis
Alkylation of 1-(4-nitrophenyl)ethanone (209) with 2-bromo-1-(4-nitrophenyl)ethanone (208) in the presence of zinc chloride produced diketone 210 in 61% yield. Asymmetric reduction of the diketone using N,N-diethylaniline borane with (S)-(-)-a,a-diphenyl-2-pyrrolidinemethanol (211) and trimethoxyborate gave diol 212 in 61% yield and 99.3% ee. The diol was then treated with methanesulfonic anhydride to generate the corresponding bis-mesylate which was reacted with 4-tert-butylaniline to give pyrrolidine 213 in 51% yield over the two steps. Hydrogenolysis of the nitro groups was accomplished using Raney nickel catalyst to give bis-aniline 214. Separately, (L)-valine (216) was reacted with methyl chloroformate to give the corresponding methyl carbamate in 90% yield which was coupled to L-proline benzyl ester in the presence of EDC and HOBt to give the corresponding dipeptide in 90% yield. Hydrogenolysis of the benzyl ester group of the protected dipeptide using Pd/alumina catalyst produced dipeptide acid 215. Aniline 214 was treated with two equivalents of acid 215 in the presence of 1-propanephosphonic acid cyclic anhydride (T3P). The crude product was recrystallized from ethanol and heptane to give ombitasvir hydrate (XXV). No yields were provided to the final steps of this synthesis.

Enzyme inhibitor
This N-phenylpyrrolidine-based, pan-genotypic HCV NS5A protease inhibitor (FW = 893.14 g/mol), also named ABT-267, targets Nonstructural protein 5A (NS5A), a zinc-binding and proline-rich hydrophilic phosphoprotein that plays a key role in Hepatitis C virus RNA replication.Ombitasvir exhibits low-picomolar EC50 values against Hepatitis C virus, with superior pharmacokinetics. Although ombitasvir shows a low barrier to resistance, when given as monotherapy, co-administration with other antivirals enhances its barrier to resistance. Indeed, a 12-week, Phase- 3 study demonstrated that a multi-targeted regimen consisting of ombitasvir, dasabuvir and ribavirin is highly effective and showed a low rate of treatment discontinuation.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
See also ritonavir interactions.
Ombitasvir:
Antibacterials: concentration possibly reduced by
rifampicin - avoid.
Antidepressants: concentration possibly reduced by
St John’s wort - avoid.
Antiepileptics: concentration reduced by
carbamazepine - avoid, concentration possibly
reduced by fosphenytoin, phenobarbital, phenytoin
and primidone - avoid.
Diuretics: concentration of furosemide reduced
(reduce furosemide dose).
Immunosuppressants: increases concentration of
ciclosporin (reduce ciclosporin dose by a fifth);
everolimus (avoid); sirolimus and tacrolimus (reduce
dose and use only if benefit outweighs risk - see
SPC).
Oestrogens: avoid with ethinyloestradiol.
Statins: avoid with atorvastatin and simvastatin.
Paritaprevir:
Antibacterials: avoid with clarithromycin;
concentration possibly reduced by rifampicin -
avoid.
Antidepressants: concentration possibly reduced by
St John’s wort - avoid.
Antiepileptics: concentration reduced by
carbamazepine - avoid; possibly reduced by
fosphenytoin, phenobarbital, phenytoin and
primidone - avoid.
Antifungals: concentration of both drugs increased
with ketoconazole and possibly itraconazole and
posaconazole - avoid.
Antivirals: concentration increased by atazanavir;
concentration increased by darunavir and
concentration of darunavir decreased; avoid with
efavirenz, etravirine, indinavir, nevirapine, saquinavir
and tipranavir; concentration increased by lopinavir
- avoid.
Diuretics: concentration of furosemide increased
(reduce furosemide dose).
Immunosuppressants: increases concentration of
ciclosporin (reduce ciclosporin dose by a fifth);
everolimus (avoid); sirolimus and tacrolimus (reduce
Antidepressants: concentration possibly reduced by
St John’s wort - avoid.
Antiepileptics: concentration reduced by
carbamazepine - avoid; possibly reduced by
fosphenytoin, phenobarbital, phenytoin and
primidone - avoid.
Antifungals: concentration of both drugs increased
with ketoconazole and possibly itraconazole and
posaconazole - avoid.
Antivirals: concentration increased by atazanavir;
concentration increased by darunavir and
concentration of darunavir decreased; avoid with
efavirenz, etravirine, indinavir, nevirapine, saquinavir
and tipranavir; concentration increased by lopinavir
- avoid.
Diuretics: concentration of furosemide increased
(reduce furosemide dose).
Immunosuppressants: increases concentration of
ciclosporin (reduce ciclosporin dose by a fifth);
everolimus (avoid); sirolimus and tacrolimus (reduce
Metabolism
Ombitasvir is mainly metabolized by amide hydrolysis followed by CYP2C8-mediated oxidative metabolism .
Metabolism
Ombitasvir is metabolised via amide hydrolysis followed
by oxidative metabolism. A total of 13 metabolites
were identified in human plasma. These metabolites
are not expected to have antiviral activity or off-target
pharmacologic activity.
Paritaprevir is metabolised mainly by CYP3A4 and to
a lesser extent CYP3A5. Following administration of
a single 200 mg / 100 mg oral dose of 14C paritaprevir
/ ritonavir to humans, the parent drug was the major
circulating component, accounting for approximately 90%
of the plasma radioactivity.
At least 5 minor metabolites
of paritaprevir have been identified in circulation that
accounted for approximately 10% of plasma radioactivity.
These metabolites are not expected to have antiviral
activity.
Ritonavir is extensively metabolised in the liver mainly by
cytochrome P450 isoenzymes CYP3A4 and to a lesser
extent by CYP2D6. Five metabolites have been identified and the major metabolite has antiviral activity, but
concentrations in plasma are low.
About 86% of a dose is eliminated through the faeces
(both as unchanged drug and as metabolites) and about
11% is excreted in the urine.
Properties of ABT-267
| Melting point: | >177°C (dec.) |
| Boiling point: | 1065.6±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.223±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 10.92±0.46(Predicted) |
| color | Off-White to Pale Beige |
Safety information for ABT-267
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for ABT-267
ABT-267 manufacturer
Varanous Labs Pvt Ltd
BDR Pharmaceuticals International Pvt Ltd
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateYou may like
-
 1258226-87-7 Ombitasvir 98%View Details
1258226-87-7 Ombitasvir 98%View Details
1258226-87-7 -
 1258226-87-7 98%View Details
1258226-87-7 98%View Details
1258226-87-7 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1