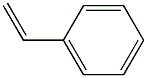
| Physical Description |
Styrene monomer, stabilized appears as a clear colorless to dark liquid with an aromatic odor. Vapors heavier than air and irritating to the eyes and mucous membranes. Subject to polymerization. If the polymerization takes place inside a closed container, the container may rupture violently. Less dense than water and insoluble in water. Used to make plastics, paints, and synthetic rubber. |
| Color/Form |
Colorless to yellowish, oily liquid |
| Odor |
Characteristic, sweet, balsamic, almost floral odor that is extremely penetrating |
| Boiling Point |
293 to 295 °F at 760 mmHg (NTP, 1992) |
| Melting Point |
-24 to -23 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| Flash Point |
88 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| Solubility |
less than 1 mg/mL at 66 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| Density |
0.906 at 68 °F (USCG, 1999) - Less dense than water; will float |
| Vapor Density |
3.6 (Air = 1) |
| Vapor Pressure |
4.3 mmHg at 59 °F ; 9.5 mmHg at 86 °F; 10 mmHg at 95 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| LogP |
log Kow = 2.95 |
| Henry's Law Constant |
Henry's Law constant = 0.00275 atm cu m/mole at 25 °C |
| Stability/Shelf Life |
Stable under recommended storage conditions. Test for peroxide formation before distillation or evaporation. Test for peroxide formation or discard after 1 year. |
| Autoignition Temperature |
914 °F (USCG, 1999) |
| Decomposition |
Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions - Carbon oxides. |
| Viscosity |
0.696 cP at 25 °C |
| Corrosivity |
Styrene will corrode copper and copper alloys |
| Heat of Combustion |
-4,395.63 kJ/mol at 25 °C |
| Heat of Vaporization |
10.50 kcal/mol at 25 °C |
| Surface Tension |
32.3 dynes/cm at 20 °C |
| Ionization Potential |
8.40 eV |
| Polymerization |
Polymerizes slowly at room temperature and readily at temp > 65 °C. |
| Odor Threshold |
Odor Threshold Low: 0.01 [mmHg] Odor Threshold High: 1.9 [mmHg] Detection odor threshold from AIHA (mean = 0.14 ppm) |
| Refractive Index |
Index of refraction: 1.5440 at 25 °C |
| Kovats Retention Index |
914 870 874 880.3 871 900.02 871 876 872 886 888 878 874.35 871 873 875 873 873 885 885 885 880 884 884 885 885 877.8 886 880 893 885 890.5 897.3 873 874.4 874.4 874.4 874.7 874.7 874.9 878 885 878 896 879 895 871 877 878 872 872 881 878 895 878 876 883.8 873 870 875 881 882.7 873.29 875 877 875 880 883 887 872 884 885 885 885 871 871 877 875 873 880 875 878 887 890 878 880 883 866 863 862 871 879 868 875 876 880 886 879 869 868 882 900 900 884 |
| Other Experimental Properties |
Heat of polymerization: -154 cal/g (-6.35X10+5 J/kg) |
| Chemical Classes |
Plastics & Rubber -> Styrenes |