SAFETY INFORMATION
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H317:Sensitisation, Skin H334:Sensitisation, respiratory |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P284:Wear respiratory protection. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. |
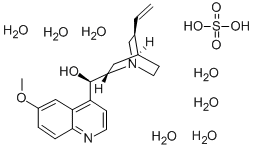
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 548.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 10 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 15 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 548.22511051 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 548.22511051 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 136 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 36 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 538 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 9 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
An alkaloid derived from the bark of the cinchona tree. It is used as an antimalarial drug, and is the active ingredient in extracts of the cinchona that have been used for that purpose since before 1633. Quinine is also a mild antipyretic and analgesic and has been used in common cold preparations for that purpose. It was used commonly and as a bitter and flavoring agent, and is still useful for the treatment of babesiosis. Quinine is also useful in some muscular disorders, especially nocturnal leg cramps and myotonia congenita, because of its direct effects on muscle membrane and sodium channels. The mechanisms of its antimalarial effects are not well understood.