2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile
Synonym(s):2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile;Dichlobenil
- CAS NO.:1194-65-6
- Empirical Formula: C7H3Cl2N
- Molecular Weight: 172.01
- MDL number: MFCD00001781
- EINECS: 214-787-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-16 17:17:29
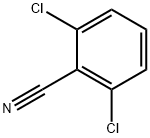
What is 2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile?
Chemical properties
2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile [1194-65-6], 1- cyano-2,6-dichlorobenzene, Mr 172.02, mp 144.5 –146.5 ℃, is a colorless, crystalline substance. Its solubility in water is 10 ppm at 25℃. 2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile is produced industrially by the ammoxidation of 2,6-dichlorotoluene. In addition the nitrile is obtained by oxidation or side-chain-chlorination of 2,6-dichlorotoluene via 2,6-dichlorobenzoic acid and 2,6-dichlorobenzaldehyde, respectively. 2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile shows herbicidal activity (Casoron, Duphar) and is used in fruit and vine cultivation. It is also used as an intermediate in the production of 2,6-difluorobenzonitrile and of 2,6-dichlorothiobenzamide (Prefix, Shell) which shows herbicidal activity.
The Uses of 2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile
Herbicide.
The Uses of 2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile
2,6-dichlorobenzonitrile in which Q-amino-G- chlorobenzonitrile is used as starting material. And it is used for the synthesis of diclofenac sodium oxacillin and guanabenz acetate.
The Uses of 2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile
Soil-applied herbicide used to control many annual and perennial broad-leaved weeds.
Definition
ChEBI: A nitrile that is benzonitrile which is substituted by chlorines at positions 2 and 6. A cellulose synthesis inhibitor, it is used as a pre-emergent and early post-emergent herbicide.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Synthetic Communications, 20, p. 2785, 1990 DOI: 10.1080/00397919008051490
Synthesis, p. 943, 1992 DOI: 10.1055/s-1992-26271
General Description
2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile is a white solid dissolved or suspended in a water-emulsifiable liquid carrier. The primary hazard is the threat to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit spread to the environment. Can easily penetrate the soil and contaminate groundwater and nearby streams. Can cause illness by inhalation, skin absorption and/or ingestion. Used as a herbicide.
Air & Water Reactions
Not soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
A halogenated nitrile. Nitriles may polymerize in the presence of metals and some metal compounds. They are incompatible with acids; mixing nitriles with strong oxidizing acids can lead to extremely violent reactions. Nitriles are generally incompatible with other oxidizing agents such as peroxides and epoxides. The combination of bases and nitriles can produce hydrogen cyanide. Nitriles are hydrolyzed in both aqueous acid and base to give carboxylic acids (or salts of carboxylic acids). These reactions generate heat. Peroxides convert nitriles to amides. Nitriles can react vigorously with reducing agents. Acetonitrile and propionitrile are soluble in water, but nitriles higher than propionitrile have low aqueous solubility. They are also insoluble in aqueous acids.
Health Hazard
SOLID: Harmful if swallowed.
Fire Hazard
Not flammable.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Agricultural Uses
Herbicide: Dichlobenil is a herbicide used on cranberry bogs, dichondra, ornamentals, blackberry, raspberry, and blueberry fields, apple, pear, filbert and cherry orchards, vineyards, hybrid poplar-cottonwood plantations, and rights-of-way to control weeds; and sewers to remove roots. It acts on dandelion, prickly oxtongue (pre-emergence), and tree roots. Not approved for use in EU countries. Actively registered in the U.S.
Trade name
BARRIER®; BH Prefix D®; CARSORON®; CASORON® 133; CARSORON® G; CARSORON® G4; CARSORON® G20-SR; CODE H 133®; DECABANE®; DU-SPREX®; DYCLOMEC®; FYDULAN; FYDUMAS; FYDUSIT; H 133®; H 1313®; NIA 5996®; NIAGARA® 5006; NIAGARA 5,996; NOROSAC®; PREFIX D®
Environmental Fate
Biological. A cell suspension of Arthrobacter sp., isolated from a hydrosol, degraded
dichlobenil to 2,6-dichlorobenzamide (71% yield) and several unidentified water soluble
metabolites (Miyazaki et al., 1975). This microorganism was capable of rapidly degrading
dichlobenil in aerobic sediment-water suspensions and in enrichment cultures (Miyazaki
et al., 1975).
Soil. The major soil metabolite is 2,6-dichlorobenzamide which undergoes further
degradation to form 2,6-dichlorobenzoic acid. The estimated half-lives ranged from 1 to
12 months (Hartley and Kidd, 1987). Under field conditions, dichlobenil persists from 2
to 12 months (Ashton and Monaco, 1991). The disappearance of dichlobenil from a
hydrosol and pond water was primarily due to volatilization and biodegradation. The time
required for 50 and 90% dissipation of the herbicide from a hydrosol were approximately
20 and 50 days, respectively (Rice et al., 1974). Dichlobenil has a high vapor pressure
and volatilization should be an important process. Williams and Eagle (1979) found that
the half-life of dichlobenil was 4 weeks in soil 4–8 weeks after application. After 1 year
following application, the half-life increased to 1 year.
Plant. In plants, dichlobenil is transformed into glucose conjugates, insoluble residues
and hydroxy products that are phytotoxic (Ashton and Monaco, 1991). These include three
phytotoxic compounds, namely 2,6-dichlorobenzonitrile, 3-hydroxy-2,6-dichlorobenzonitrile
and 4-hydroxy-2,6-dichlorobenzonitrile (Duke et al., 1991). Massini (1961) provided
some evidence that dichlobenil is metabolized by plants. French dwarf beans, tomatoes,
gherkin and oat plants were all exposed to a saturated atmosphere of dichlobenil at room
temperature for 4 days. Most of the herbicide was absorbed and translocated by the plants
in 3 days. After 6 days of exposure, bean seedlings were analyzed for residues using thinlayer
plate chromatography. In addition to dichlobenil, another compound was found but
it was not 2,6-dichlorobenzoic acid (Massini, 1963).
Surface Water. The time required for 50 and 90% dissipation of the herbicide from
New York pond water was approximately 21 and 60 days, respectively (Rice et al., 1974).
Photolytic. When dichlobenil was irradiated in methanol with a 450-W mercury lamp
and a Corex filter for 8 hours, o-chlorobenzonitrile and benzonitrile formed as the major
and minor products, respectively (Plimmer, 1970).
Chemical/Physical. Dichlobenil is hydrolyzed, especially in the presence of alkali, to
2,6-dichlorobenzamide (Briggs and Dawson, 1970; Worthing and Hance, 1991).
Emits toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides and chlorine when heated to decomposition (Sax
and Lewis, 1987).
Metabolic pathway
Twelve metabolites are isolated from either urine or
bile from either rats (11 metabolites) or goats (seven
metabolites) given single oral doses of 14C-labeled
2,6-dichlorobenzonitrile (DCBN). Five of these
metabolites are also excreted in urine from rats dosed
orally with 2,6-dichlorothiobenzamide (DCTBA) which
is an acid amide analog. All metabolites from either DCBN or DCTBA are benzonitriles with the following
ring substituents: Cl2, OH (three isomers); Cl2, (OH)2;
Cl, (OH)2; Cl, OH, SH; Cl, OH, SCH3; SOCH3, OH;
Cl2, S-(N-acetyl)cysteine; Cl, S-(N-acetyl)cysteine; Cl,
OH, S-(N-acetyl)cysteine.
The thiobenzamide moiety of DCTBA is converted
to the nitrile in all extracted urinary metabolites. No
hydrolysis of the nitrile in DCBN to either amide or an
acid is detected. Urine is the major route for excretion;
however, enterohepatic circulation occurs.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the nitrile from acetone. [Beilstein 9 IV 1006.]
Properties of 2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile
| Melting point: | 143-146 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 270-275 °C |
| Density | 1.4980 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 0.14Pa at 25℃ |
| refractive index | 1.6000 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 270°C |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| form | neat |
| color | White to Almost white |
| Water Solubility | 25 mg/L (25 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,3042 |
| BRN | 1909167 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1194-65-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 2,6-Dichlorobenzoic acid nitrile(1194-65-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Dichlobenil (1194-65-6) |
Safety information for 2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H312:Acute toxicity,dermal H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for 2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile
| InChIKey | YOYAIZYFCNQIRF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
CEFA CILINAS BIOTICS PVT LTD
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
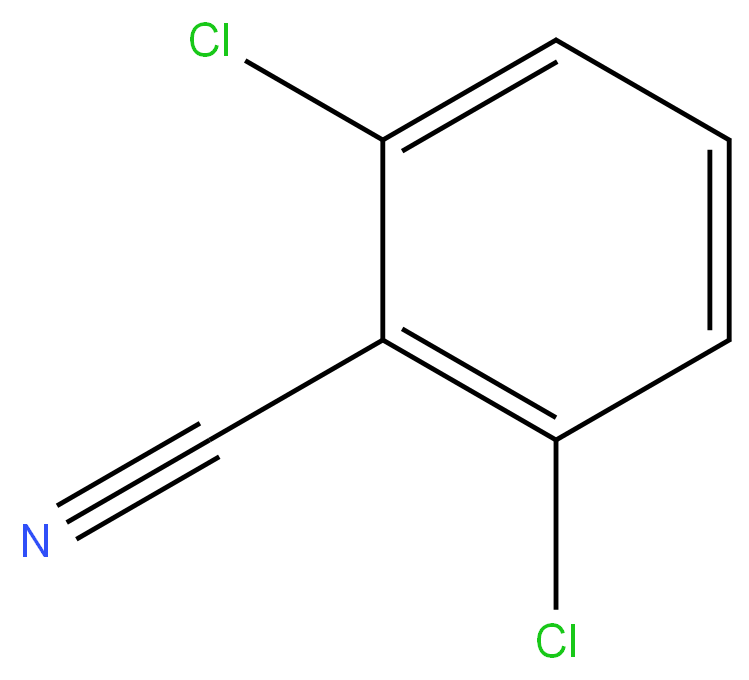 1194-65-6 2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile 99%View Details
1194-65-6 2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile 99%View Details
1194-65-6 -
 Dichlobenil 1194-65-6 99%View Details
Dichlobenil 1194-65-6 99%View Details
1194-65-6 -
 2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile, 97% 99%View Details
2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile, 97% 99%View Details
1194-65-6 -
 2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile 99.00%View Details
2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile 99.00%View Details
1194-65-6 -
 2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile CAS 1194-65-6View Details
2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile CAS 1194-65-6View Details
1194-65-6 -
 2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile CAS 1194-65-6View Details
2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile CAS 1194-65-6View Details
1194-65-6 -
 2,6-DichlorobenzonitrileView Details
2,6-DichlorobenzonitrileView Details
1194-65-6 -
 Reagent Grade 2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile, For IndustrialView Details
Reagent Grade 2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile, For IndustrialView Details
1194-65-6
