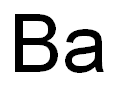CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Barium appears as a silver to white metallic solid. Contact may cause burns to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. May be toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption. Used to make other chemicals. |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | Silvery-white, slightly lustrous, body-centered cubic structure |
| Boiling Point | 2984 °F at 760 mmHg (NTP, 1992) |
| Melting Point | 1337 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| Solubility | Reacts with water; slightly soluble in ethanol |
| Density | 3.51 at 68 °F (NTP, 1992) - Denser than water; will sink |
| Vapor Pressure | 10 mmHg at 1920 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| Stability/Shelf Life | The free element oxidizes readily in moist air. |
| Surface Tension | 224 dynes/cm (liq form of barium) at 720 °C in argon atmosphere as determined by bubbler pressure method |
| Other Experimental Properties | Soft, ductile; pyrophoric when finely divided; emits yellow-green color in flame; dissolves in liquid ammonia; electromotive force (aq) barium(2+)/barium = -2.91 Volts |
| Chemical Classes | Metals -> Metals, Inorganic Compounds |
SAFETY INFORMATION
| Signal word | Danger |
|---|---|
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H228:Flammable solids H260:Substances And Mixtures Which, In Contact With Water,Emit Flammable Gases H301:Acute toxicity,oral H314:Skin corrosion/irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P231+P232:Handle under inert gas. Protect from moisture. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 137.33 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 0 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 137.905247 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 137.905247 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 0 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 1 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 0 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Barium is a silvery-white metal which exists in nature only in ores containing mixtures of elements. It combines with other chemicals such as sulfur or carbon and oxygen to form barium compounds. Barium compounds are used by the oil and gas industries to make drilling muds. Drilling muds make it easier to drill through rock by keeping the drill bit lubricated. They are also used to make paint, bricks, ceramics, glass, and rubber. Barium sulfate is sometimes used by doctors to perform medical tests and to take x-rays of the gastrointestinal tract.