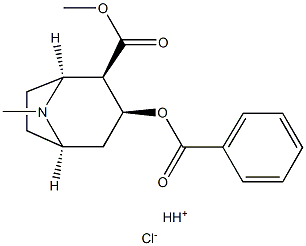
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 339.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 339.1237359 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 339.1237359 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 55.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 432 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Cocaine Hydrochloride is the hydrochloride salt form of the tropane alkaloid cocaine, with central nervous systems (CNS) stimulating and local anesthetic activity. Cocaine binds to the dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine transport proteins and inhibits the re-uptake of dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine into pre-synaptic neurons. This leads to an accumulation of the respective neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft and may result in increased postsynaptic receptor activation. Its effect on dopamine levels causes CNS stimulation and euphoria, and ultimately dependence. The mechanism of action through which cocaine exerts its local anesthetic effects is by binding to and blocking the voltage-gated sodium channels in the neuronal cell membrane. By stabilizing neuronal membranes, cocaine inhibits the initiation and conduction of nerve impulses and produces a reversible loss of sensation.