CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Solid |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 171 - 173 °C |
| LogP | 0.93 |
| Collision Cross Section | 149.8 Ų [M+Na]+ [CCS Type: DT, Method: single field calibrated with Agilent tune mix (Agilent)] |
SAFETY INFORMATION
| Signal word | Warning |
|---|---|
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 207.23 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 0.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 207.08954328 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 207.08954328 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 66.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 15 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 234 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
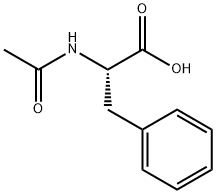
N-acetyl-L-phenylalanine is the N-acetyl derivative of L-phenylalanine. It has a role as a metabolite. It is a N-acyl-L-phenylalanine, a N-acetyl-L-amino acid and a N-acetylphenylalanine. It is a conjugate acid of a N-acetyl-L-phenylalaninate. It is an enantiomer of a N-acetyl-D-phenylalanine.