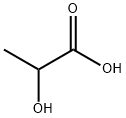
3,6-Dimethyl-1,4-dioxane-2,5-dione homopolymer
Synonym(s):Lactide polymer;PDLLA;Polylactide;Resomer R 205 S, PDLLA;Resomer R 207 S, PDLLA
- CAS NO.:26680-10-4
- Empirical Formula: C6H8O4
- Molecular Weight: 144.12532
- MDL number: MFCD00217751
- Update Date: 2023-05-04 17:34:36
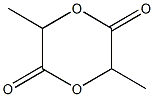
What is 3,6-Dimethyl-1,4-dioxane-2,5-dione homopolymer?
Chemical properties
Poly(DL-lactic acid) is a glassy material, occurring as white to golden-yellow pellets or granules.
The Uses of 3,6-Dimethyl-1,4-dioxane-2,5-dione homopolymer
Controlled release
The Uses of 3,6-Dimethyl-1,4-dioxane-2,5-dione homopolymer
May be used to make drug delivery materials for controlled release.
Production Methods
Lactic acid is a chiral molecule and has two optically active forms: Llactic acid and D-lactic acid. Poly(DL-lactic acid) is produced from the racemic mixture of lactic acid. Lactic acid is produced either from ethylene (petrochemical pathway) or by bacterial fermentation of D-glucose derived from food stocks. The former pathway involves an oxidation step followed by treatment with hydrogen cyanide and produces only racemic DL-lactic acid. In contrast, lactic acid produced by fermentation occurs mainly as L-lactic acid. Lowmolecular- weight poly-DL-(lactic acid) (500–10 000 Da) is produced directly from lactic acid by condensation. Higher-molecular-weight product is produced by one of two major pathways. The first involves a depolymerization of low-molecular-weight polymer into the cyclic dimer form (lactide) followed by ring-opening polymerization. Alternatively, it can be produced by a direct condensation using azeotropic distillation.
Definition
ChEBI: Lactide is a member of dioxanes.
General Description
Resomer? R 207 S, Poly(D,L-lactide) (PDLLA), a biodegradable and biocompatible polymer, can be used for a variety of biological applications. It shows properties like long degradation time, mechanical stiffness and hydrophobicity.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Poly(DL-lactic acid) is used in drug delivery systems in implants, injections, and oral solid dispersions. It is also used as a coating agent.
Safety
Poly(DL-lactic acid) degrades to produce lactic acid, which is considered a well-tolerated nontoxic material. Several in vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated that poly(lactic acid) in general (including poly(DL-lactic acid)) is well tolerated and does not induce a significant immune response.However, some studies have illustrated signs of a mild immune response.The FDA has also reported some rare cases of inflammatory responses in patients treated with cosmetic poly(DL-lactic acid) injections.
storage
Poly(DL-lactic acid) is stable under dry conditions. However, it typically biodegrades over a period of 10–15 months according to the molecular weight. Increasing moisture and temperature enhances biodegradation; the onset of degradation in water at 25°C is 6 months.In contrast to many other biodegradable polymers, poly(DL-lactic acid) degrades through a two-step mechanism. The primary degradation step involves the hydrolysis of the ester bonds independently of microbial activity to produce a low-molecular-weight polymer. When the molecular weight drops below 10 000, microorganisms digest the polymer into carbon dioxide and water. Poly(DL-lactic acid) is more stable than poly(L-lactic acid) or poly(D-lactic acid) alone.Poly(DL-lactic acid) should be stored in a dry inert environment at a temperature of -15°C to -20°C.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with strong acids or alkaline materials.
Regulatory Status
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (IM, powder, for injection, suspension, and lyophilization). Poly(DL-lactic acid) is considered as ‘not hazardous’ according to the European Directive 67/548/EEC. Included in parenteral preparations (prolongedrelease powder for suspension for subcutaneous or intramuscular injection) licensed in the UK.
Properties of 3,6-Dimethyl-1,4-dioxane-2,5-dione homopolymer
| Melting point: | 215 °C |
| Density | 1.23 g/cm3 |
| Flash point: | 113°C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in dichloromethane, tetrahydrofuran, ethyl
acetate, chloroform, hexafluoroisopropanol, and acetone. Insoluble
in water. |
| form | solid |
Safety information for 3,6-Dimethyl-1,4-dioxane-2,5-dione homopolymer
Computed Descriptors for 3,6-Dimethyl-1,4-dioxane-2,5-dione homopolymer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Resomer® R 202 H, Poly(D,L-lactide) CAS 26680-10-4View Details
Resomer® R 202 H, Poly(D,L-lactide) CAS 26680-10-4View Details
26680-10-4 -
 Resomer® R 205 S, Poly(D,L-lactide) CAS 26680-10-4View Details
Resomer® R 205 S, Poly(D,L-lactide) CAS 26680-10-4View Details
26680-10-4 -
 Poly(D,L-lactide) CAS 26680-10-4View Details
Poly(D,L-lactide) CAS 26680-10-4View Details
26680-10-4 -
 Resomer® R 207 S, Poly(D,L-lactide) CAS 26680-10-4View Details
Resomer® R 207 S, Poly(D,L-lactide) CAS 26680-10-4View Details
26680-10-4 -
 Resomer® R 203 H, Poly(D,L-lactide) CAS 26680-10-4View Details
Resomer® R 203 H, Poly(D,L-lactide) CAS 26680-10-4View Details
26680-10-4 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1