CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Solid |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 70-72 °C |
| Solubility | 451 mg/L |
| LogP | 2.81 |
| Caco2 Permeability | -4.81 |
| Dissociation Constants | 9.21 |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 307.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 2.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Exact Mass | 307.21474379 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 307.21474379 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 50.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 286 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
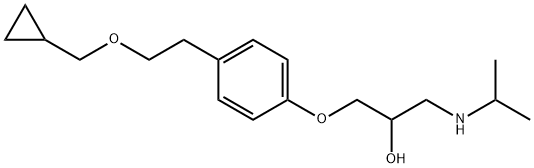
Betaxolol is a propanolamine that is 3-aminopropane-1,2-diol in which the hydrogen of the primary hydoxy is substituted by a 4-[2-(cyclopropylmethoxy)ethyl]phenyl group and one of the hydrogens attached to the amino group is substituted by isopropyl. It is a selective beta1-receptor blocker and is used in the treatment of glaucoma as well as hypertension, arrhythmias, and coronary heart disease. It is also used to reduce non-fatal cardiac events in patients with heart failure. It has a role as a beta-adrenergic antagonist, an antihypertensive agent and a sympatholytic agent.