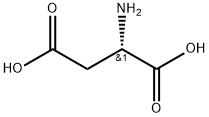
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Dry Powder |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | White, crystalline solid |
| Taste | Acidic/neutral |
| Melting Point | 270 °C |
| Solubility | 5390 mg/L (at 25 °C) |
| Density | 1.6603 at 13 °C |
| Vapor Pressure | 0.0000013 [mmHg] |
| LogP | -3.89 |
| Optical Rotation | Specific optical rotation: -2.0 deg at 25 °C (c=3.93 in 5N HCl) /d-Aspartic acid/ |
| Decomposition | 324 °C |
| Ionization Efficiency | Negative |
| Dissociation Constants | 9.67 |
| Collision Cross Section | 121.92 Ų [M-H]- [CCS Type: DT, Method: stepped-field] |
| Other Experimental Properties | ASPARTIC ACID HAS RELATIVELY HIGH SOUR, RELATIVELY LOW MSG-LIKE TASTE INTENSITIES /ASPARTIC ACID/ |
| Chemical Classes | Biological Agents -> Amino Acids and Derivatives |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 133.10 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | -2.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 133.03750770 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 133.03750770 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 101 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 9 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 133 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
L-aspartic acid is the L-enantiomer of aspartic acid. It has a role as an Escherichia coli metabolite, a mouse metabolite and a neurotransmitter. It is an aspartate family amino acid, a proteinogenic amino acid, an aspartic acid and a L-alpha-amino acid. It is a conjugate acid of a L-aspartate(1-). It is an enantiomer of a D-aspartic acid.