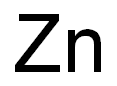CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Zinc ashes appears as a grayish colored powder. May produce toxic zinc oxide fumes when heated to very high temperatures or when burned. Insoluble in water. Used in paints, bleaches and to make other chemicals. |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | Bluish-white, lustrous metal; distorted hexagonal close-packed structure; when heated to 100-150 °C becomes malleable, at 210 °C becomes brittle and pulverizable |
| Boiling Point | 907 |
| Melting Point | 419 |
| Solubility | Soluble in acids and alkalies; insoluble in water |
| Density | 7.133 g/cu cm at 25 °C; 6.830 g/cu cm at 419.5 °C (solid); 6.620 g/cu cm at 419.5 °C (liquid); 6.250 g/cu cm at 800 °C |
| Vapor Pressure | 1.47X10-6 Pa (1.10X10-8 mm Hg) at 400 K (127 °C); 0.653 Pa (4.9X10-3 mm Hg) at 600 K (327 °C) |
| Stability/Shelf Life | Stable in dry air; becomes covered with white coating of basic carbonate on exposure to moist air. |
| Autoignition Temperature | 460 °C |
| Decomposition | When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of /zinc oxide/. |
| Heat of Vaporization | 114.8 kJ/mol at 907 °C |
| Other Experimental Properties | Natural zinc is composed of five stable isotopes: zinc-64 (48.6%); zinc-66 (27.9%); zinc-67 (4.1%); zine-68 (18.8%); zinc-70 (0.6%); 18 artificial radioactive isotopes are known, most with very short (millisecond, seconds) or short (minutes) half-lives; zinc-65: half-life = 243.8 days |
| Chemical Classes | Metals -> Elements, Metallic |
SAFETY INFORMATION
| Signal word | Danger |
|---|---|
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H302:Acute toxicity,oral H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H336:Specific target organ toxicity,single exposure; Narcotic effects H351:Carcinogenicity H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 65.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 0 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 63.929142 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 63.929142 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 0 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 1 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 0 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Zinc is one of the most common elements in the earth's crust. It is found in air, soil, and water, and is present in all foods. Pure zinc is a bluish-white shiny metal. Zinc has many commercial uses as coatings to prevent rust, in dry cell batteries, and mixed with other metals to make alloys like brass, and bronze. A zinc and copper alloy is used to make pennies in the United States. Zinc combines with other elements to form zinc compounds. Common zinc compounds found at hazardous waste sites include zinc chloride, zinc oxide, zinc sulfate, and zinc sulfide. Zinc compounds are widely used in industry to make paint, rubber, dyes, wood preservatives, and ointments.