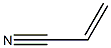| Physical Description |
Acrylonitrile, stabilized appears as a clear colorless liquid with a strong pungent odor. Flash point 32 °F. Prolonged exposure to the vapors or skin contact harmful. Density 6.7 lb / gal. Vapors heavier than air. Combustion produces toxic oxides of nitrogen. Requires storage and handling in closed systems. Used in insecticides and to make plastics, fibers and other chemicals. Rate of onset: Immediate Persistence: Minutes to hours Odor threshold: 17 ppm Source/use/other hazard: Plastics, coatings, adhesives industries; dyes; pharmaceuticals; flam gas. |
| Color/Form |
Clear, colorless liquid at room temperature |
| Odor |
Practically odorless, or with a very slight odor of peach kernels |
| Boiling Point |
171 °F at 760 mmHg (EPA, 1998) |
| Melting Point |
-116 °F (EPA, 1998) |
| Flash Point |
32 °F (EPA, 1998) |
| Solubility |
10 to 50 mg/mL at 70.9 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| Density |
0.8004 at 77 °F (EPA, 1998) - Less dense than water; will float |
| Vapor Density |
1.9 (EPA, 1998) - Heavier than air; will sink (Relative to Air) |
| Vapor Pressure |
100 mmHg at 73.4 °F (EPA, 1998) |
| LogP |
log Kow = 0.25 |
| Henry's Law Constant |
Henry's Law constant = 1.38X10-4 atm cu m/mole at 25 °C |
| Stability/Shelf Life |
Stable under recommended storage conditions. |
| Autoignition Temperature |
898 °F (USCG, 1999) |
| Decomposition |
Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions - Carbon oxides, nitrogen oxides (NOx). |
| Viscosity |
0.34 sq mm/s at 25 °C |
| Corrosivity |
Attacks copper and copper alloys ... attacks aluminum in high concentration |
| Heat of Combustion |
1761.8 kJ/mol at 25 °C (liquid) |
| Heat of Vaporization |
32.6 kJ/mol at 25 °C |
| pH |
pH = 6.0-7.5 |
| Surface Tension |
27.76 dyn/cm at 15.1 °C; 27.54 mN/m at 17.8 °C |
| Ionization Potential |
10.91 eV |
| Polymerization |
Hazardous polymerization may occur. Polymerization may be caused by elevated temperature or alkalies. Uninhibited monomer vapor may form polymer in vents and other confined spaces. |
| Odor Threshold |
Odor Threshold Low: 21.6 [mmHg] The odor threshold was based on results from a panel of human subjects. [ACGIH] VP from HSDB |
| Refractive Index |
Index of refraction: 1.3911 at 20 °C/D |
| Relative Evaporation Rate |
4.54 (Butyl acetate = 1) |
| Kovats Retention Index |
520 496.4 500 491 495 499.1 493.4 495 492 495 490 492 516 |
| Other Experimental Properties |
... Yellowing upon exposure to light indicates photo-alteration to saturated derivatives. |
| Chemical Classes |
Nitrogen Compounds -> Nitriles |