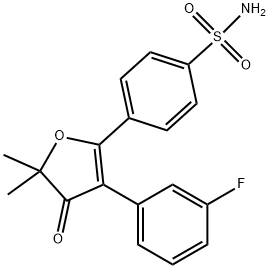
4-(3-(3-fluorophenyl)-5,5-dimethyl-4-oxo-4,5-dihydrofuran-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide
Synonym(s):4-[3-(3-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5,5-dimethyl-4-oxo-2-furanyl]-benzenesulfonamide;CG100649
- CAS NO.:301692-76-2
- Empirical Formula: C18H16FNO4S
- Molecular Weight: 361.39
- MDL number: MFCD22570958
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
What is 4-(3-(3-fluorophenyl)-5,5-dimethyl-4-oxo-4,5-dihydrofuran-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide?
Description
Polmacoxib, also known as (CG-100649), is a first-in-class NSAID which is a dual inhibitor of COX-2 and carbonic anhydrase (CA). The drug, which was approved in South Korea for the treatment of colorectal cancer (CRC) in 2015 and whose discovery has been described by workers at AmorePacific R&D, interacts with CA in red blood cells, providing a novel “tissue-specific” transport mechanism that is designed to deliver sustained levels of drug to inflamed tissues while maintaining low systemic exposure. Although the unique dual COX-2/CA inhibition is designed to provide potentially superior safety to cardiovascular, renal, and gastrointestinal tissues compared to traditional NSAIDs or COX-2 inhibitor drugs, the long-term safety profile of the drug, particularly cardiovascular risks notoriously associated with inhibition of COX-2, has yet to be determined, and the drug is currently not approved for use in any other country outside of South Korea.
Description
Polmacoxib is an inhibitor of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) and the carbonic anhydrase subtypes I (CAI) and CAII. It inhibits COX-2 in the absence of carbonic anhydrase II with an IC50 value of 40 nM, which increases by approximately 4- and 17-fold in the presence of a CAII at a molar ratio of 1:1 and 1:5, respectively. It also inhibits CAI and CAII (IC50s = 210 and 95 nM, respectively). Polmacoxib prevents >95 and 90% of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) production in HCA-7 and HT-29 human colon cancer cells, respectively, using concentrations of 0.01 and 0.001 μg/ml. It inhibits polyp formation in a transgenic mouse model of intestinal polyp formation and tumor growth in human colorectal carcinoma mouse xenograft models when used at a dose of 7 mg/kg. The inhibition of COX-2 and CAII by polmacoxib has the potential for fewer serious systemic adverse effects, including cardiovascular events associated with COX-2 selective inhibitors such as celecoxib . Formulations containing polmacoxib have been used in the treatment of osteoarthritis.
The Uses of 4-(3-(3-fluorophenyl)-5,5-dimethyl-4-oxo-4,5-dihydrofuran-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide
Polmacoxib is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug that inhibits both cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and carbonic anhydrase enzymes.
Synthesis
Subjection of commercial propargyl alcohol 172 to nbutyllithium at cryogenic temperatures followed by quenching with commercial benzaldehyde 173 resulted in the formation of benzyl alcohol 174 in 81% yield. This alcohol could be oxidized by three different means, but the authors report that the most suitable method on scale was through the use of manganese dioxide in methylene chloride, which furnished ketone 175 in 80%. Next, an interesting cyclization reaction secured the key furanone residue 176. Mechanistically, subjection of ynone 175 to dimethylamine likely resulted in a conjugate addition followed by tautomerization of the resulting allenol to the corresponding ketone. The resulting ketone then probably underwent intramolecular nucleophilic attack by the pendant tertiary alcohol and after ejection of a molecule of water through iminium-mediated lone pair assistance, hydrolysis of the iminium species to the corresponding ketone delivered 176. Next, mCPBA was employed to oxidize sulfide 176 to the corresponding sulfoxide. Subsequently, iodination of the furanone through use of bis(trifluoroacetoxy)iodobenzene (BTI), followed by a three-step sequence to convert the methylsulfoxide to the corresponding primary sulfonamide 178 occurred in 41% overall from the four-step sequence. Finally, Suzuki installation of the fluorobenzene resulted in the completion of the synthesis of polmacoxib (XXII).

Properties of 4-(3-(3-fluorophenyl)-5,5-dimethyl-4-oxo-4,5-dihydrofuran-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide
| Melting point: | 155-156 °C |
| Boiling point: | 527.7±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.361±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | DMF: 20 mg/ml; DMSO: 20 mg/ml; DMSO:PBS (pH 7.2)(1:8): 0.5 mg/ml; Ethanol: 5 mg/ml |
| form | A crystalline solid |
| pka | 10.21±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | Light yellow to green yellow |
Safety information for 4-(3-(3-fluorophenyl)-5,5-dimethyl-4-oxo-4,5-dihydrofuran-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide
Computed Descriptors for 4-(3-(3-fluorophenyl)-5,5-dimethyl-4-oxo-4,5-dihydrofuran-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide
4-(3-(3-fluorophenyl)-5,5-dimethyl-4-oxo-4,5-dihydrofuran-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide manufacturer
Honour Lab Limited
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateYou may like
-
 301692-76-2 Polmacoxib 98%View Details
301692-76-2 Polmacoxib 98%View Details
301692-76-2 -
 Polmacoxib CAS 301692-76-2View Details
Polmacoxib CAS 301692-76-2View Details
301692-76-2 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1