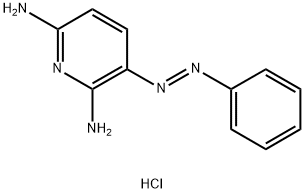
3-(PHENYLAZO)-2,6-PYRIDINEDIAMINE
- CAS NO.:94-78-0
- Empirical Formula: C11H11N5
- Molecular Weight: 213.24
- MDL number: MFCD00091843
- EINECS: 202-363-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
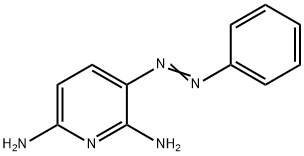
What is 3-(PHENYLAZO)-2,6-PYRIDINEDIAMINE?
Absorption
Phenazopyridine is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. The mean Cmax is 65.00 ± 29.23 ng/mL, the mean Tmax is 2.48 ± 0.50 h, and the mean AUC(0 – ∞)is 431.77 ± 87.82 ng.h/mL.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 of phenazopyridine in rats is 472 mg/kg.
Overdose information
Administering excess phenazopyridine above the daily recommended dose in those with healthy or impaired kidney function may increase the drug concentration and predispose the patient to toxicity. When a large overdose occurs, methemoglobinemia results. To treat this condition, Methylene blue at 1 to 2 mg/kg/dose should be administered intravenously as a 1% solution as deemed necessary. Its administration is likely to cause a rapid reduction of the methemoglobinemia state and relieve the associated cyanosis. Hemolytic anemia is also a risk when an overdose occurs, and “bite cells” may be observed in a blood smear after an overdose with phenazopyridine. Red blood cell G6PD deficiency may increase the risk of hemolysis, and even normal doses can lead to methemoglobinemia in patients with this condition. Nephrotoxicity, renal failure, and hepatic impairment may also occur in a case of overdose with this drug. Administer symptomatic and supportive treatment as necessary.
Chemical properties
Phenazopyridine is a red crystalline compound. Slightly soluble in water.
Originator
Phenazopyridine ,AroKor Holdings Inc.
The Uses of 3-(PHENYLAZO)-2,6-PYRIDINEDIAMINE
An azo dye used in treatment of urinary tract infections. 3-(Phenylazo)-2,6-pyridinediamine is used as an analgesic (urinary tract).
The Uses of 3-(PHENYLAZO)-2,6-PYRIDINEDIAMINE
An azo dye used in treatment of urinary tract infections. Used as an analgesic (urinary tract).
Background
Phenazopyridine, also known as Pyridium, is a urinary tract analgesic used for the short-term management of urinary tract irritation and its associated unpleasant symptoms such as burning and pain during urination. In the USA, this drug was previously marked by Roche but has been discontinued by the FDA. It is still used in various parts of the world. Ingestion of phenazopyridine is found to change the appearance of the urine by imparting an orange or red color, as it is considered an azo dye.
Indications
Phenazopyridine hydrochloride is indicated to relieve uncomfortable symptoms that occur as a consequence of mucosal irritation of the lower urinary tract in adults. The irritation may be a result of trauma, surgery, endoscopic procedures, infection, or the insertion of instruments or urinary catheters. Phenazopyridine may be used in combination with antimicrobial therapy but is not used as an antimicrobial agent. It contributes to the relief of discomfort and pain before antimicrobial therapy begins to take effect. It is important to note that the duration of treatment with this drug should last a maximum of 2 days. Phenazopyridine is available in many countries as an over the counter drug.
Definition
ChEBI: A diaminopyridine that is 2,6-diaminopyridine substituted at position 3 by a phenylazo group. A local anesthetic that has topical analgesic effect on mucosa lining of the urinary tract. Its use is limited by problems with toxicity (primarily blood disorder ) and potential carcinogenicity.
Manufacturing Process
Phenyldiazene chloride reacted with 2,6-diaminopyridine and in the result 2,6diamino-3-(phenylazo)pyridine was obtained.
In practice it is usually used as monohydrochloride.
brand name
Pyridium (Parke-Davis);Azo gantrisin;Azodine;Phenazo;Pyridiate;Pyronium;Sedural.
Therapeutic Function
Urinary analgesic, Antiseptic, Diagnostic aid
World Health Organization (WHO)
Phenazopyridine, an azo dye, was introduced in the 1950s as a urinary antiseptic. It was withdrawn in Greece in 1984 on grounds that it has a carcinogenic potential but it remains available in other countries, most frequently as a constituent of combination products.
Pharmacokinetics
Phenazopyridine acts as a local anesthetic offering relief from irritating conditions of the urinary tract. It relieves urinary urgency frequency, burning, pain, and discomfort.
A note on urine and skin discoloration and interference with test results
Yellowing of the skin or sclerae of the eyes may indicate that the accumulation of phenazopyridine has occurred. This may be a consequence of overdose, decreased renal function, taking the drug for over two days. Elderly patients may be at particular risk due to a decline in renal function, potentiating the risk of phenazopyridine accumulation. The drug should be discontinued if yellowing of the skin or sclerae is observed. Hemolytic anemia is a risk of phenazopyridine, especially in cases of overdose. In addition to the above effects, this drug may impart an orange or red color of urine and feces, causing staining of clothing. Other body fluids may also be stained, and in patients wearing contact lenses, phenazopyridine may cause lens staining. Due to its orange-red color, this drug may interfere with laboratory requiring colorimetric, spectrophotometric or fluorometric methods of analysis. In patients with G6PD enzyme deficiency, this drug poses a greater risk of hemolysis, even at normal doses and is not recommended.
A note on carcinogenesis
Based on the results of in vivo studies in rats, this drug has been listed as a carcinogen in the USA since 1981. Rats given this drug were found to demonstrate increased rates of hepatocellular carcinoma and colorectal tumors. Use this agent with caution and limit the administration of this drug when possible.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by intraperitoneal route. Questionable carcinogen with experimental neoplastigenic data. Used as a local anesthetic. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Metabolism
Phenazopyridine is metabolized in the liver, and acetaminophen has been discovered to be one metabolite of this drug. Hydroxylation is a pathway by which this drug is metabolized. In humans, 5-hydroxyl PAP is the major metabolite (48.3% of the dose) and small amounts of other hydroxy metabolites are produced. The metabolism of phenazopyridine produces aniline, which is likely associated with methemoglobinemia in some patients or in the case of an overdose. This dye accumulates in the skin, and yellow skin pigmentation has been observed when high doses of this drug have been taken. Triaminopyridine is also a metabolite of phenazopyridine. During a pharmacokinetic study, aniline contributed to approximately 6.9% of urinary metabolites. N acetyl-p-aminophenol (acetaminophen) contributes to about 18%, P-aminophenol (PAP) contributes 24%, and finally, DPP (unchanged phenazopyridine) contributes to about 41% of excreted urinary metabolites.
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. UN3249 Medicine, solid, toxic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides.
Properties of 3-(PHENYLAZO)-2,6-PYRIDINEDIAMINE
| Melting point: | 136-137° |
| Boiling point: | 343.23°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.2597 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6880 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Amber Vial, -20°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | pKa 5.15(H2O,t =25) (Uncertain) |
| color | Red crystals |
| Water Solubility | 904.20g/L(25 ºC) |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Phenazopyridine (94-78-0) |
Safety information for 3-(PHENYLAZO)-2,6-PYRIDINEDIAMINE
Computed Descriptors for 3-(PHENYLAZO)-2,6-PYRIDINEDIAMINE
| InChIKey | QPFYXYFORQJZEC-FOCLMDBBSA-N |
Abamectin manufacturer
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 94-78-0 Phenazopyridine 98%View Details
94-78-0 Phenazopyridine 98%View Details
94-78-0 -
 2,6-DIAMINO-3-(PHENYLAZO)PYRIDINE CAS 94-78-0View Details
2,6-DIAMINO-3-(PHENYLAZO)PYRIDINE CAS 94-78-0View Details
94-78-0 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4