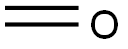| Physical Description |
Solids containing varying amounts of formaldehyde, probably as paraformaldehyde (polymers of formula HO(CH2O)xH where x averages about 30). A hazard to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit spread to the environment. |
| Color/Form |
Nearly colorless gas [Note: Often used in an aqueous solution]. /Pure formaldehyde/ |
| Odor |
Pungent, suffocating odor |
| Boiling Point |
-6 °F at 760 mmHg (NIOSH, 2023) |
| Melting Point |
-134 °F (NIOSH, 2023) |
| Flash Point |
185 °F (85 °C) (Closed cup) /Gas/ |
| Solubility |
Miscible (NIOSH, 2023) |
| Density |
0.815 g/cu cm at -20 °C |
| Vapor Density |
1.04 (NIOSH, 2023) - Heavier than air; will sink (Relative to Air) |
| Vapor Pressure |
greater than 1 atm (NIOSH, 2023) |
| LogP |
0.35 |
| Henry's Law Constant |
Henry's Law constant = 3.37X10-7 atm-cu m/mol at 25 °C |
| Stability/Shelf Life |
On standing, especially in the cold, may become cloudy, and on exposure to very low temperature ppt of trioxymethylene formed; in air it slowly oxidizes to formic acid /40% solution/. |
| Autoignition Temperature |
795 °F (424 °C) |
| Decomposition |
Uncatalyzed decomposition is very slow below 300 °C; extrapolation of kinetic data to 400 °C indicates that the rate of decomposition is about 0.44%/min at 101 kPa (1 atm). The main products are carbon monoxide and hydrogen. Metals such as platinium, copper, chromia, and alumina also catalyze the formation of methanol, methylformate, formic acid, carbon dioxide, and methane. |
| Viscosity |
0.1421 cP at 25 °C |
| Corrosivity |
Aqueous formaldehyde is corrosive to carbon steel, but formaldehyde in gas phase is not. |
| Heat of Combustion |
570.7 kJ/mol (gas) |
| Heat of Vaporization |
23.3 kJ/mol at 19 °C |
| pH |
pH: 2.8 to 4.0 /Formaldehyde soln/ |
| Surface Tension |
27.3797 dyn/cm at 25 °C |
| Ionization Potential |
10.88 eV |
| Polymerization |
... Polymerizes easily. |
| Odor Threshold |
Odor Threshold Low: 0.02 [ppm] Odor Threshold High: 1.9 [ppm] Odor threshold from CHEMINFO In HSDB: odor threshold = 0.5-1 ppm Odor threshold estimated at less than 0.5 ppm |
| Refractive Index |
Index of refraction: 1.3746 at 20 °C/D /Formaldehyde soln/ |
| Dissociation Constants |
13.3 (at 25 °C) |
| Kovats Retention Index |
229 273 247 247 |
| Other Experimental Properties |
Clear, water-white, very slightly acid, gas or liquid. |
| Chemical Classes |
Other Classes -> Aldehydes |