2-PHENYL-1,3-INDANDIONE
- CAS NO.:83-12-5
- Empirical Formula: C15H10O2
- Molecular Weight: 222.24
- MDL number: MFCD00003782
- EINECS: 201-454-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 21:30:31
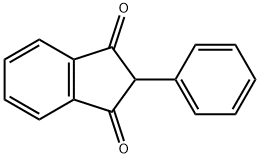
What is 2-PHENYL-1,3-INDANDIONE?
Absorption
Absorbed slowly from the gastrointestinal tract.
Toxicity
Oral, mouse: LD50 = 175 mg/kg; Oral, rat: LD50 = 163 mg/kg.
Description
Phenindione is an anticoagulant and vitamin K antagonist. It inhibits the reduction of vitamin K1 epoxide to vitamin K1 by vitamin K1 epoxide reductase in rat liver homogenates in a concentration-dependent manner. In vivo, phenindione (500 mg/kg) inhibits prothrombin synthesis and conversion of vitamin K1 epoxide to vitamin K1 in rats by 50 and 57%, respectively. Dietary administration of phenindione (4 mg/kg per day) inhibits aortic atherosclerosis or intracardial thrombosis in rat models of diet-induced atherosclerosis or intravascular thrombosis, respectively.
Chemical properties
light yellow fluffy fine flakes
The Uses of 2-PHENYL-1,3-INDANDIONE
Oral anticoagulant (indanedione).
The Uses of 2-PHENYL-1,3-INDANDIONE
Like coumarin derivatives, phenindione, a compound of the indandione class, acts by altering biosynthesis of coagulant proteins in the liver. It is used for preventing and treating thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, and thromboembolism. However, because of a number of side effects such as polyurea, polydipsia, tachycardia, and others, it is rarely used in practical medicine.
Background
An indandione that has been used as an anticoagulant. Phenindione has actions similar to warfarin, but it is now rarely employed because of its higher incidence of severe adverse effects. (From Martindale, The Extra Pharmacopoeia, 30th ed, p234)
Indications
For the treatment of pulmonary embolism, cardiomyopathy, atrial fibrillation and flutter, cerebral embolism, mural thrombosis, and thrombophili. Also used for anticoagulant prophylaxis.
Definition
ChEBI: Phenindione is a beta-diketone and an aromatic ketone. It has a role as an anticoagulant. It derives from a hydride of an indane.
brand name
Hedulin (Sanofi Aventis).
Pharmacokinetics
Phenindione thins the blood by antagonizing vitamin K which is required for the production of clotting factors in the liver. Anticoagulants such as Phenindione have no direct effect on an established thrombus, nor do they reverse ischemic tissue damage (damage caused by an inadequate blood supply to an organ or part of the body). However, once a thrombus has occurred, the goal of anticoagulant treatment is to prevent further extension of the formed clot and prevent secondary thromboembolic complications which may result in serious and possibly fatal sequelae. Phenindione has actions similar to warfarin, but it is now rarely employed because of its higer incidence of severe adverse effects.
Clinical Use
Anticoagulant
Synthesis
Phenindione, 3-phenylindan-1,3-dion (24.1.16), is synthesized in two ways. The first consists of condensating benzaldehyde with phthalide in the presence of sodium ethoxide. Evidently, the resulting phenylmethylenphthalide (24.1.15) rearranges under the reaction conditions to give the desired phenindione (24.1.16). The second method consists of condensation of phenylacetic acid with phthalic anhydride, forming phenylmethylenphthalide (24.1.15), which rearranges further in the presence of sodium ethoxide to phenindione.

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs There are many significant interactions with
coumarins. Prescribe with care with regard to the
following:
Anticoagulant effect enhanced by: alcohol,
amiodarone, anabolic steroids, aspirin, aztreonam,
bicalutamide, cephalosporins, chloramphenicol,
cimetidine, ciprofloxacin, dronedarone, fibrates,
clopidogrel, cranberry juice, danazol, dipyridamole,
disulfiram, fibrates, grapefruit juice, levofloxacin,
macrolides, metronidazole, nalidixic acid, neomycin,
norfloxacin, NSAIDs, ofloxacin, paracetamol,
penicillins, ritonavir, rosuvastatin, sulphonamides,
thyroid hormones, testosterone, tetracyclines,
tigecycline, tramadol, trimethoprim.
Anticoagulant effect decreased by: oral
contraceptives, rifamycins, vitamin K.
Anticoagulant effects enhanced/reduced by: anion
exchange resins, corticosteroids, dietary changes,
enteral feeds.
Analgesics: increased risk of bleeding with IV
diclofenac and ketorolac - avoid.
Anticoagulants: increased risk of haemorrhage with
apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban and rivaroxaban -
avoid.
Ciclosporin: there have been a few reports of altered
anticoagulant effect; decreased ciclosporin levels have
been seen rarely
Metabolism
Hepatic.
Metabolism
Hepatically metabolised. Metabolites of phenindione often colour the urine pink or orange.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the dione from EtOH (m 156o) or CHCl3 (m 148-150o). [Beilstein 7 H 808, 7 III 4100, 7 IV 2570.]
Properties of 2-PHENYL-1,3-INDANDIONE
| Melting point: | 144-148 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 243.3 °C (0.3 mmHg) |
| Density | 1.1404 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6600 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 208 °C |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Very slightly soluble in water; slightly soluble in ethanol (96%) and in ether. Solutions are yellow to red. |
| form | powder to crystal |
| pka | pKa 4.09(H2O,t =25,I=0.1) (Uncertain) |
| color | White to Light yellow |
| Merck | 14,7234 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 83-12-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for 2-PHENYL-1,3-INDANDIONE
Computed Descriptors for 2-PHENYL-1,3-INDANDIONE
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

![(Dihydroxy-3,4 phenyl)-2 hydroxy-2 indanedione-1,3 [French]](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20180808/GIF/75840-14-1.gif)
You may like
-
 2-Phenyl-1,3-indandione CAS 83-12-5View Details
2-Phenyl-1,3-indandione CAS 83-12-5View Details
83-12-5 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
