CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Solid |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 184-186 |
| Solubility | 1.37e-02 g/L |
| LogP | 3.6 |
| Collision Cross Section | 168.2 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW, Method: Major Mix IMS/Tof Calibration Kit (Waters)] |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 301.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 3.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 301.16779360 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 301.16779360 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 72.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 305 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
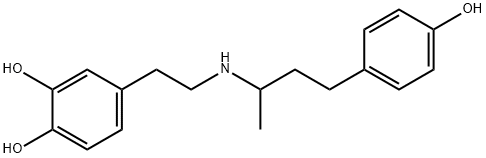
Dobutamine is a catecholamine that is 4-(3-aminobutyl)phenol in which one of the hydrogens attached to the nitrogen is substituted by a 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethyl group. A beta1-adrenergic receptor agonist that has cardiac stimulant action without evoking vasoconstriction or tachycardia, it is used as the hydrochloride to increase the contractility of the heart in the management of acute heart failure. It has a role as a cardiotonic drug, a sympathomimetic agent and a beta-adrenergic agonist. It is a secondary amine and a catecholamine.