1,3-Diphenyl-2-thiourea
Synonym(s):1,3-Diphenyl-2-thiourea;Diphenylsulfourea;N,N′-Diphenylthiourea;Thiocarbanilide;Thiocarbanilide, 1,3-Diphenylthiourea
- CAS NO.:102-08-9
- Empirical Formula: C13H12N2S
- Molecular Weight: 228.31
- MDL number: MFCD00004921
- EINECS: 203-004-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
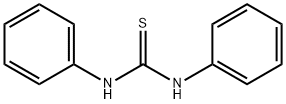
What is 1,3-Diphenyl-2-thiourea?
Description
Diphenylthiourea is a rubber chemical used as an accelerator and stabilizer in neopren.
Chemical properties
white powder
The Uses of 1,3-Diphenyl-2-thiourea
Vulcanizing accelerator; sulfur dyes.
The Uses of 1,3-Diphenyl-2-thiourea
N,N'-Diphenylthiourea is a vulcanizing accelerator; sulfur dyes; pharmaceutieals; floatation agent; acid inhibitor; intermediate for organic synthesis; accelerator and activator for chloroprene rubber and ethylene-propylene-diene terpolymers; as heat stabilizer in PVC adhesive-tape backing.
The Uses of 1,3-Diphenyl-2-thiourea
N,N'-Diphenylthiourea possesses a wide dipole moment and thus is involved in the forming wide metal chelated complexes as the radioactive-compound which used in radiopharmaceutical imaging, and to treat metal poisoning. It is used in co-crystals development used in the field of nonlinear optics to generate new coherent wavelengths.
Definition
ChEBI: N,N'-diphenylthiourea is thiourea in which each nitrogen carries a phenyl substituent. It has a role as an allergen.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Tetrahedron Letters, 15, p. 1191, 1974 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(01)82442-4
General Description
White to off-white powder.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
An organosulfide amide. Organosulfides are incompatible with acids, diazo and azo compounds, halocarbons, isocyanates, aldehydes, alkali metals, nitrides, hydrides, and other strong reducing agents. Reactions with these materials generate heat and in many cases hydrogen gas. Many of these compounds may liberate hydrogen sulfide upon decomposition or reaction with an acid. Organic amides/imides react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. Flammable gases are formed by the reaction of organic amides/imides with strong reducing agents. Amides are very weak bases (weaker than water). Imides are less basic yet and in fact react with strong bases to form salts. That is, they can react as acids. Mixing amides with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates the corresponding nitrile. The combustion of these compounds generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
Health Hazard
ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: When heated to decomposition 1,3-Diphenyl-2-thiourea emits highly toxic fumes.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for 1,3-Diphenyl-2-thiourea are not available. 1,3-Diphenyl-2-thiourea is probably combustible.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Industrial uses
Thiocarbanilide (diphenyl thiourea) is a crystalline compound, only marginally soluble
in water. In solution, it can assume a tautomeric form, typical of thiocarbanilide.
The first tautomer has acidic characteristics. The hydrogen can easily react with cations from
the mineral surface and therefore can act as a collector. The second form (II) does not have
collecting properties. Thiocarbanilide is a very effective and selective collector for galena.
Diphenylthiocarbazide (C6H5–NH–NH)2–C=S. This collector also appears in two forms;
in the active form the hydrogen is connected to sulfur. This reagent can be both anionic
and cationic. This collector can be utilized for flotation of nickel and cobalt minerals after
treatment of the pulp with copper sulfate.
Contact allergens
It is a rubber chemical used as an accelerator and stabilizing agent in neoprene
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Experimental reproductive effects. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of SOx, and NOx,.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the thiourea from boiling EtOH by adding hot water and allowing to cool. [Beilstein 12 H 394, 12 IV 810.]
Properties of 1,3-Diphenyl-2-thiourea
| Melting point: | 152-155 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 50℃ |
| Density | 1.32 |
| vapor pressure | 0.001Pa at 25℃ |
| refractive index | 1.5700 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| form | Crystalline Powder |
| pka | 12.68±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | White to pale yellow |
| Water Solubility | <0.01 g/100 mL at 19 ºC |
| Merck | 14,3333 |
| BRN | 644277 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 102-08-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Thiourea, n,n'-diphenyl-(102-08-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Diphenylthiourea (102-08-9) |
Safety information for 1,3-Diphenyl-2-thiourea
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for 1,3-Diphenyl-2-thiourea
| InChIKey | FCSHMCFRCYZTRQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
1,3-Diphenyl-2-thiourea manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Yasho Industries Ltd
ARRAKIS INDUSTRIES LLP
Anand Agencies
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran





You may like
-
 N,N'-Diphenylthiourea 98%View Details
N,N'-Diphenylthiourea 98%View Details -
 N,N'-Diphenylthiourea CAS 102-08-9View Details
N,N'-Diphenylthiourea CAS 102-08-9View Details
102-08-9 -
 Thiocarbanilide, 98% CAS 102-08-9View Details
Thiocarbanilide, 98% CAS 102-08-9View Details
102-08-9 -
 Diphenyl Thiourea pure CAS 102-08-9View Details
Diphenyl Thiourea pure CAS 102-08-9View Details
102-08-9 -
 N,N-Diphenylthiourea CAS 102-08-9View Details
N,N-Diphenylthiourea CAS 102-08-9View Details
102-08-9 -
 Diphenylthiourea CAS 102-08-9View Details
Diphenylthiourea CAS 102-08-9View Details
102-08-9 -
 Diphenyl Thiourea pure CAS 102-08-9View Details
Diphenyl Thiourea pure CAS 102-08-9View Details
102-08-9 -
 N,N'-Diphenylthiourea CAS 102-08-9View Details
N,N'-Diphenylthiourea CAS 102-08-9View Details
102-08-9